
Rare earth elements are essential for modern military and civilian technology. They’re found most often in hard-to-reach places, often in unfriendly countries. Given their necessity and the profits to be made, the search for these elements is likely to be a major driver of aggressive mineral exploration on Earth and even in space. Here’s your primer on what rare earth elements are, what we use them for, where they’re found, and possible alternative sources.
Key Points
-
Rare earth elements are used to build essential components of high technology, including phones, computers, cars, and weapons components.
-
China is the largest source of rare earth elements in the world. In the event of a trade war, they are likely to restrict the supply to get a better bargaining position.
-
Finding alternative sources of these elements may drive more aggressive exploration in melting polar regions, under the ocean, and in space.
-
Check out: 2 Dividend Legends To Hold Forever and Discover “The Next NVIDIA
What Are Rare Earth Elements?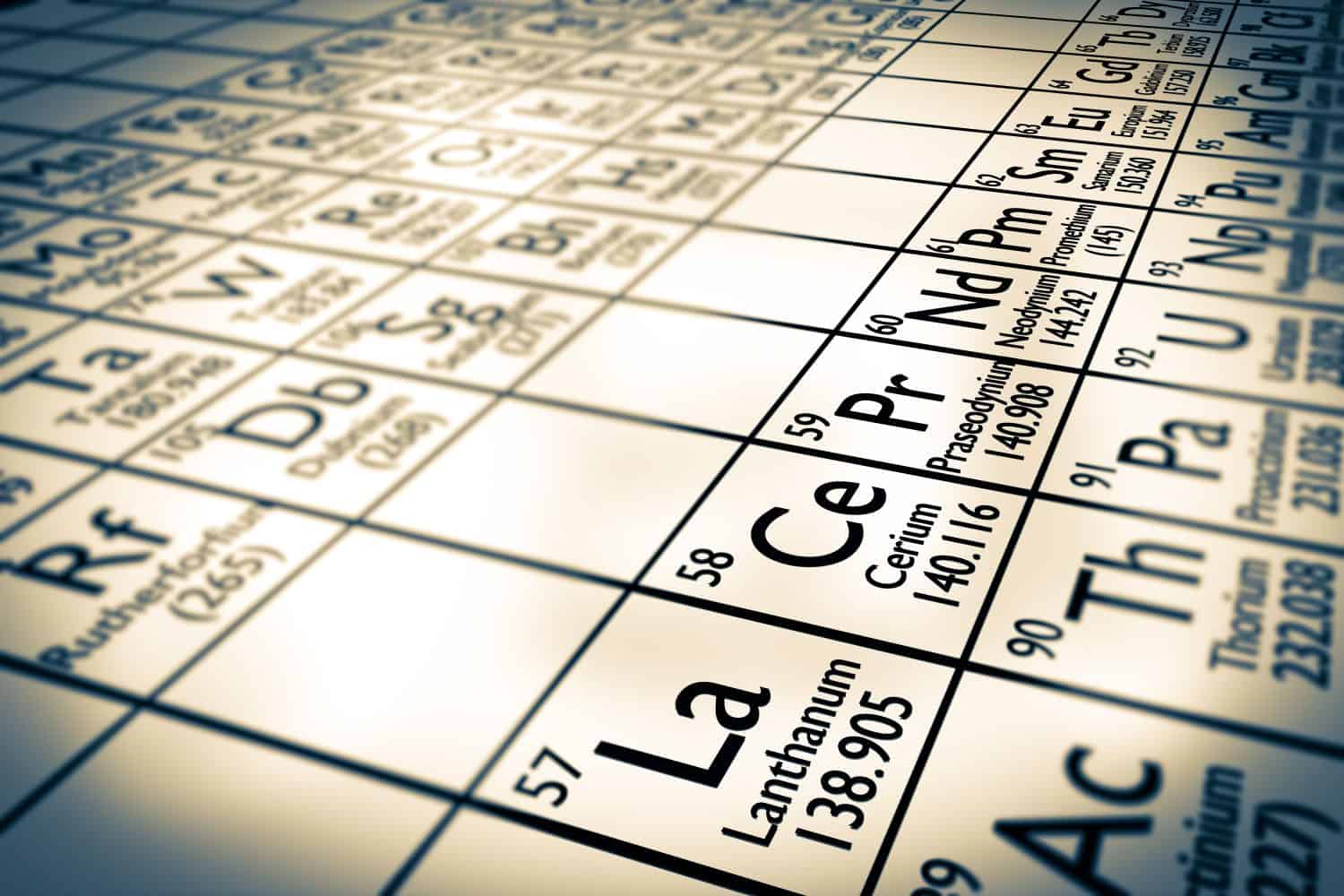

Rare earth elements are a group of 17 metals that are essential for manufacturing high tech components for modern technology. In their natural state they are usually silvery gray and malleable. Here’s a complete list:
- Scandium (Sc)
- Yttrium (Y)
- Lanthanum (La)
- Cerium (Ce)
- Praseodymium (Pr)
- Neodymium (Nd)
- Promethium (Pm)
- Samarium (Sm)
- Europium (Eu)
- Gadolinium (Gd)
- Terbium (Tb)
- Dysprosium (Dy)
- Holmium (Ho)
- Erbium (Er)
- Thulium (Tm)
- Ytterbium (Yb)
- Lutetium (Lu)
Uses of Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements are used in many essential applications for modern life, including:
- Wind turbines, batteries for electric vehicles, and LED lights
- Catalysts, high-performance magnets, and industrial robots
- Smartphones, televisions, computers, video game systems, monitors.
- Cancer treatments, robotic surgical tools, x-rays and MRIs
- Electronic components of advanced weaponry, like lasers, missiles, and radars
Why Not Use Something Else?

Rare earth metals have some properties that make them superior to other, more common materials. For example, they make stronger and more lightweight magnets so that electronics can be more portable. They perform well at high temperatures, they are more electrically conductive than other metals, and they are more effective catalysts in chemical reactions. Some of them also emit bright colors, so they are useful in electronic displays and sensors. Given the expense of these materials, however, researchers are looking in to synthetic alternatives.
Are Rare Earth Elements Actually Rare?

The term “rare earth element” is a little deceiving, because not all of these 17 elements are actually rare. There are 78 common elements in the Earth’s crust, and Cerium, one of the “rare earth elements” is the 25th most plentiful on the list. Its concentration is 60 parts per million. On the other hand, the rarest of the rare earth elements are thulium and lutetium, which make up only 0.5 part per million of the crust. With all of these elements, though, production to industrially-useful levels is difficult because they do not occur in large concentrations and require a great deal of soil and rock to be processed to produce what is necessary.
Now these are the world’s largest producers of rare earth elements:
1. China

China is the source of about 75% of the rare earth elements mined globally. In 2023 their output was 210,000 metric tons. China and the U.S. have deeply intertwined economies, but their relationship is fraught over many issues. Trade tariffs, theft of intellectual property, spying, hacking, unfair trade practices, trade imbalances, environmental protection, and the use of slave labor and child labor are all thorny outstanding issues. Politically, China claims the entire South China Sea and is building artificial islands and harassing international shipping to assert its claims. It also threatens to invade Taiwan and supports American enemies like North Korea and Russia. Needless to say, it is highly inconvenient that the U.S. must depend on China for a good deal of its rare earth element needs.
2. United States
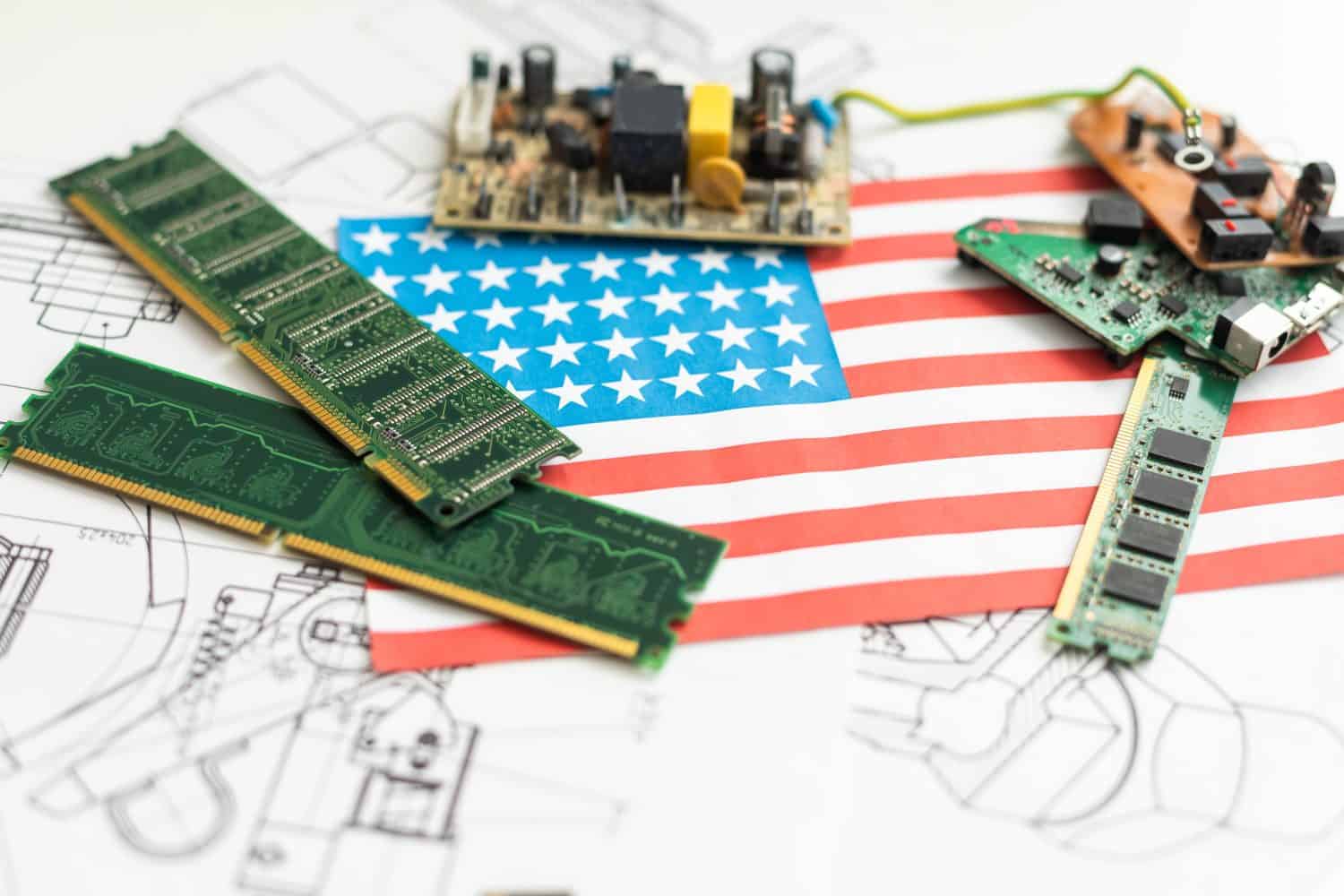
The United States mines about 43,000 metric tons of rare earth elements each year, mainly in California. To meet demand, it also imports them from China, Malaysia, Japan, and Estonia.
3. Australia
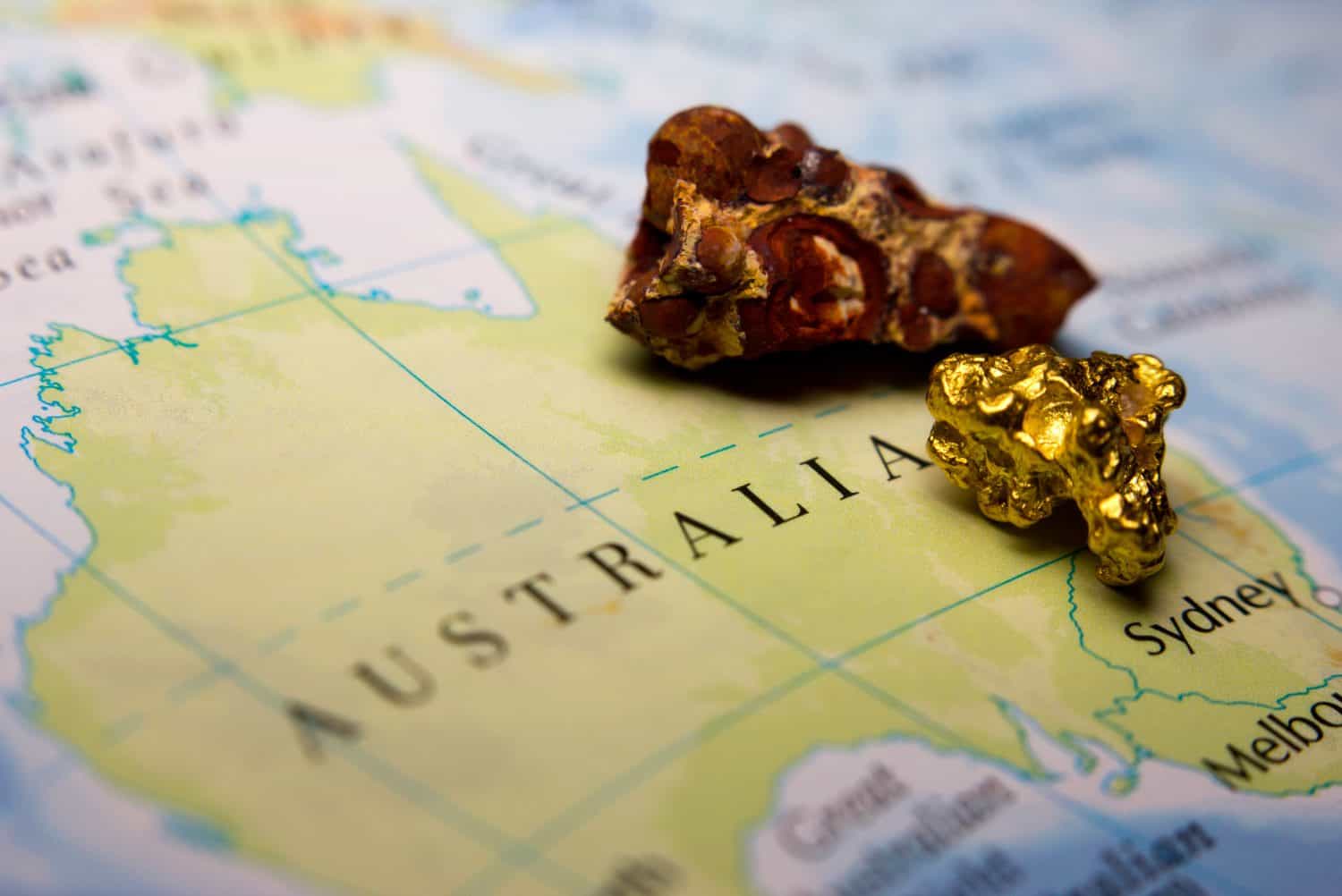
Australia has signifcant rare earth metal reserves of 4.4 million metric tons and currently produces about 18,000 metric tons a year. It produces about 8% of the world’s total. The country’s largest deposits are in Western Australia. The United States is helping Australia develop its domestic processing facilities so that its ore does not have to be exported to China and other countries for reprocessing.
4. Myanmar
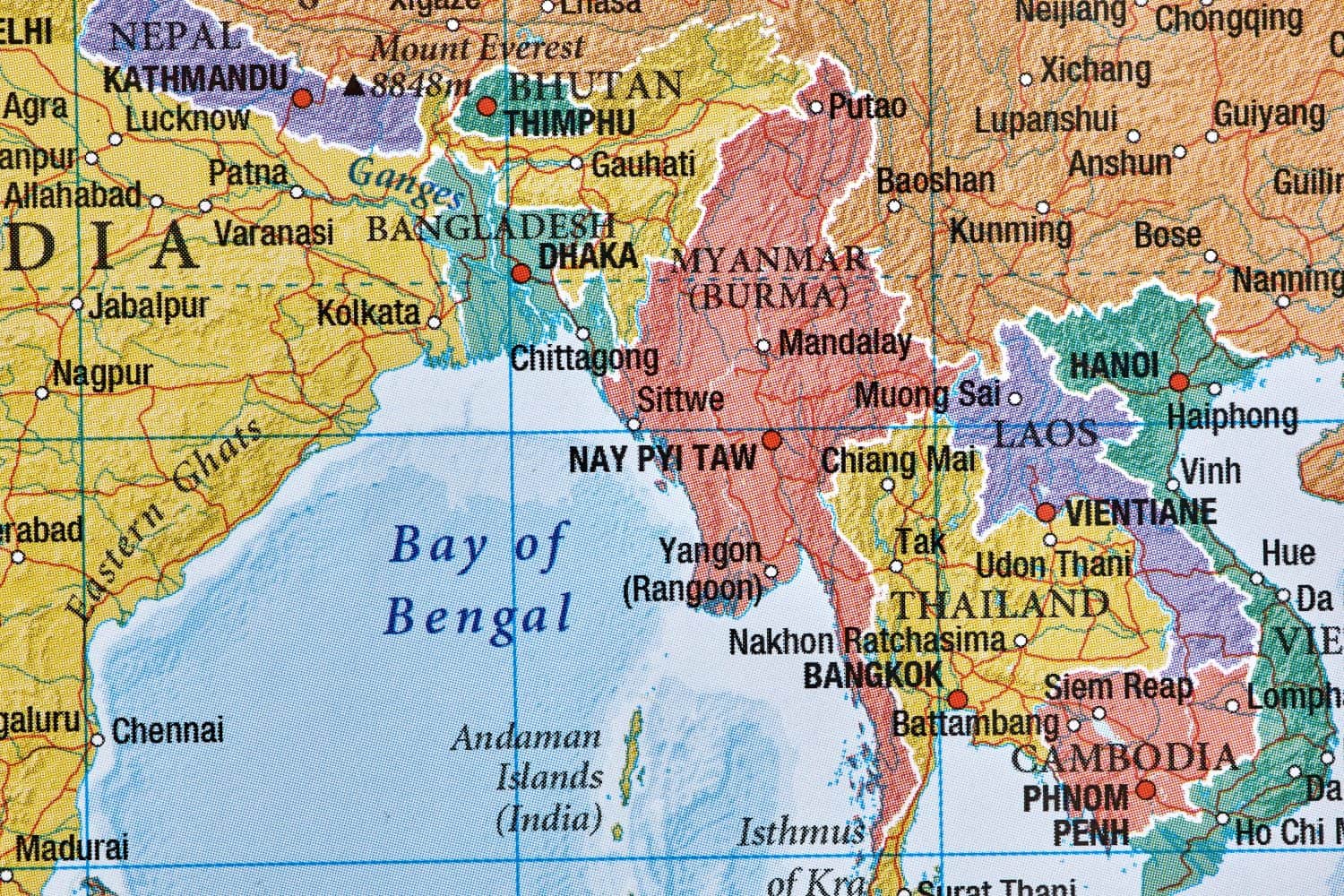
Myanmar mines about 12,000 metric tons of rare earth metals annually. It has a tense relationship with western countries due to its poor human rights record, but maintains friendlier relations with China.
5. Thailand

Thailand produces about 7,100 metric tons of rare earths a year. Geopolitically, it is aligned with the United States and other western democracies.
6. Vietnam
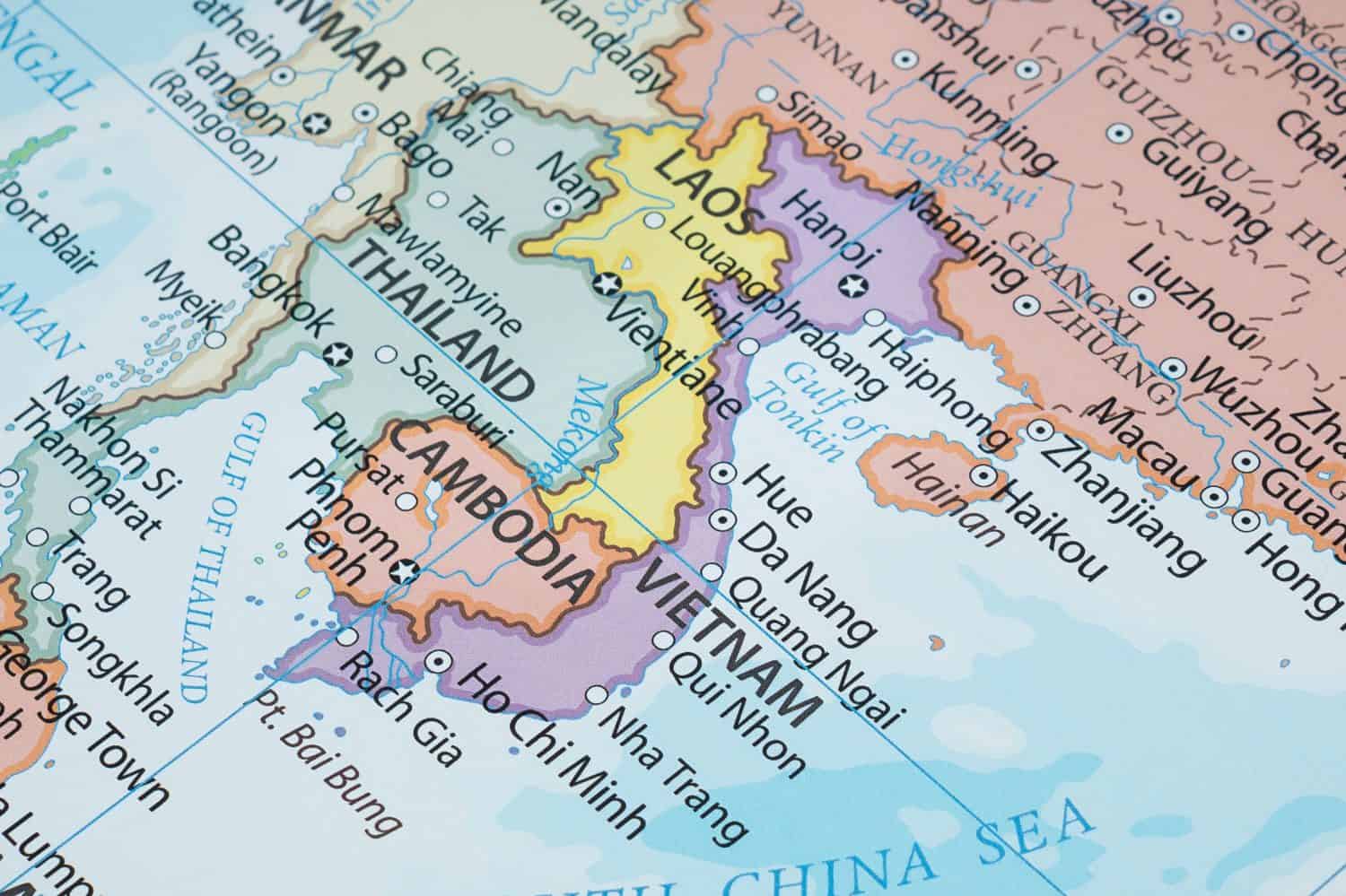
Vietnam produces 4,300 metric tons of rare earth elements annually. Despite the fact that it fought a bitter war with the United States, the two countries are now developing closer ties out of their common concern about Chinese ambitions in the region. The United States is even selling advanced fighter aircraft, with rare earth element components, to Vietnam.
7. Russia
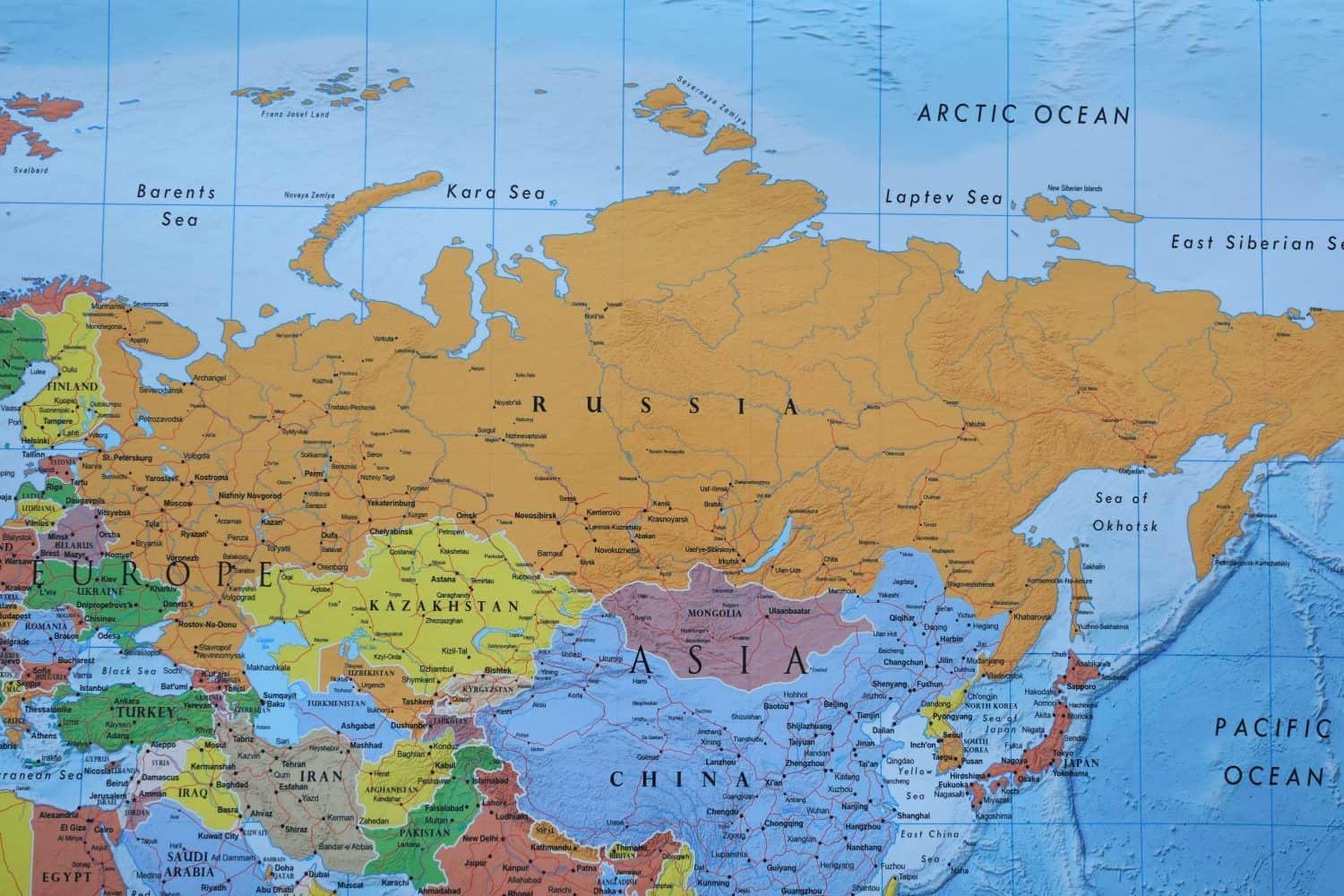
Russia produces about 2,600 metric tons of rare earth elements. It is currently under stringent economic sanctions due to its invasion of Ukraine. Although rare earth elements have not been specifically targeted by the sanctions, other types of metals and raw materials have. This makes trade with Russia risky, so companies prefer to seek other sources when they can.
Recycling Rare Earth Elements

One of the best ways to reduce our dependence on foreign imports of rare earth elements is to recycle what we already have. Retrieving these valuable minerals from e-waste like discarded phones, computers, electric vehicle batteries, medical equipment, wind turbines, and industrial machinery can significantly reduce our needs.
New Sources of Rare Earth Elements

It may also be possible to find new sources to mine rare earth elements, such as extracting it from coal, mining in the deep sea or in thawing areas of the Arctic, or even mining the moon or the asteroids. All of these are expensive, dangerous, and environmentally hazardous places to extract raw materials, so for now, we would do well to moderate our use, find alternatives, and recycle what we already have.
Take Charge of Your Retirement In Just A Few Minutes (Sponsor)
Retirement planning doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. The key is finding expert guidance—and SmartAsset’s simple quiz makes it easier than ever for you to connect with a vetted financial advisor.
Here’s how it works:
- Answer a Few Simple Questions. Tell us a bit about your goals and preferences—it only takes a few minutes!
- Get Matched with Vetted Advisors Our smart tool matches you with up to three pre-screened, vetted advisors who serve your area and are held to a fiduciary standard to act in your best interests. Click here to begin
- Choose Your Fit Review their profiles, schedule an introductory call (or meet in person), and select the advisor who feel is right for you.
Why wait? Start building the retirement you’ve always dreamed of. Click here to get started today!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.


