24/7 Wall St. Insights:
- The Su-57 Felon is the newest Sukhoi fighter to enter Russian military service and it is one of the newest fifth-generation fighter jets
- Only a few nations on the planet are capable of producing fifth-generation aircraft, the United States, China, and Russia
- There is an ongoing debate about air superiority between the fifth-generation fighter jets of Russia and the United States
- Also: Discover “The Next NVIDIA”
The Russian Air Force is widely known for its offensive capabilities. As such, it is home to a series of MiG and Sukhoi fighter jets that are easily some of the fastest and most technologically advanced in the world. They primarily act as air superiority fighters, but also retain the capacity for strike missions and various other operations. (Russian aircraft dominate the world’s fighter jets in vertical climb capabilities.)
The Su-57 Felon is the newest Sukhoi fighter jet to enter service. This series of jets falls under the fifth-generation designation as it incorporates advanced avionics and stealth technology into these aircraft. The Felon is also capable of serious firepower as well.
Only a few nations on the planet are capable of producing fifth-generation aircraft, the United States, China, and Russia. This elite club of nations is currently involved in an arms race for these aircraft, but there is no clear victor, yet.
The Felon is meant to rival its American counterpart, the F-35 Lightning II. These aircraft measure up on a number of specs and features, but again there has been no overt competition or engagement between these two aircraft, so it is left to speculation at the moment.
However, there have been previous engagements between Russian and American aircraft over the years, notably in the Korean War and Vietnam War. There were Cold War incidents that occurred over international waters, but these typically did not escalate to full-scale combat. If these are any indicator of the future, they might shine some light on the fifth-generation aircraft debate. (Militaries around the world have thousands of this Russian fighter jet.)
For now, 24/7 Wall St. is taking a look at what aircraft are in the Russian arsenal. To identify every aircraft in the Russian military, 24/7 Wall St. reviewed the 2024 World Air Forces report from FlightGlobal, an aviation and aerospace industry publication. We ordered these aircraft alphabetically. We also included supplemental data on the type of aircraft and top speed. We excluded trainer aircraft.
Here is a look at every aircraft in the Russian military:
Why Are We Covering This?

Understanding the aircraft in Russia’s Air Force is important because they play a big part in the country’s defense and global influence. Each type of aircraft has a specific job, like controlling the skies, bombing long-range targets, or using advanced technology to disrupt enemy systems. Knowing which aircraft are in use gives context to Russian military strategies and military capabilities.
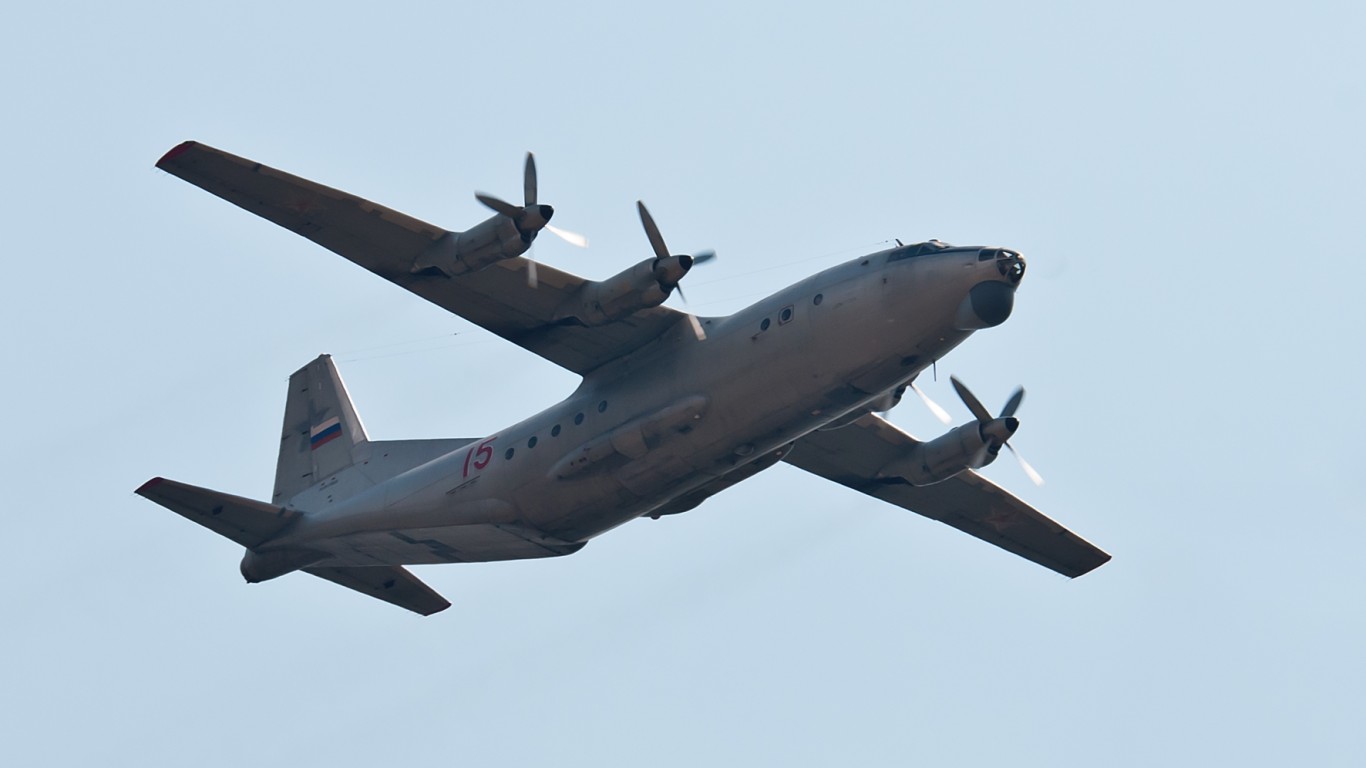
An-12 Cub
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1959
- Active aircraft: 64
- Top speed: 300 mph
- Armament: Typically none, sometimes tail-mounted 23mm cannons
The An-12 Cub, introduced in 1959, is a Soviet-era transport aircraft that has remained in service with 64 active units today. The An-12 can hit top speeds around 300 mph. Although this aircraft is typically unarmed, some variants feature tail-mounted 23mm cannons for defensive purposes. The An-12 has been widely used in both military and civilian roles, handling cargo transport.
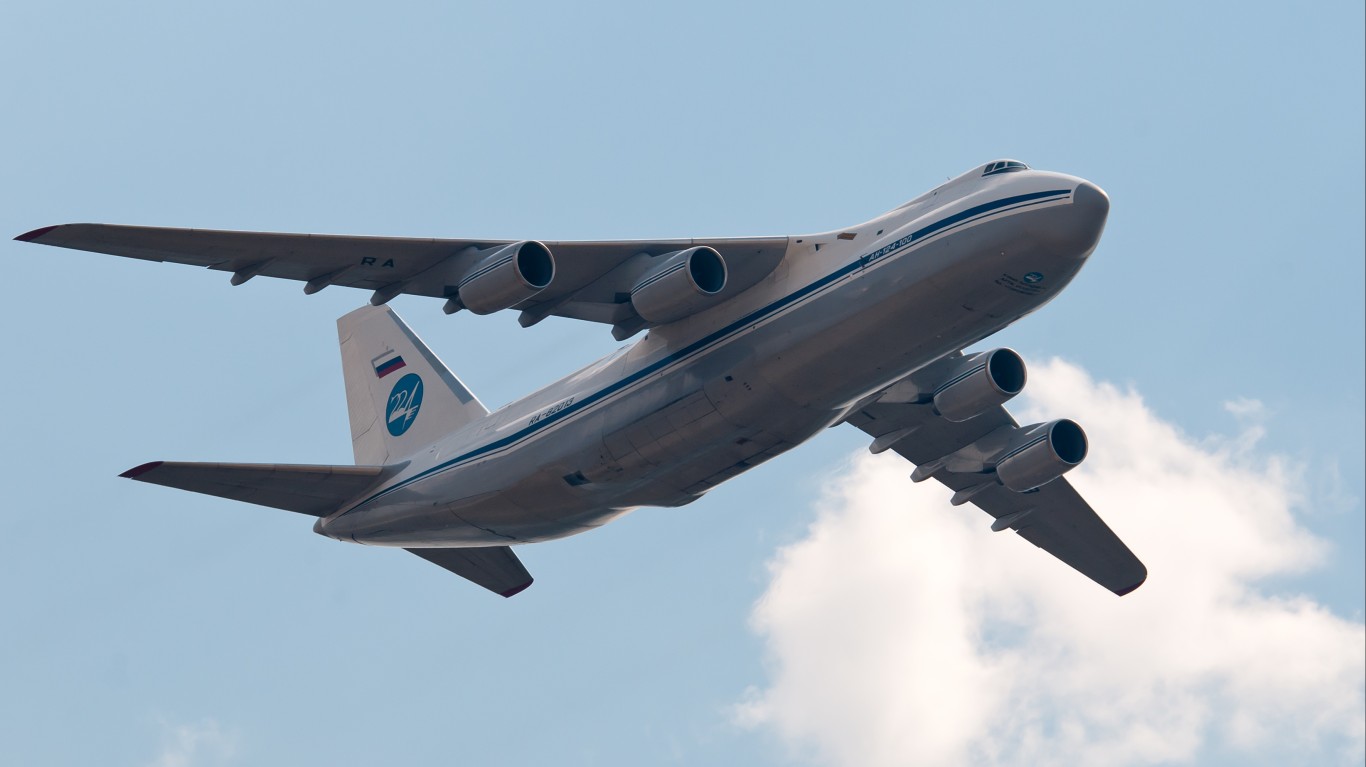
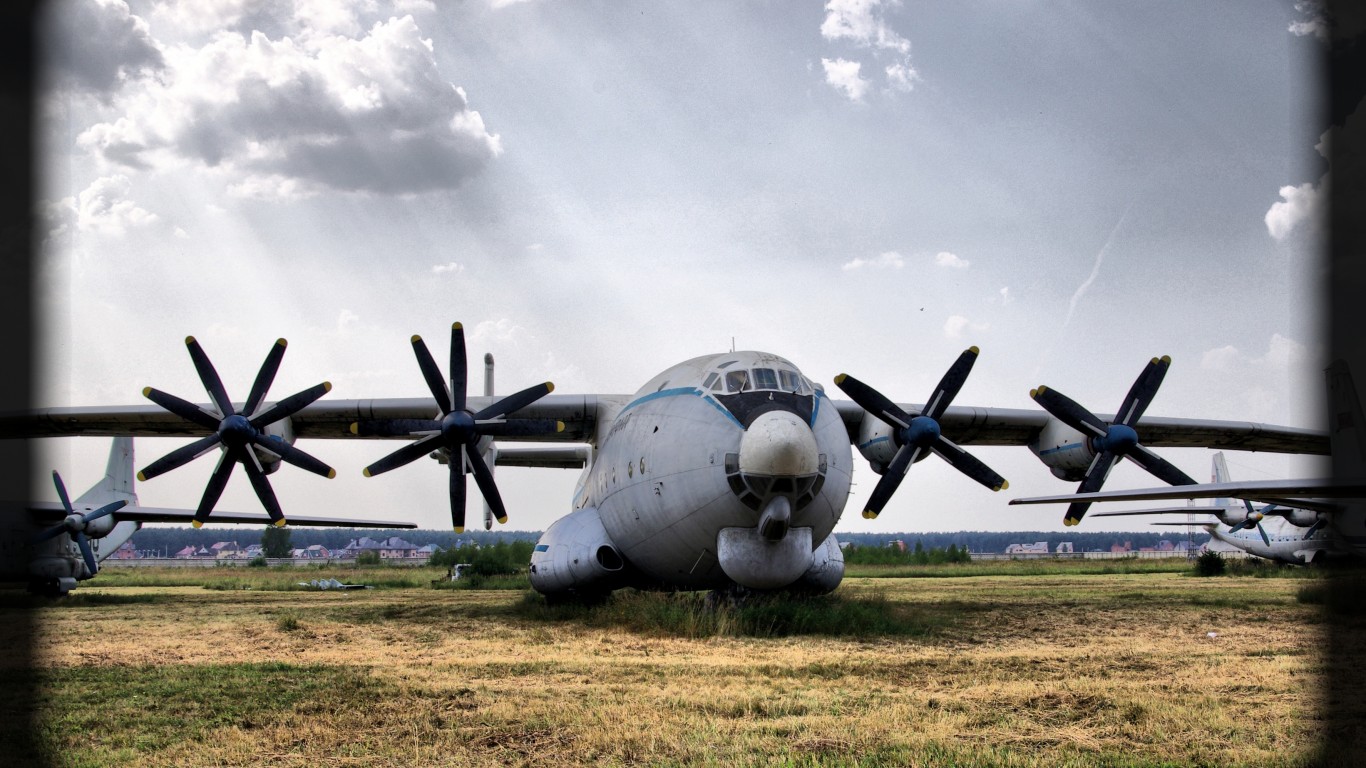
An-124 Ruslan Condor
- Type: Strategic heavy-lift transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1986
- Active aircraft: 5
- Top speed: 537 mph
- Armament: N/A
For a number of years, the AN-124 Ruslan Condor was the largest cargo aircraft in the world but it has since been surpassed. It was introduced in 1986 as a strategic heavy-lift transport aircraft. The Ruslan Condor is one of the faster aircraft in its class with a top speed of 537 mph. Currently there are 5 active aircraft in the Russian military.
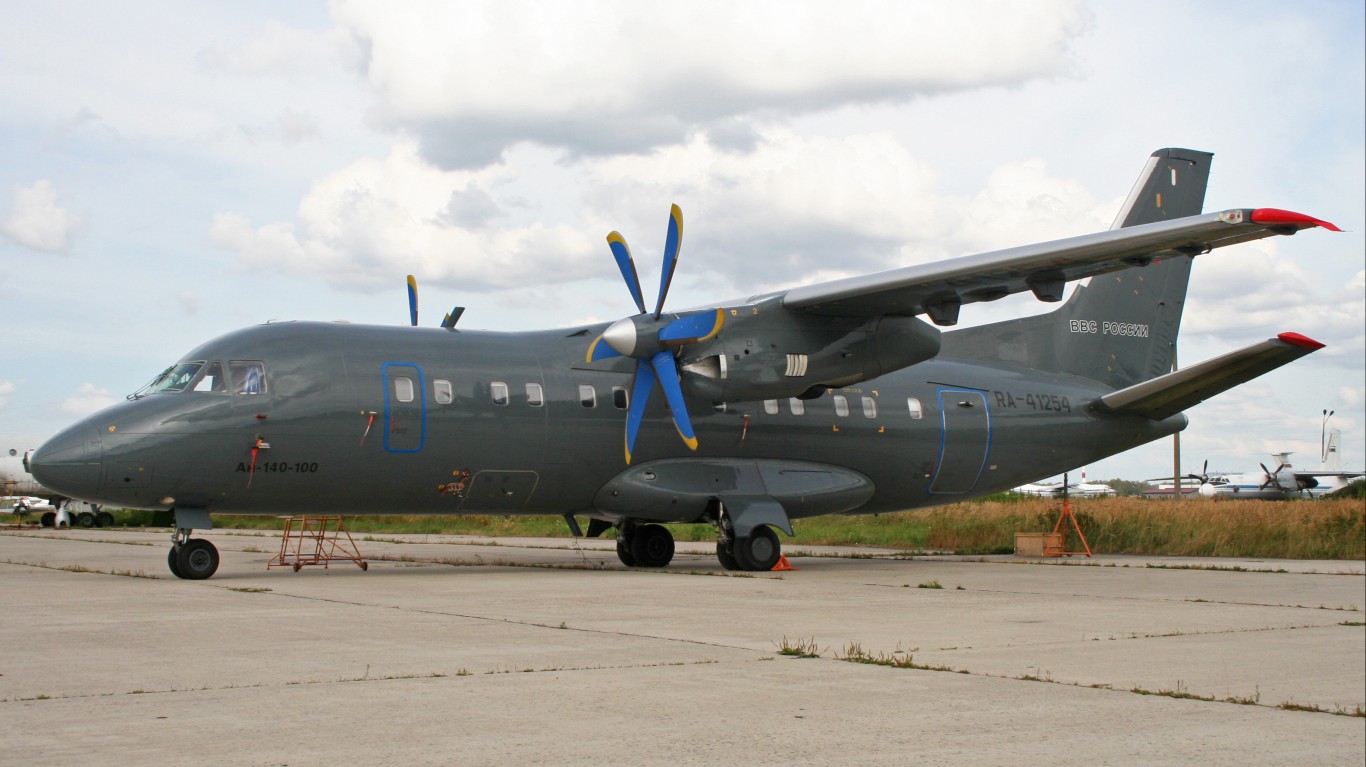
Antonov An-140
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 2002
- Active aircraft: 8
- Top speed: 357 mph
- Armament: N/A
The An-140 is a fairly versatile transport aircraft introduced in 2002. It is often used in harsh environments, like Siberia, and its design is meant for extreme weather conditions and tough runways. With a top speed of 357 mph, it is primarily used for regional cargo and passenger transport.
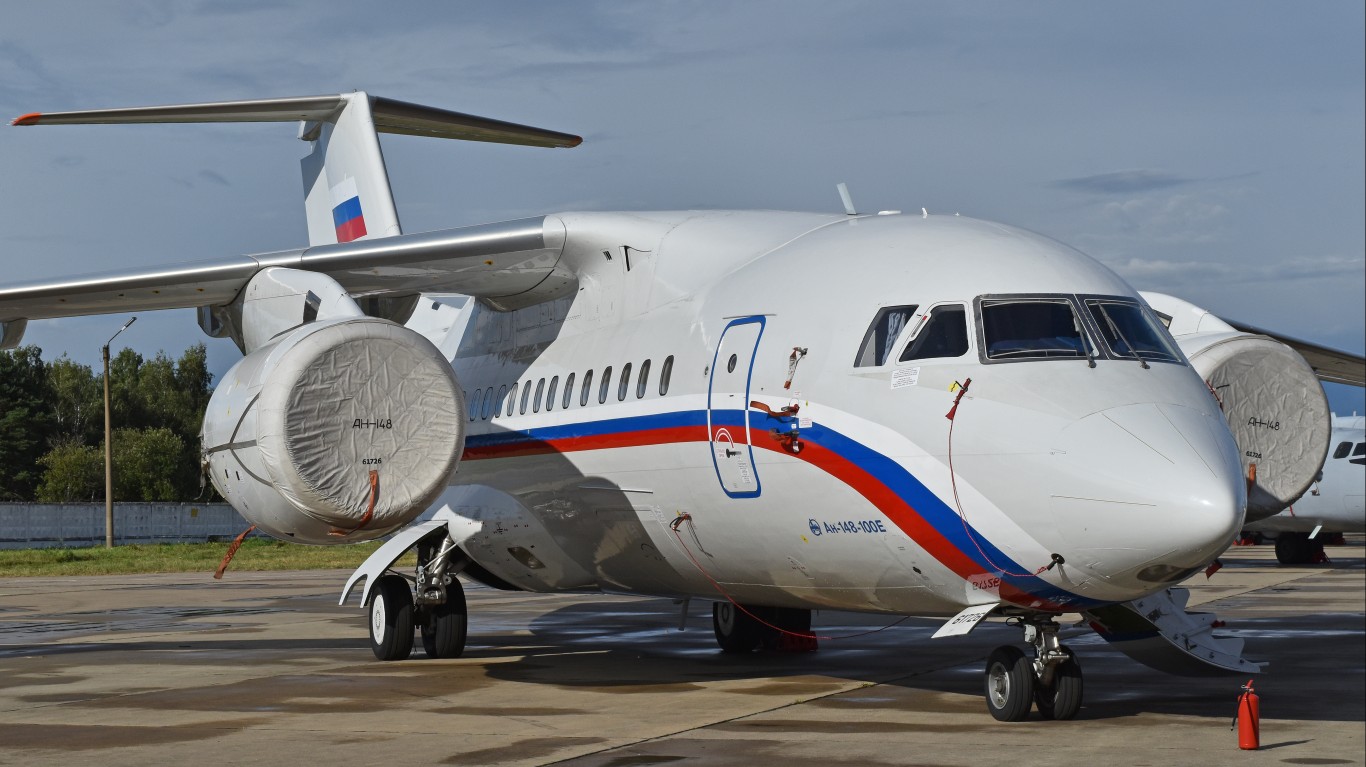
Antonov An-148
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 2009
- Active aircraft: 15
- Top speed: 513 mph
- Armament: N/A
The Antonov An-148 is unique among Russian aircraft for its ability to operate in subzero temperatures. It is typically used for transport in the Artic region, with its hull designed to withstand these temperatures and its D-436 turbofan engines designed to handle cold-start conditions. This aircraft was introduced in 2009, and can hit top speeds over 513 mph.
An-22 Antei
- Type: Heavy-lift transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1967
- Active aircraft: 3
- Top speed: 460 mph
- Armament: N/A
The An-22 has seen extensive use in humanitarian missions, acting as a heavy-lift transport aircraft. It was introduced in 1967, and there are only 3 of these aircraft currently in service. With a top speed of 460 mph, the An-22 was the largest turboprop-powered aircraft in the world at the time of its introduction. It still holds that distinction today, but it is expected to be retired from service soon.
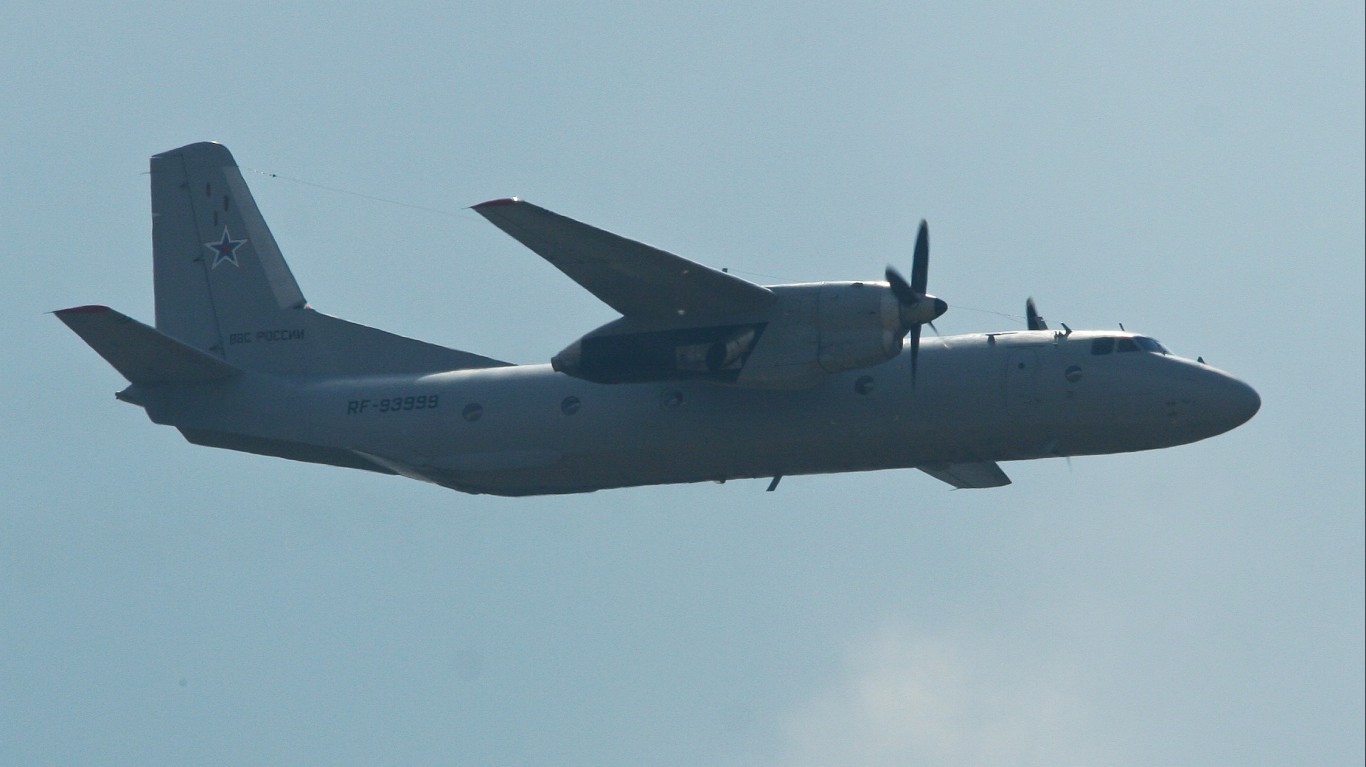
An-26 Curl
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1969
- Active aircraft: 139
- Top speed: 277 mph
- Armament: N/A
Introduced in 1969, the An-26 Curl is a transport aircraft for the Russian military. There are only 139 of these aircraft in current operation. These have a top speed of 277 mph, and have become a workhorse for many air forces around the world. Currently, over 30 countries are putting this aircraft to use, making it one of the most widely flown transport aircraft in the world.
An-30 Clank
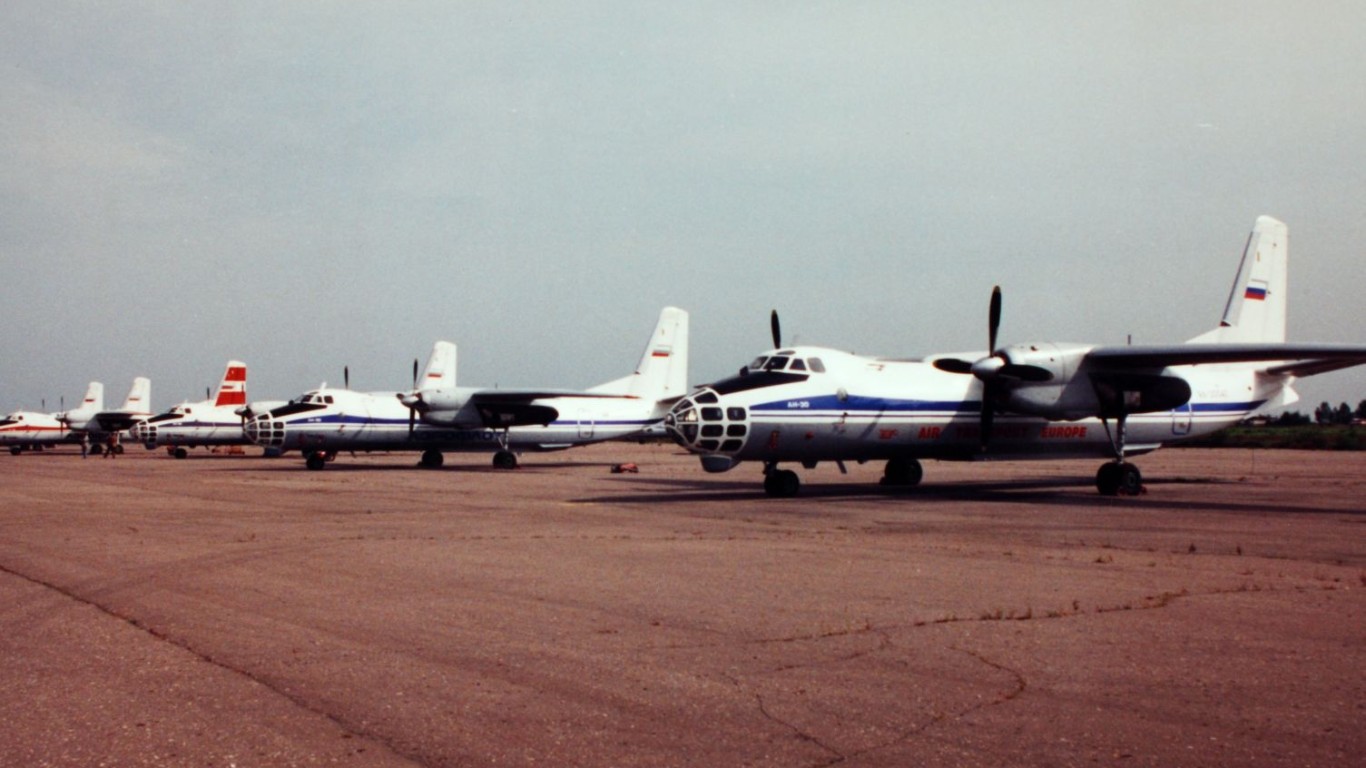

- Type: Transport / reconnaissance aircraft
- Year introduced: 1968
- Active aircraft: 16
- Top speed: 336 mph
- Armament: N/A
The An-30 Clank, introduced in 1968, is a specialized transport and reconnaissance aircraft, designed for surveillance and mapping missions. With a top speed of 336 mph, it’s equipped with advanced cameras and sensors that allow it to perform detailed reconnaissance.
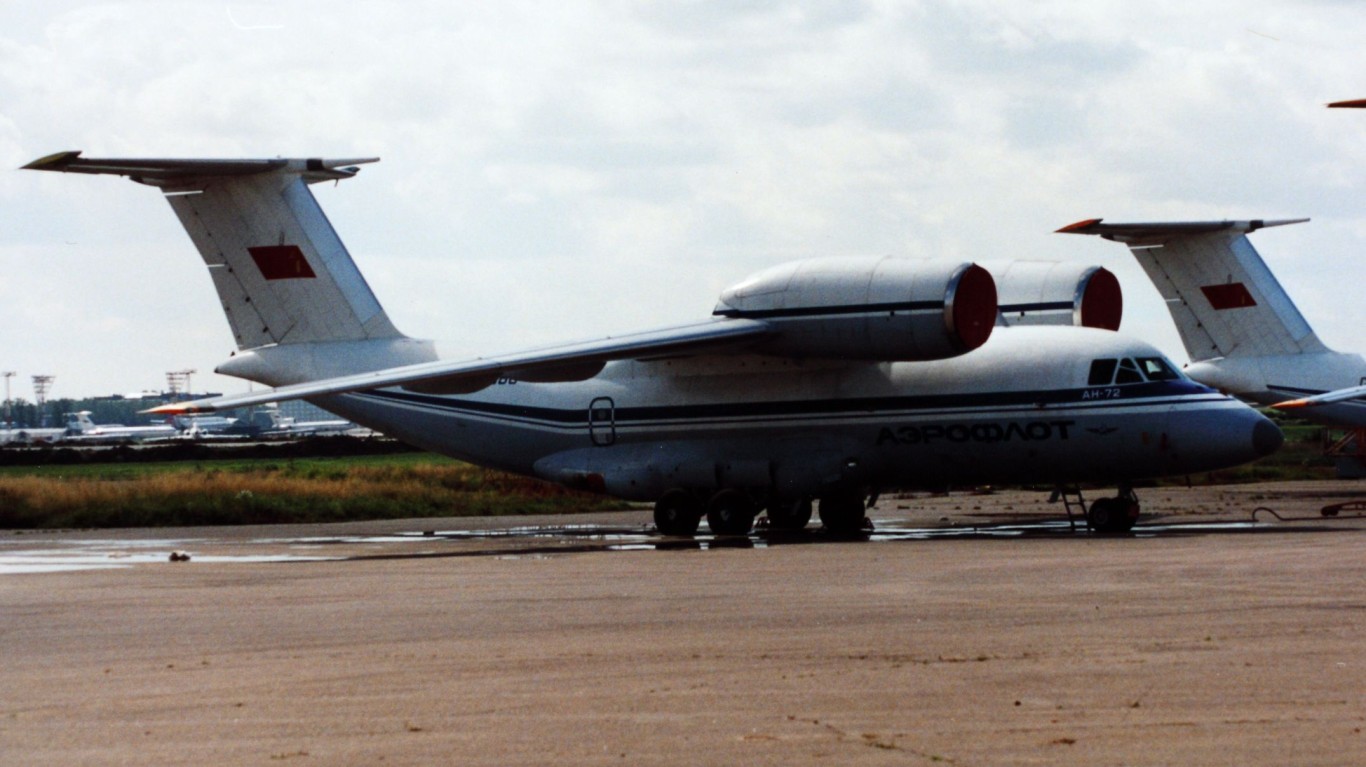
An-72 Coaler
- Type: Tactical medium-lift transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1986
- Active aircraft: 35
- Top speed: 438 mph
- Armament: 23mm gun pods, UB-23M rocket launcher system, conventional drop bombs
The An-72 Coaler has a very unique engine placement, compared to any other Russian aircraft. The engines are above the wings to create extra lift, allowing it to take off from shorter runways. It has earned the nickname of “Cheburashka” in Russia, for the resemblance of its engines to the ears of a popular Soviet cartoon character.
AS355 Twin Squirrel
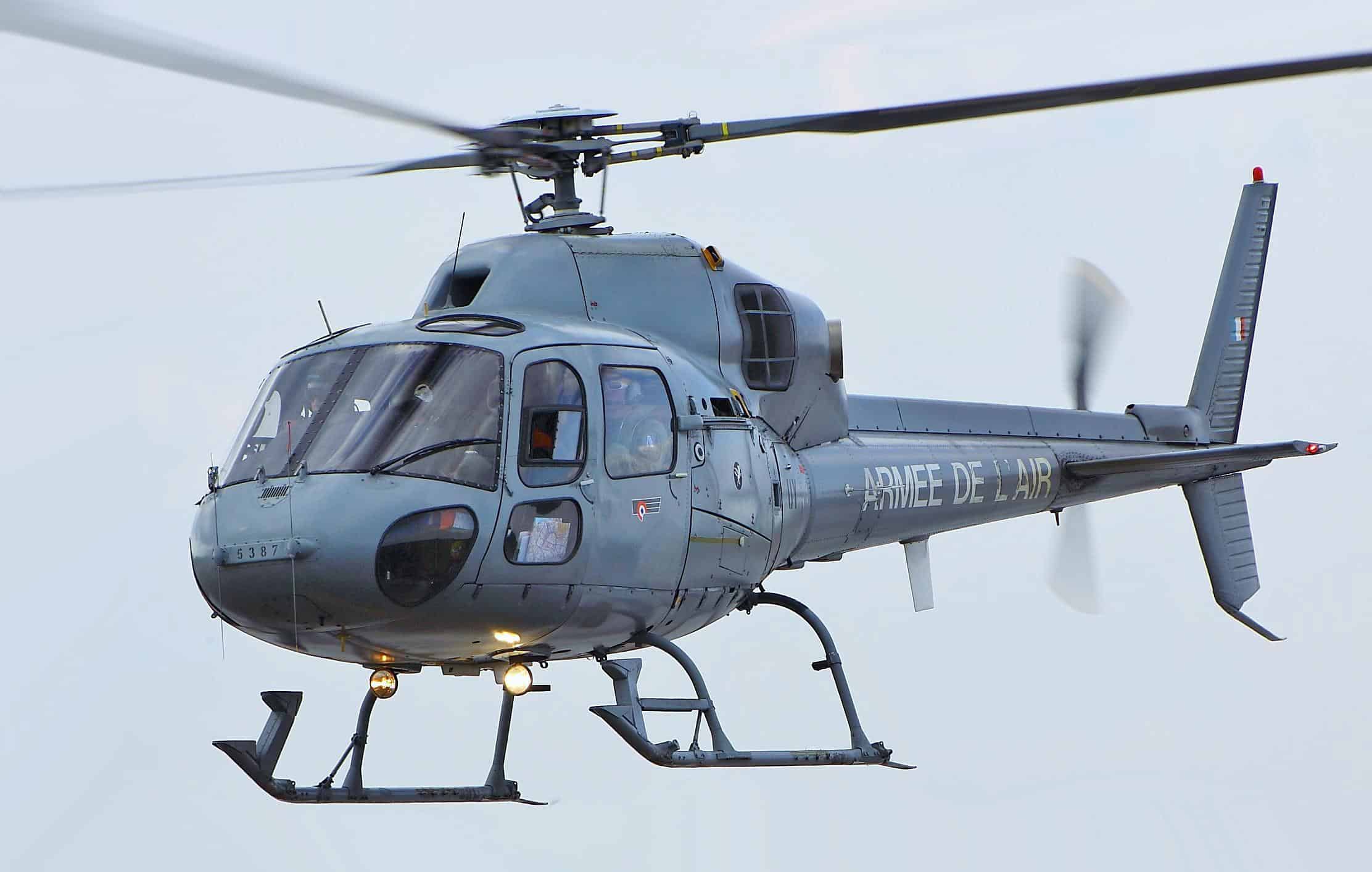

- Type: Light utility helicopter
- Year introduced: 1979
- Active aircraft: 2
- Top speed: 173 mph
- Armament: Light machine guns, rocket pods, air-to-ground, air-to-air missiles
With a top speed of 173 mph, the AS355 is used in a range of missions, including reconnaissance, transport, and even light combat roles. The Twin Squirrel was introduced in 1979, and there are currently 2 of these helicopters in active service. Despite its small size, it can be armed with light machine guns, rocket pods, and air-to-ground or air-to-air missiles. It does see some use among civilians as well, without the armament of course.
Be-12 Mail
- Type: Reconnaissance / maritime patrol aircraft
- Year introduced: 1961
- Active aircraft: 7
- Top speed: 329 mph
- Armament: Torpedoes, depth charges, mines, conventional drop bombs
The Be-12 was originally designed as an amphibious aircraft, allowing it to land on both runways and bodies of water. It was introduced in 1961 as a reconnaissance and maritime patrol aircraft, primarily for anti-submarine warfare. With a top speed of 329 mph, the Be-12 is typically used for long-duration missions over the ocean and it can equip a range of weapons reflecting this distinction.
Be-200 Altair
- Type: Amphibious flying boat aircraft
- Year introduced: 2003
- Active aircraft: 2
- Top speed: 435 mph
- Armament: N/A
Introduced in 2003, the Be-200 Altair is a modern amphibious flying boat aircraft designed for a variety of missions, including firefighting, search and rescue, and maritime patrol. With a top speed of 435 mph, it stands out for its speed and versatility in both air and water operations. These flying boats do not come with armament, unlike its predecessors.
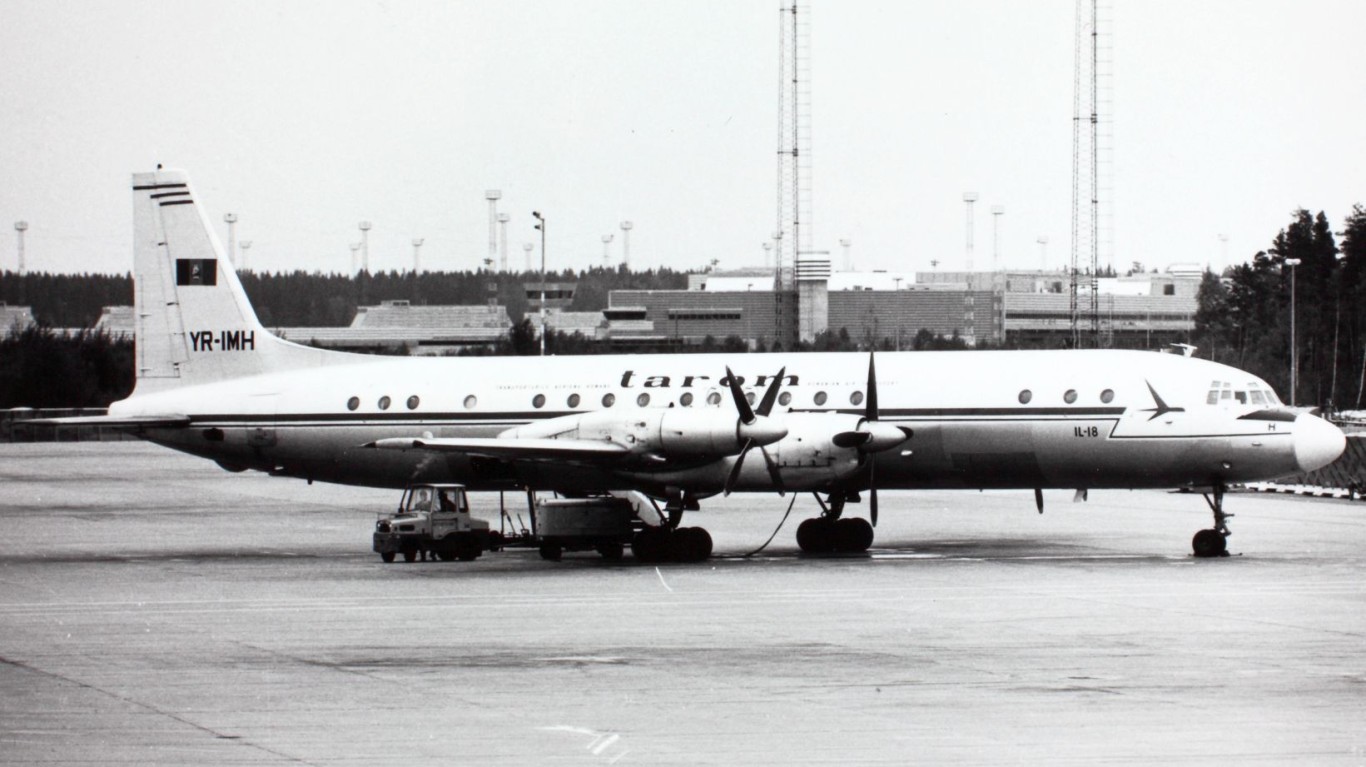
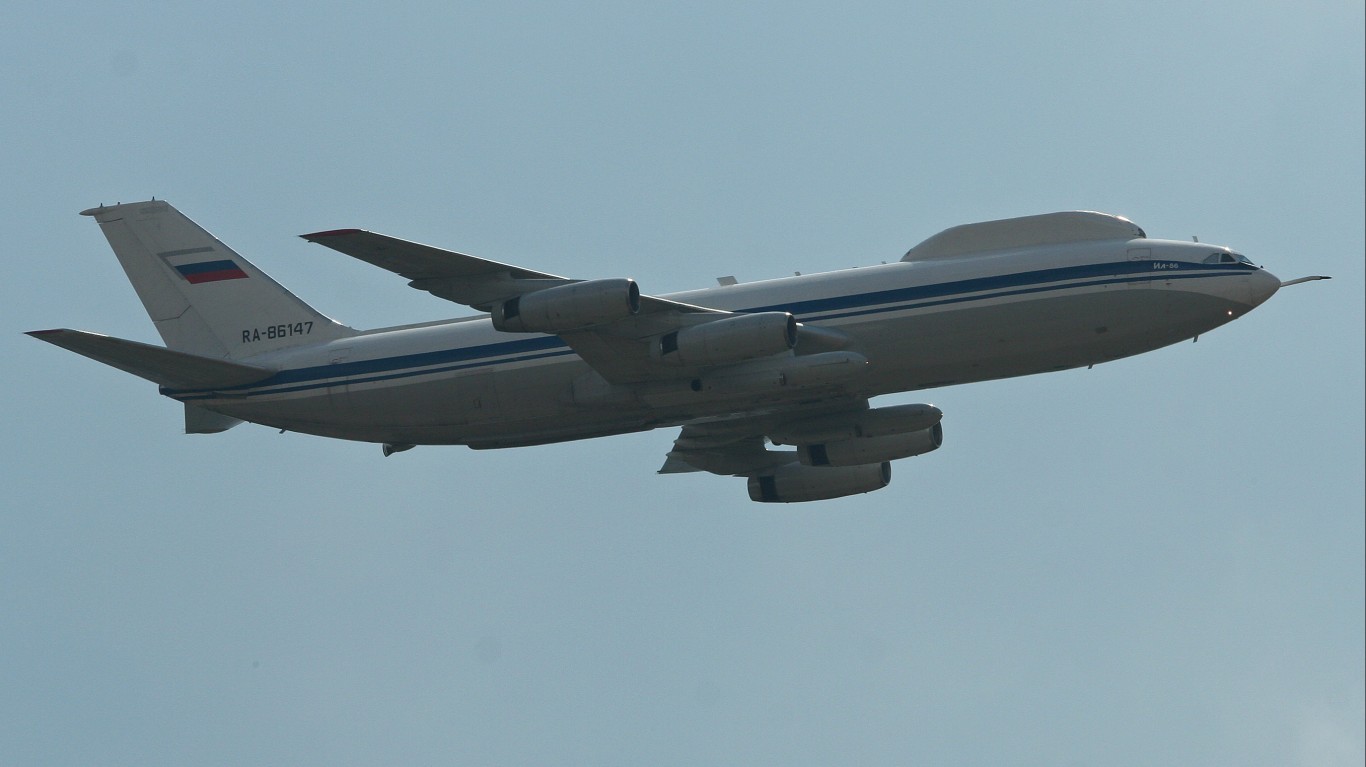
IL-18 Coot
- Type: Transport / maritime patrol aircraft
- Year introduced: 1957
- Active aircraft: 4
- Top speed: 419 mph
- Armament: N/A
The IL-18 Coot, introduced in 1957, is a versatile aircraft that has served in both transport and maritime patrol roles for decades. Currently, there are 4 active IL-18 aircraft in service of the Russian military.
IL-20 Coot-A
- Type: Electronic signals intelligence aircraft
- Year introduced: 1969
- Active aircraft: 31
- Top speed: 419 mph
- Armament: N/A
The IL-20 Coot-A was introduced in 1969 as a specialized electronic signals intelligence aircraft designed to gather, intercept, and analyze electronic communications and radar signals. Currently, 31 IL-20 aircraft are active, and these continue to provide critical intelligence in modern conflicts.
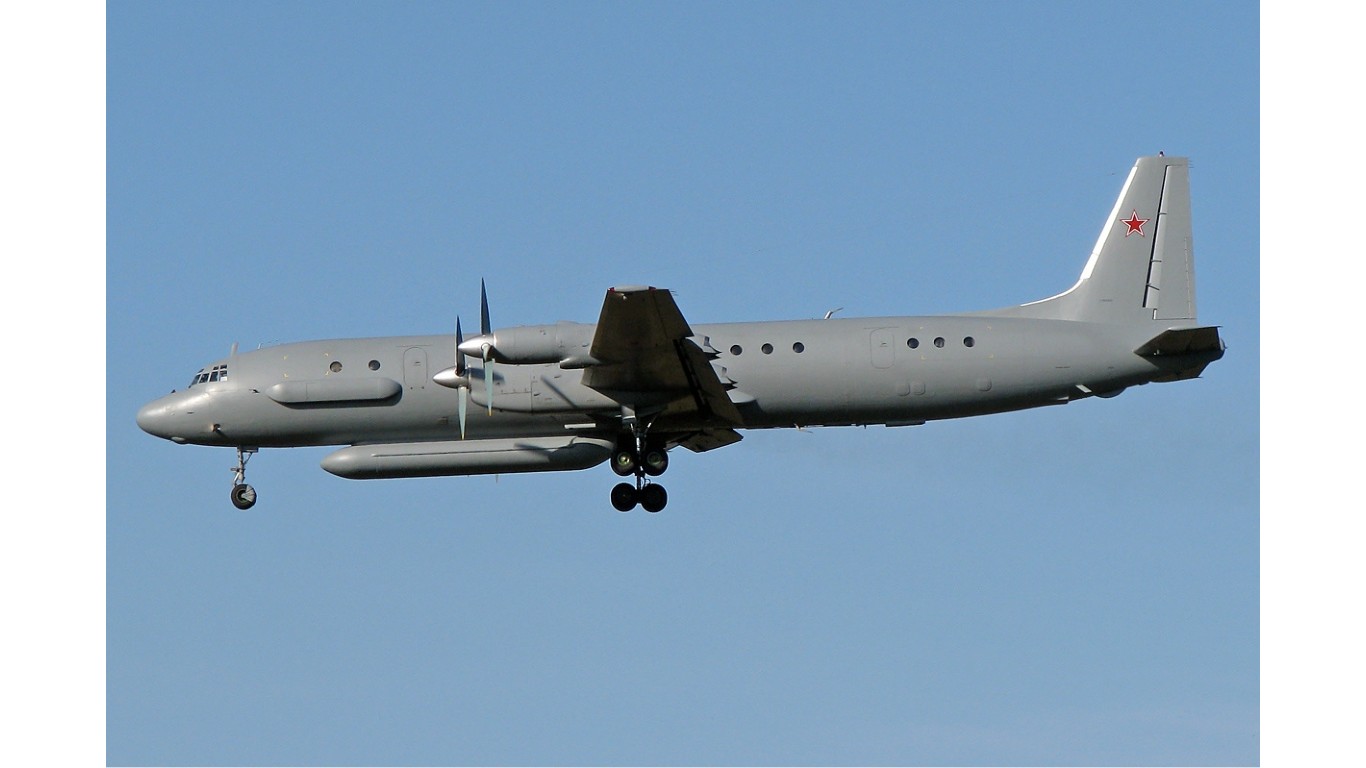
Il-38 Dolphin
- Type: Anti-submarine maritime patrol aircraft
- Year introduced: 1968
- Active aircraft: 21
- Top speed: 404 mph
- Armament: Conventional drop bombs, depth charges, anti-ship missiles, torpedoes
Introduced in 1968 as an anti-submarine warfare and maritime patrol aircraft, the IL-38 Dolphin is designed to protect Russian naval assets. The Dolphin can hit top speeds over 400 mph. The IL-38 was originally based on the IL-18 design, but this was heavily modified for maritime conditions.
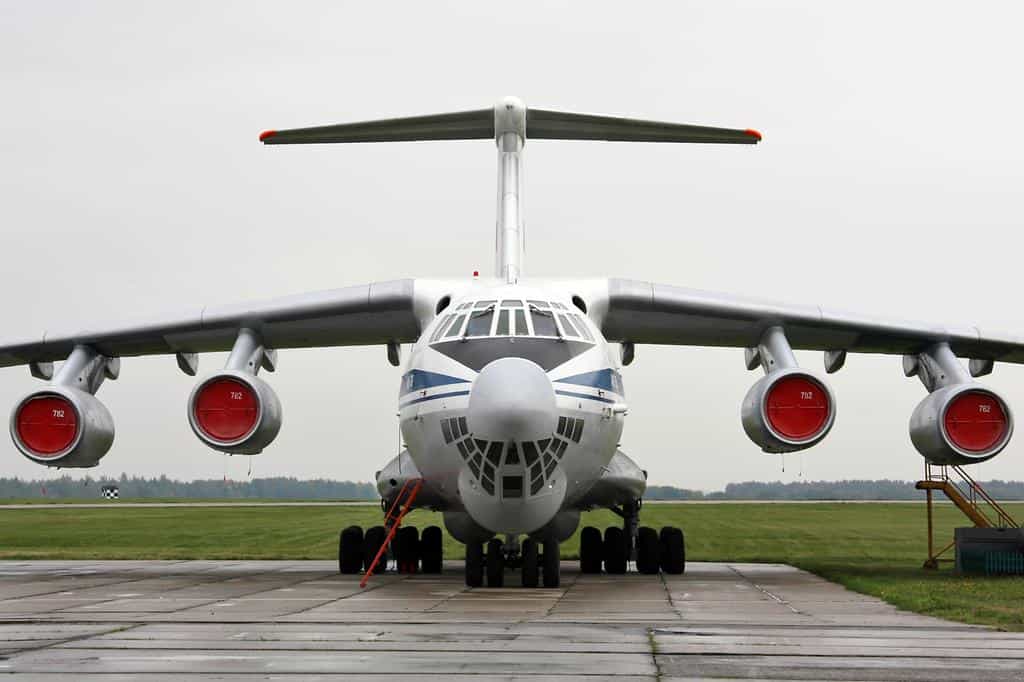
IL-76 Candid
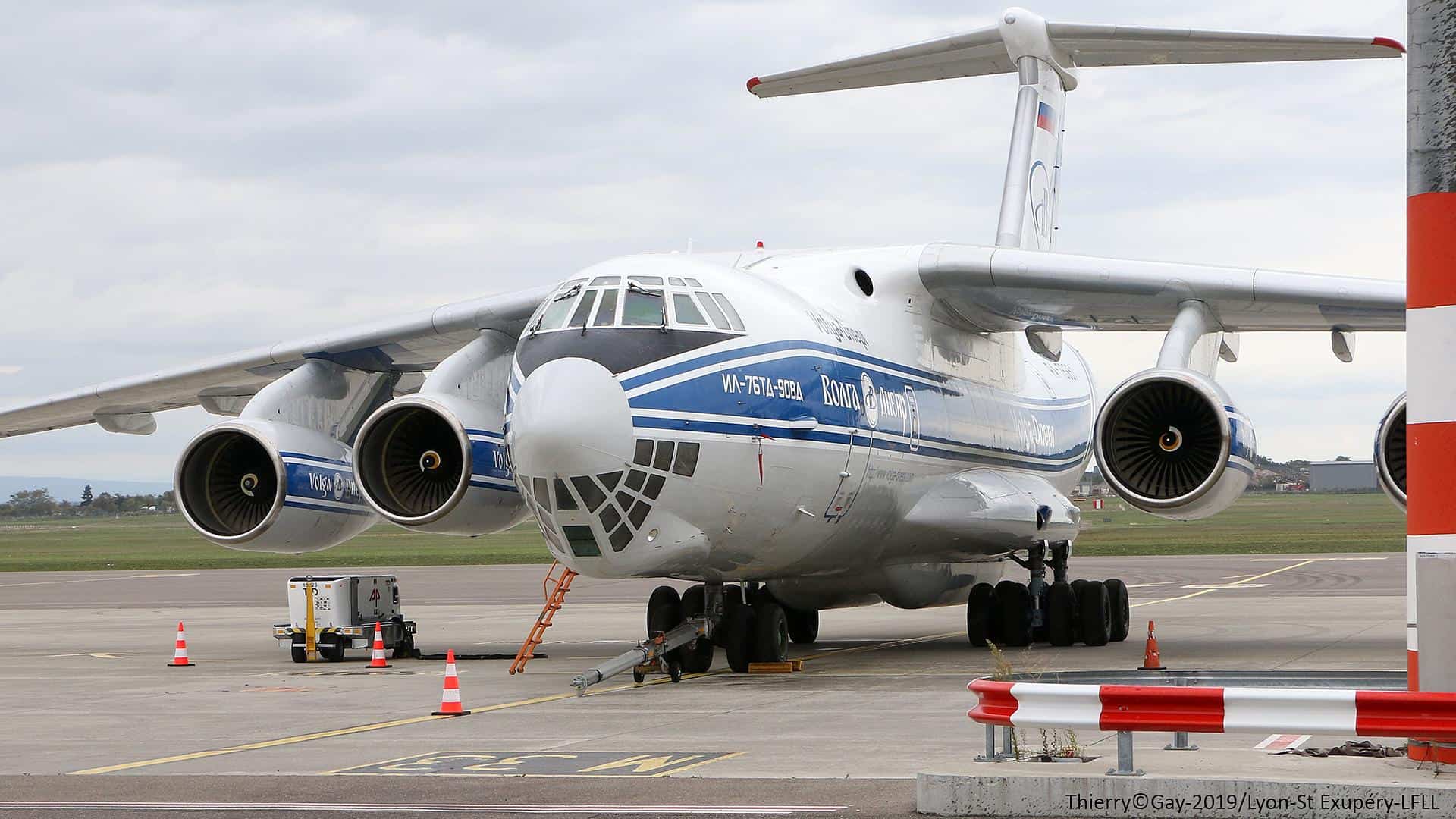

- Type: Strategic transport / tanker aircraft
- Year introduced: 1975
- Active aircraft: 143
- Top speed: 559 mph
- Armament: 23mm GSh-23L tail-mounted cannons, conventional drop bombs
The IL-76 Candid, introduced in 1975, is a strategic transport and tanker aircraft used for moving large amounts of cargo, military personnel, and even refueling operations.
IL-78 Midas
- Type: In-flight refueling tanker aircraft
- Year introduced: 1984
- Active aircraft: 19
- Top speed: 528 mph
- Armament: N/A
Introduced in 1984, the IL-78 Midas is a dedicated in-flight refueling tanker aircraft designed to extend the operational range of other military aircraft. It can hit a top speed of 528 mph and is capable of refueling multiple aircraft in a single flight.
IL-80 Maxdome
- Type: Airborne command post
- Year introduced: 1992
- Active aircraft: 3
- Top speed: 186 mph
- Armament: N/A
The IL-80 Maxdome is a specialized airborne command post designed to serve as a mobile headquarters during national emergencies or nuclear conflicts. The Maxdome only entered service in 1992 and has a fairly low top speed of 186 mph. It is equipped with advanced communications systems that allow high-ranking officials to control military operations from the air. This is more or less the equivalent of the U.S. “Doomsday” plane.
Ka-226 Sergei (Hoodlum)
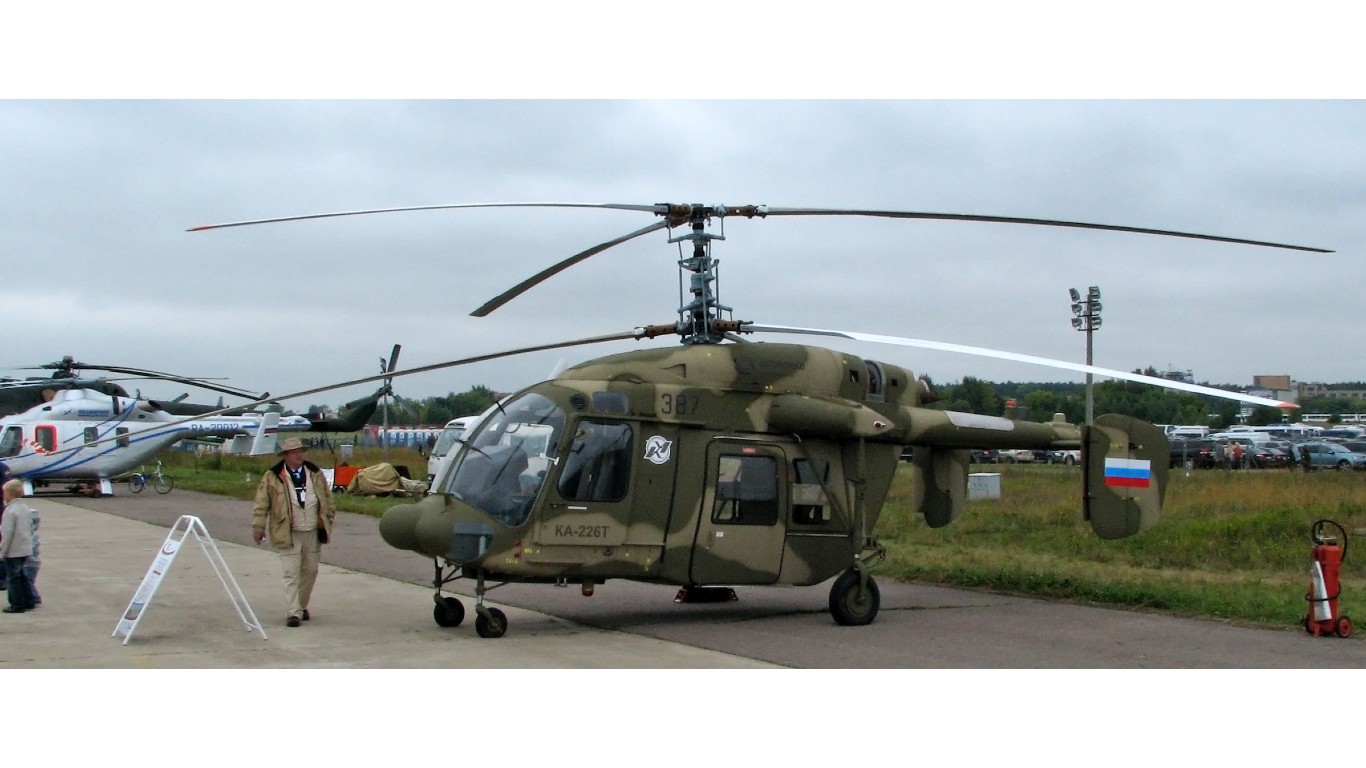

- Type: Light utility helicopter
- Year introduced: 2002
- Active aircraft: 36
- Top speed: 127 mph
- Armament: Light machine guns, rocket pods
Recognized by the NATO reporting name of Hoodlum, the Ka-226 Sergei was introduced in 2002 as a light utility helicopter. It has a fairly low top speed of 127 mph. The Ka-226 can be outfitted with various light machine guns and rocket pods. It also sees some civilian use.
Ka-27/28/29 Helix
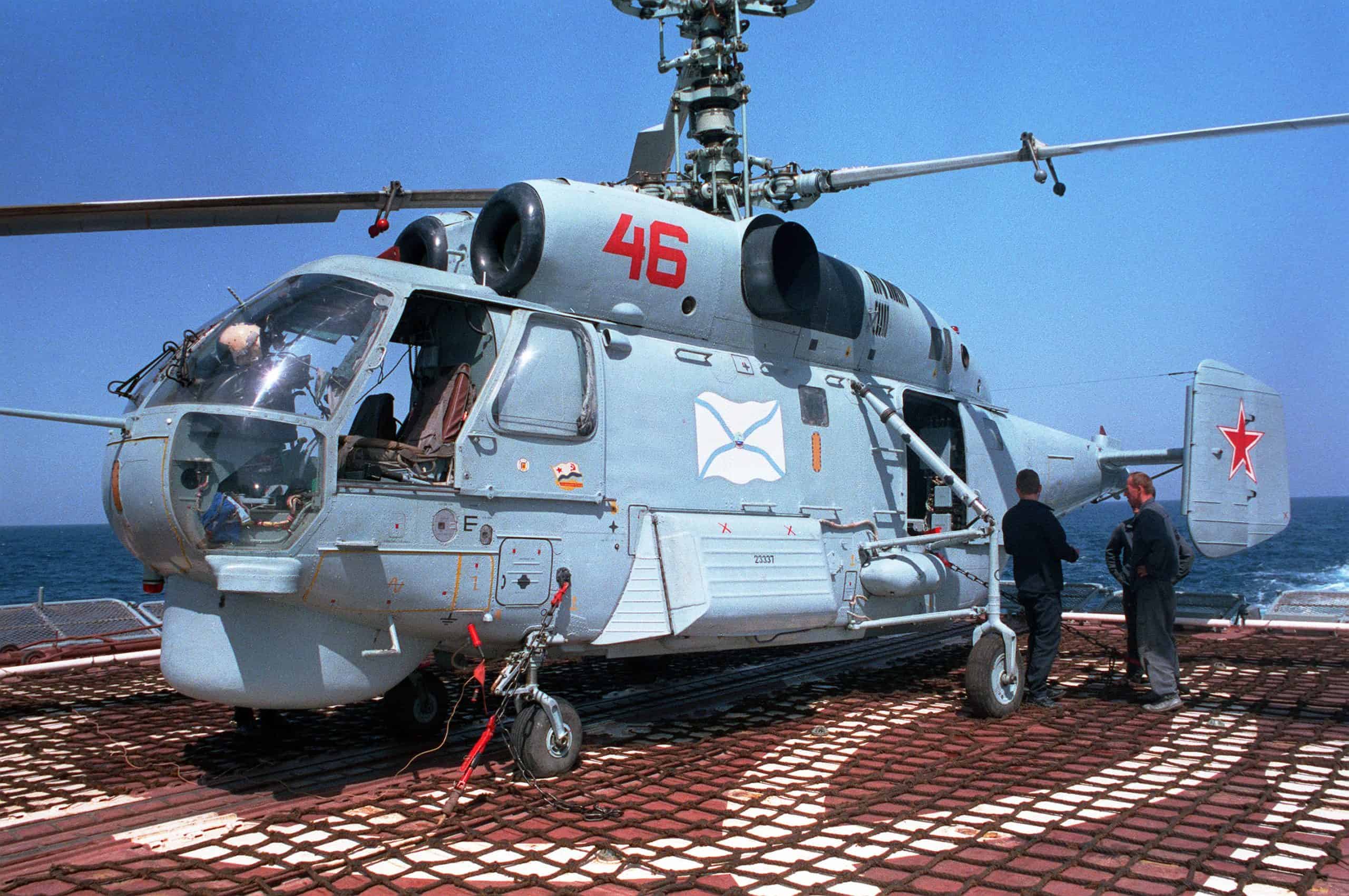

- Type: Multi-role helicopter
- Year introduced: 1982
- Active aircraft: 108
- Top speed: 143 mph
- Armament: Rocket pods, gun pods, anti-tank missiles, aerial torpedos, depth charges
The Ka-27/28/29 Helix, introduced in 1982, is a multi-role helicopter series designed for anti-submarine warfare, search and rescue, and combat support. With a top speed of 143 mph, the Helix series is known for its versatility in naval and military operations.
Ka-31 Helix
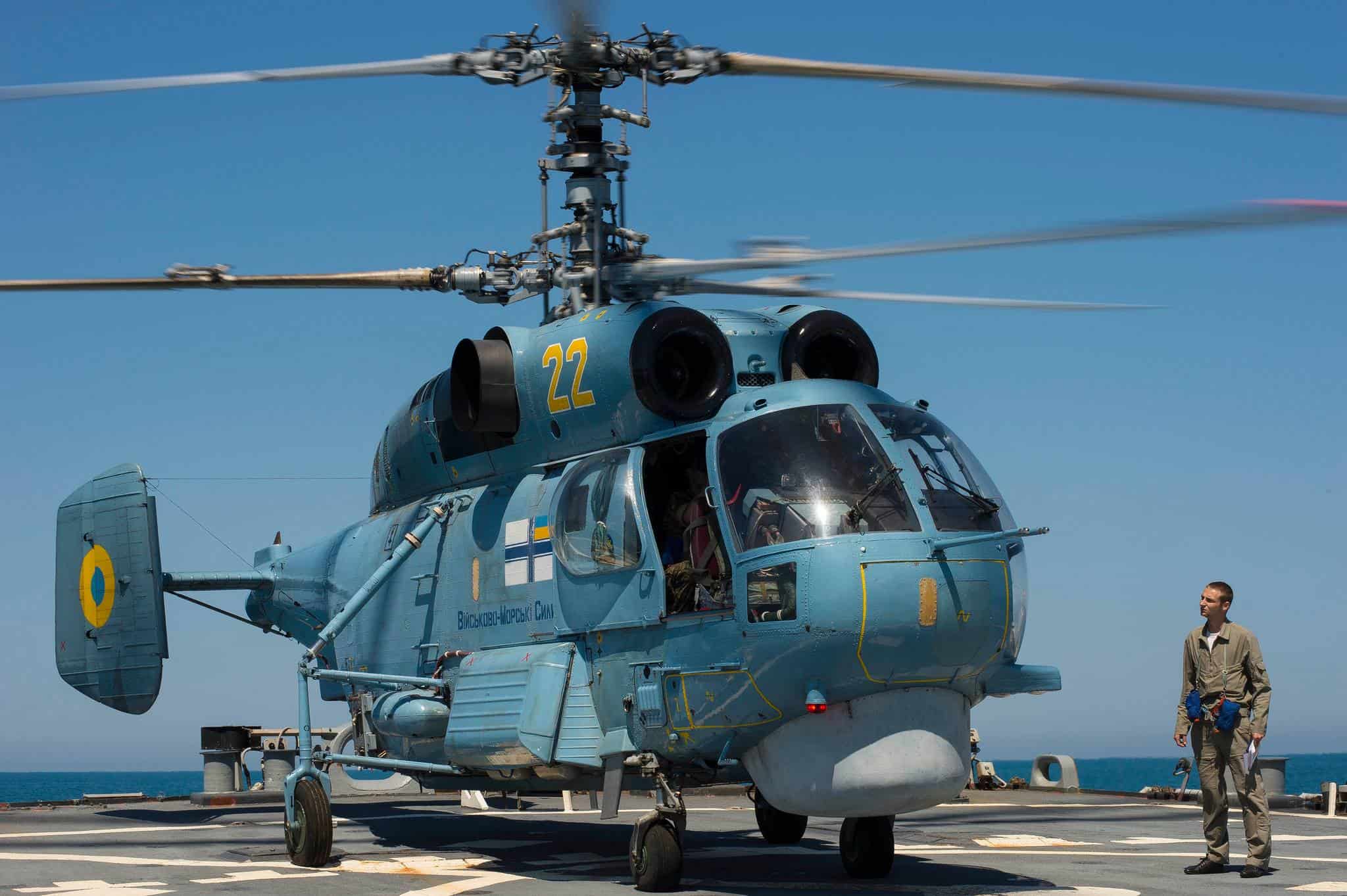

- Type: Airborne early warning naval helicopter
- Year introduced: 1995
- Active aircraft: 3
- Top speed: 155 mph
- Armament: Light machine guns
Introduced in 1995, the Ka-31 Helix is an airborne early warning helicopter that provides long-range radar coverage for Russian naval forces. While its main role is reconnaissance, it can also be armed with light machine guns for self-defense. It can reach top speeds around 155 mph, and there are only 3 of these helicopters in active service.
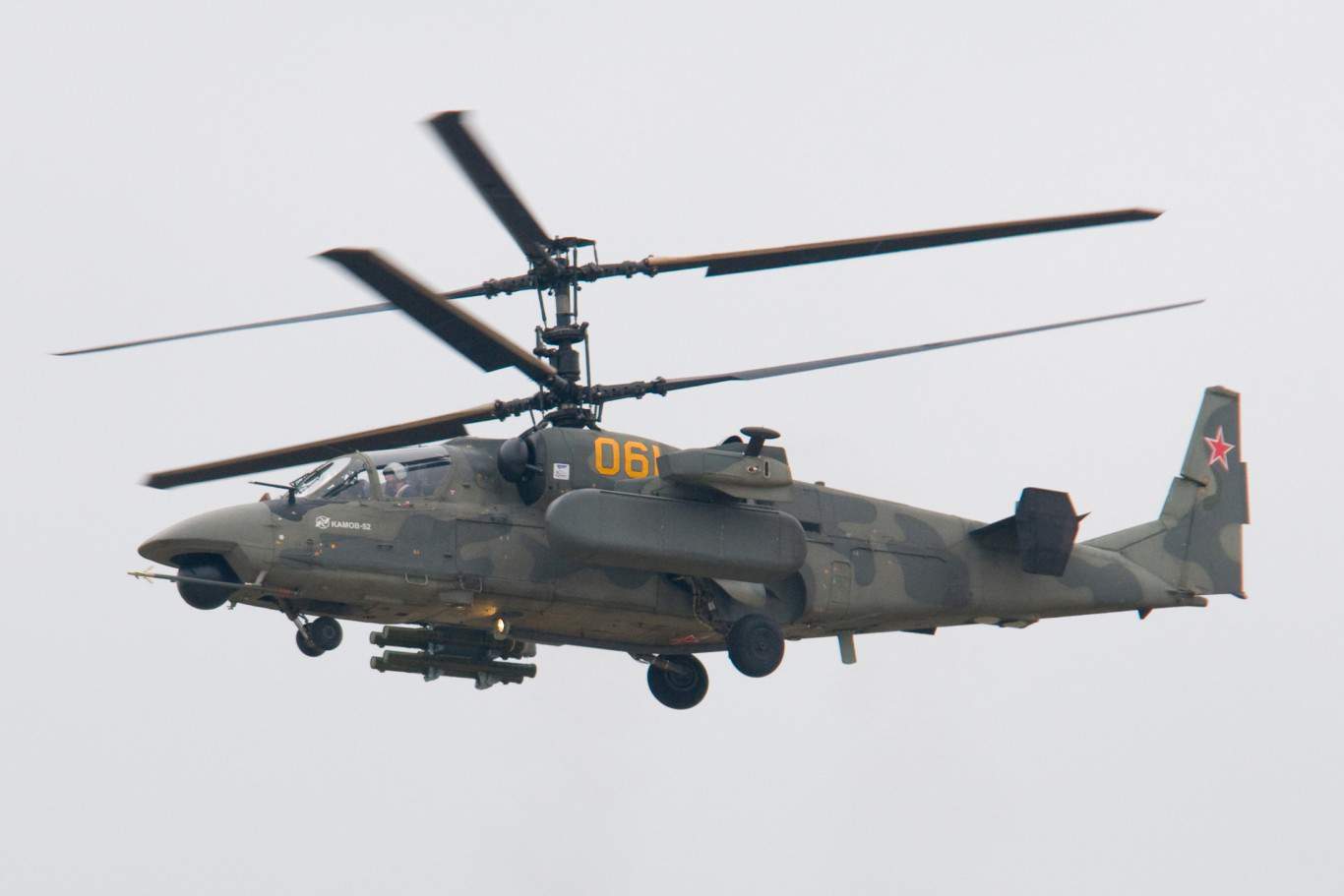
Ka-52 Alligator
- Type: Attack / reconnaissance helicopter
- Year introduced: 2010
- Active aircraft: 140
- Top speed: 186 mph
- Armament: 30mm automatic cannon, air-to-surface anti-tank missiles, rocket pods, cannon pods
The Ka-52 Alligator is one of the newest combat helicopters to come out of Russia. Introduced in 2010, these are state-of-the-art attack helicopters designed for close-air support and anti-tank operations. These come standard with a 30mm automatic cannon, and can be equipped with air-to-surface anti-tank missiles, rocket pods, and cannon pods. The coaxial design for the main rotor is truly unique and actually eliminates the need for a tail rotor.
Let L-410 Turbolet
- Type: Twin-turboprop utility aircraft
- Year introduced: 1970
- Active aircraft: 53
- Top speed: 252 mph
- Armament: N/A
The Let L-410 Turbolet, introduced in 1970, is a twin-turboprop utility aircraft widely used for short-haul transport in both military and civilian operations.
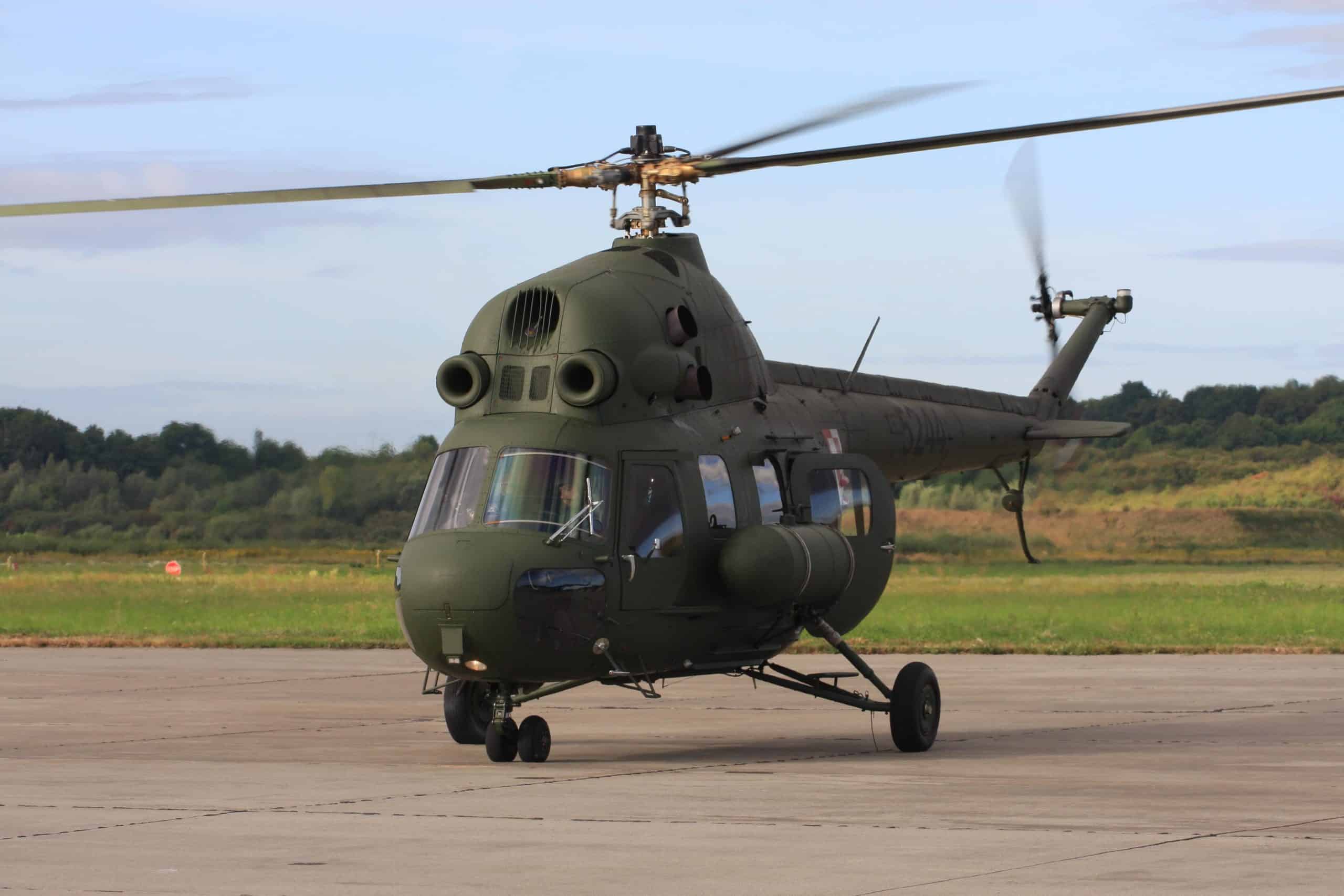
Mil Mi-2 Hoplite
- Type: Light utility helicopter
- Year introduced: 1965
- Active aircraft: 4
- Top speed: 124 mph
- Armament: 23mm automatic cannons, rocket pods, anti-tank guided missiles, air-to-air missiles
The Mil Mi-2 Hoplite is one of the older helicopters currently in service of Russia’s military with only 4 active. These helicopters were introduced in 1965 and can equip a wide array of armament including 23mm automatic cannons (standard), rocket pods, anti-tank guided missiles, and air-to-air missiles.
Mil Mi-24/35 Hind
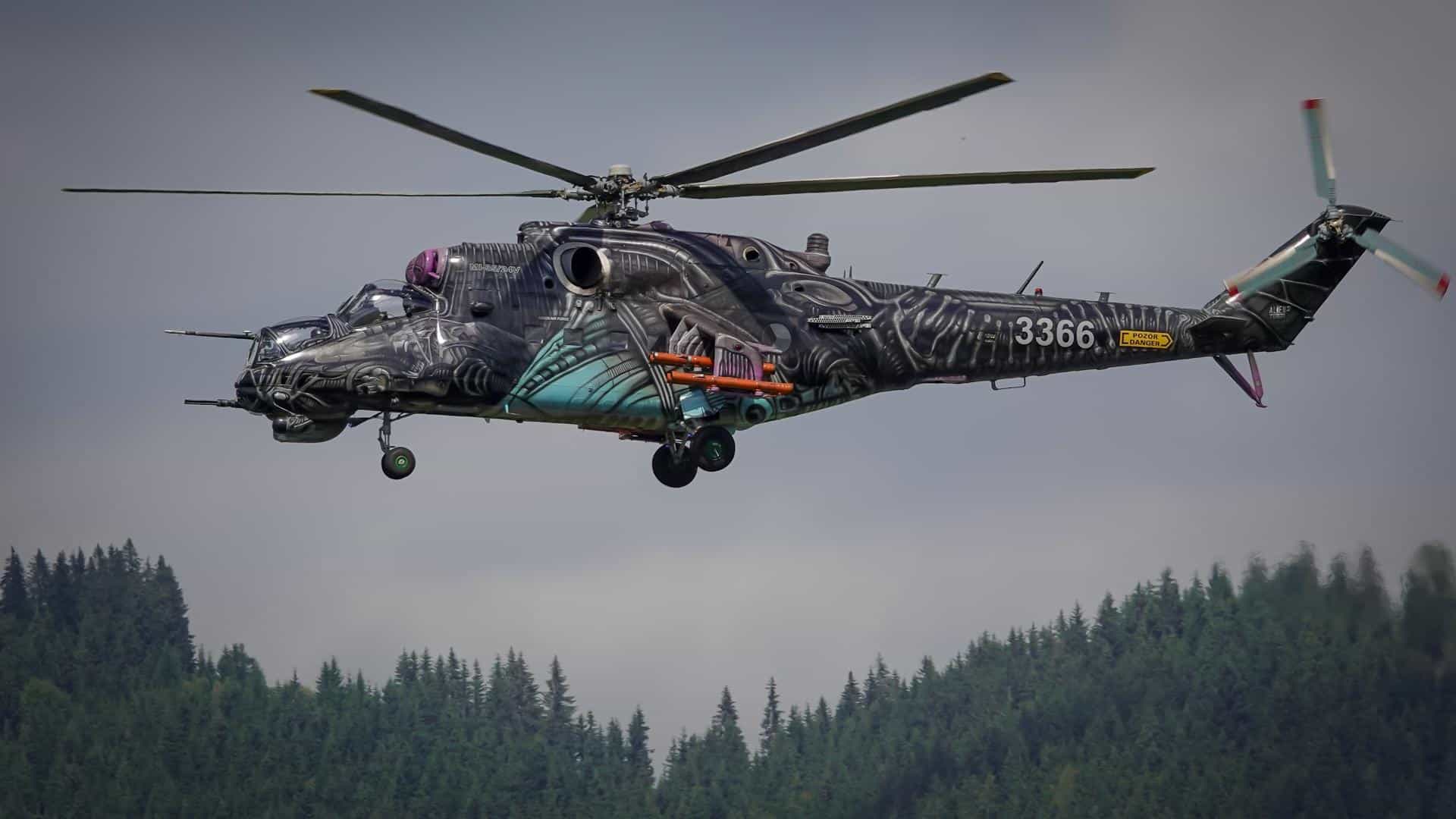

- Type: Attack helicopter
- Year introduced: 1973
- Active aircraft: 325
- Top speed: 208 mph
- Armament: 12.7mm heavy machine guns, 23mm cannon, 30mm cannon, anti-tank missiles, rocket pods, machine gun pods, cannon pods, conventional drop bombs
The Mi-24 earned the nickname the “flying tank” as a result of its heavy armor and incredible firepower. These helicopters have a top speed around 208 mph and can equip 12.7mm heavy machine guns, 23mm and 30mm cannons, anti-tank missiles, rocket pods, and conventional drop bombs. With 325 active aircraft, the Mi-24/35 is the backbone of Russia’s attack helicopter force.
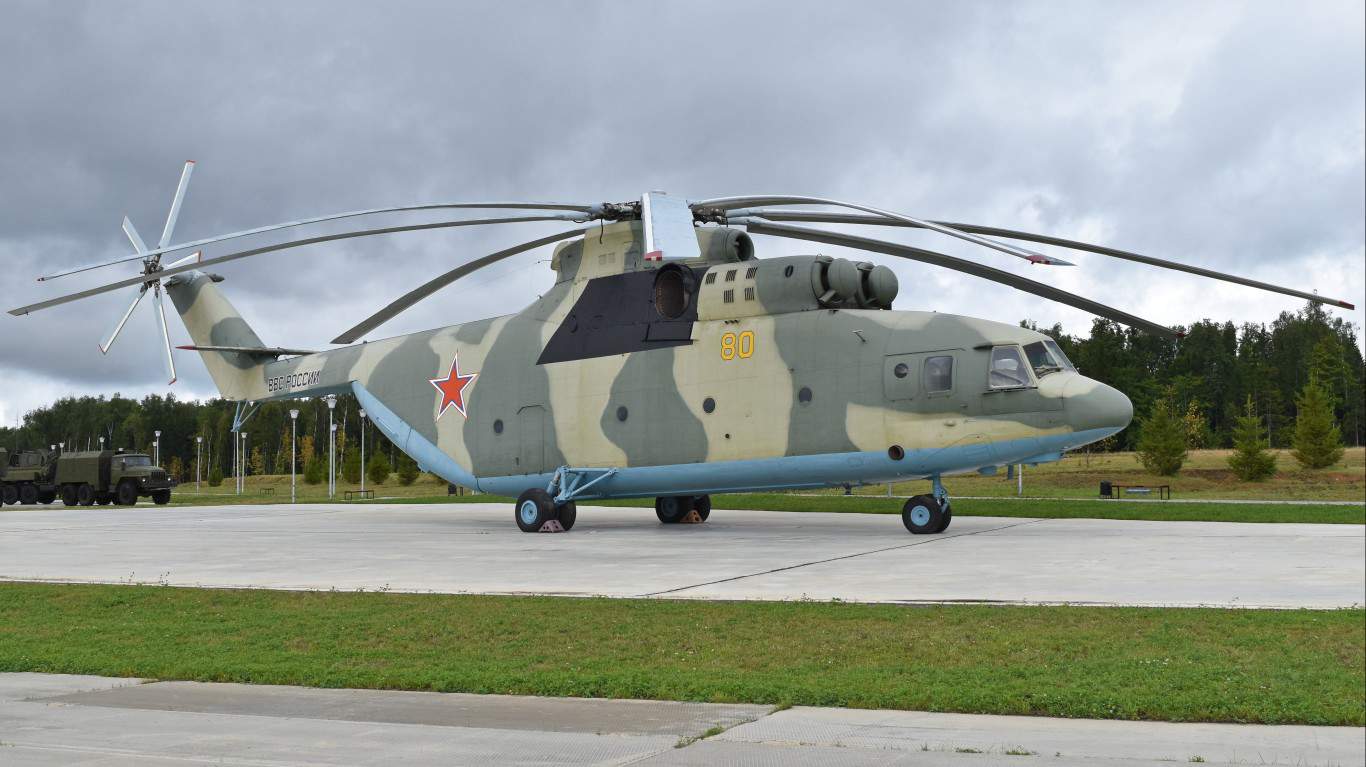
Mil Mi-26 Halo
- Type: Heavy-lift transport helicopter
- Year introduced: 1983
- Active aircraft: 44
- Top speed: 183 mph
- Armament: Light machine guns, air-to-ground missiles, air-to-air missiles, rocket pods
The Mi-26 Halo is typically a heavy-lift transport helicopter, but it can equip a wide range of armament for combat scenarios. It was introduced in 1983, and there are currently 44 in active service of the Russian military. This helicopter actually holds the world record for the heaviest helicopter lift, having transported a 56-ton piece of machinery.
Mil Mi-28 Havoc
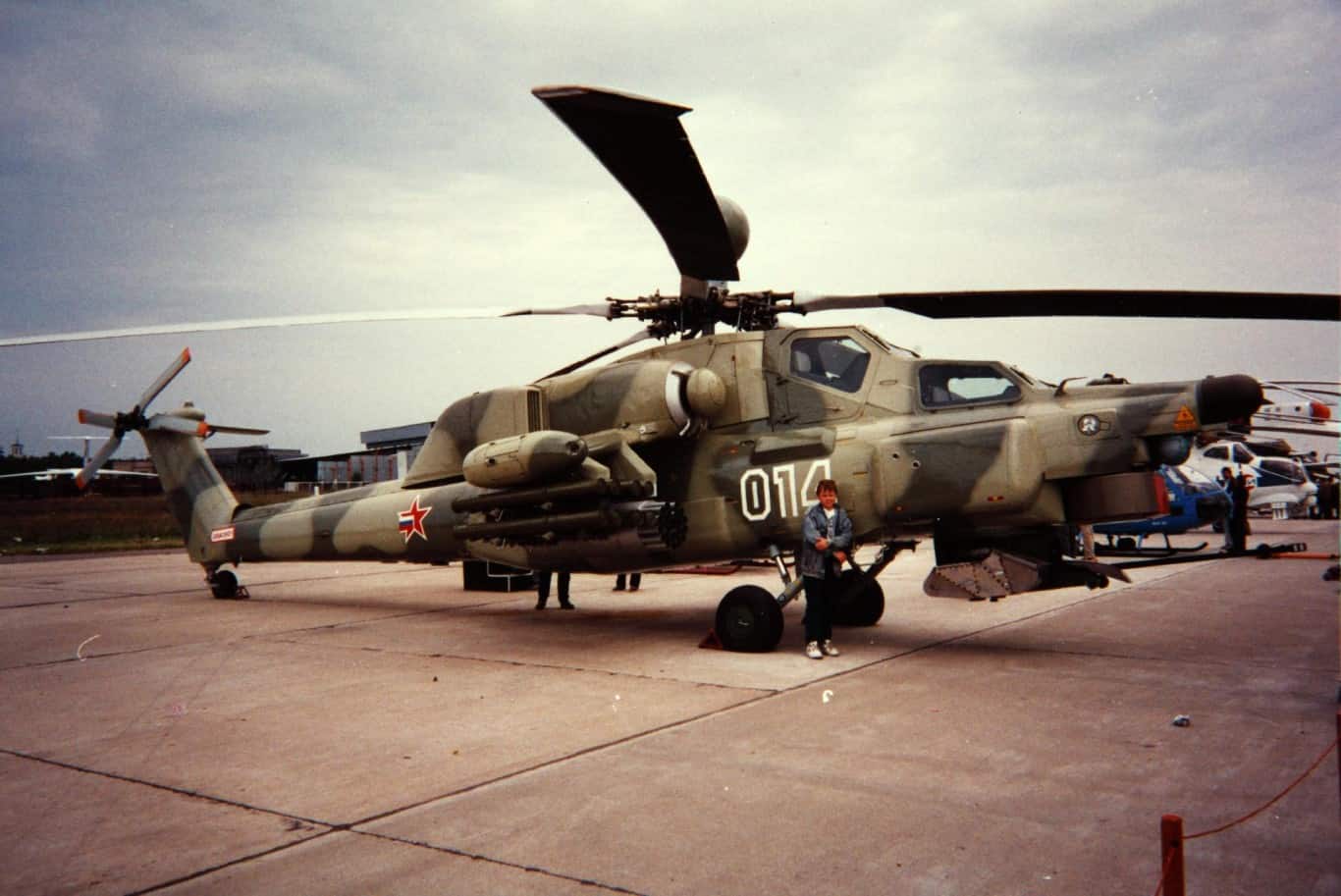

- Type: Twin-engine attack helicopter
- Year introduced: 2009
- Active aircraft: 94
- Top speed: 199 mph
- Armament: 30mm Shipunov 2A42 cannon, rocket pods, Spiral missiles, gun pods, cannon pods
The Mil Mi-28 Havoc is a twin-engine attack helicopter designed for precision strikes on armored targets and close air support for ground troops. One interesting fact about this helicopter that sets it apart from most others is that it can perform advanced maneuvers, like loops and rolls, which are rare for attack helicopters. This coupled with its firepower gives the Havoc a serious edge in almost any engagement.
Mil Mi-38
- Type: Medium-lift twin-engine transport helicopter
- Year introduced: 2019
- Active aircraft: 2
- Top speed: 186 mph
- Armament: Light machine guns, rocket pods
The Mil Mi-38, introduced in 2019, is a medium-lift twin-engine transport helicopter designed for a variety of missions, including cargo transport, troop movement, and medical evacuation. It can equip some small armament, but it is typically used for non-combat roles.
Mi-8/17/171 Hip-H
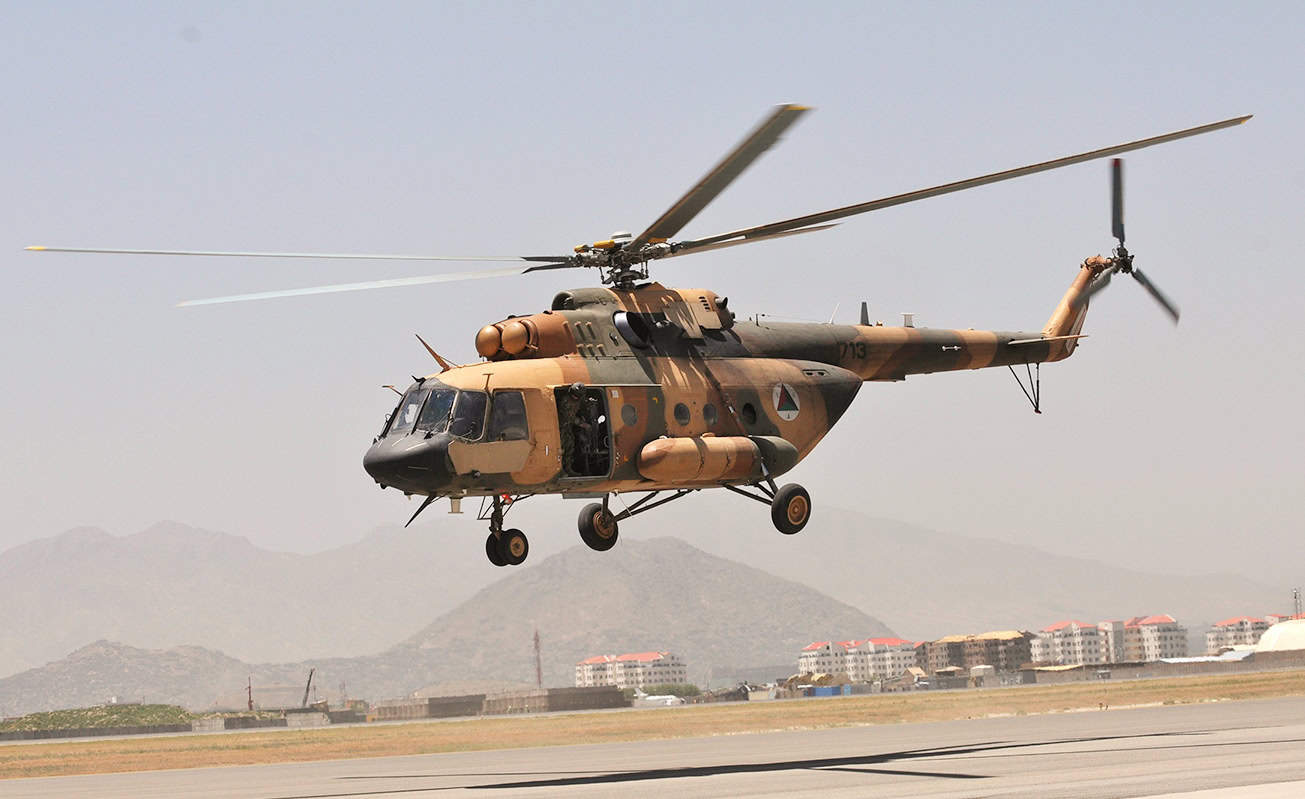

- Type: Medium-lift transport helicopter
- Year introduced: 1981
- Active aircraft: 792
- Top speed: 158 mph
- Armament: Shturm missiles, rocket pods, 23mm cannon pods, 7.62mm machine guns
The Mi-8 series is the most-produced helicopter in the world since its introduction in the 1960s. Its later iterations in the Mi-17 and Mi-171 build on the base design but obviously with upgraded avionics, coming about in the 1980s. These helicopters can equip Shturm missiles, rocket pods, 23mm cannon pods, and 7.62mm machine guns.
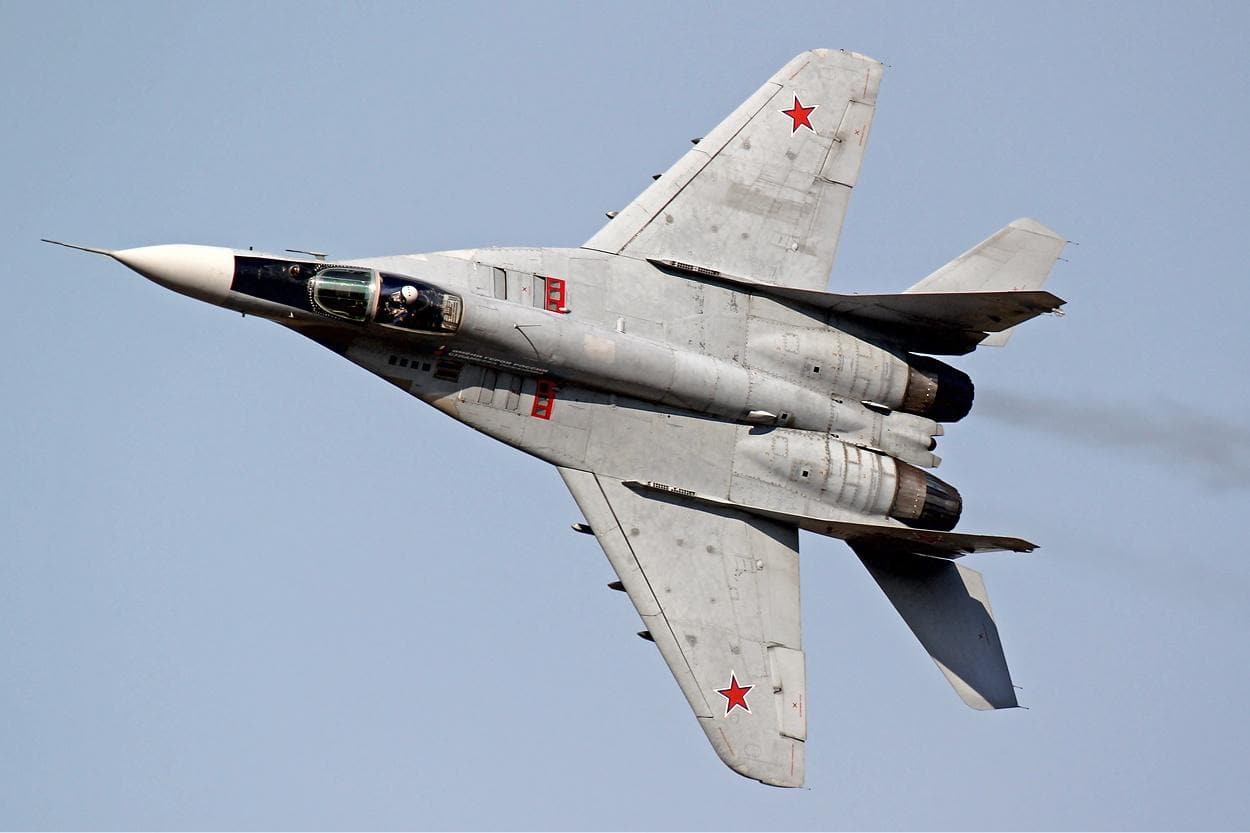
MiG-29/35 Fulcrum
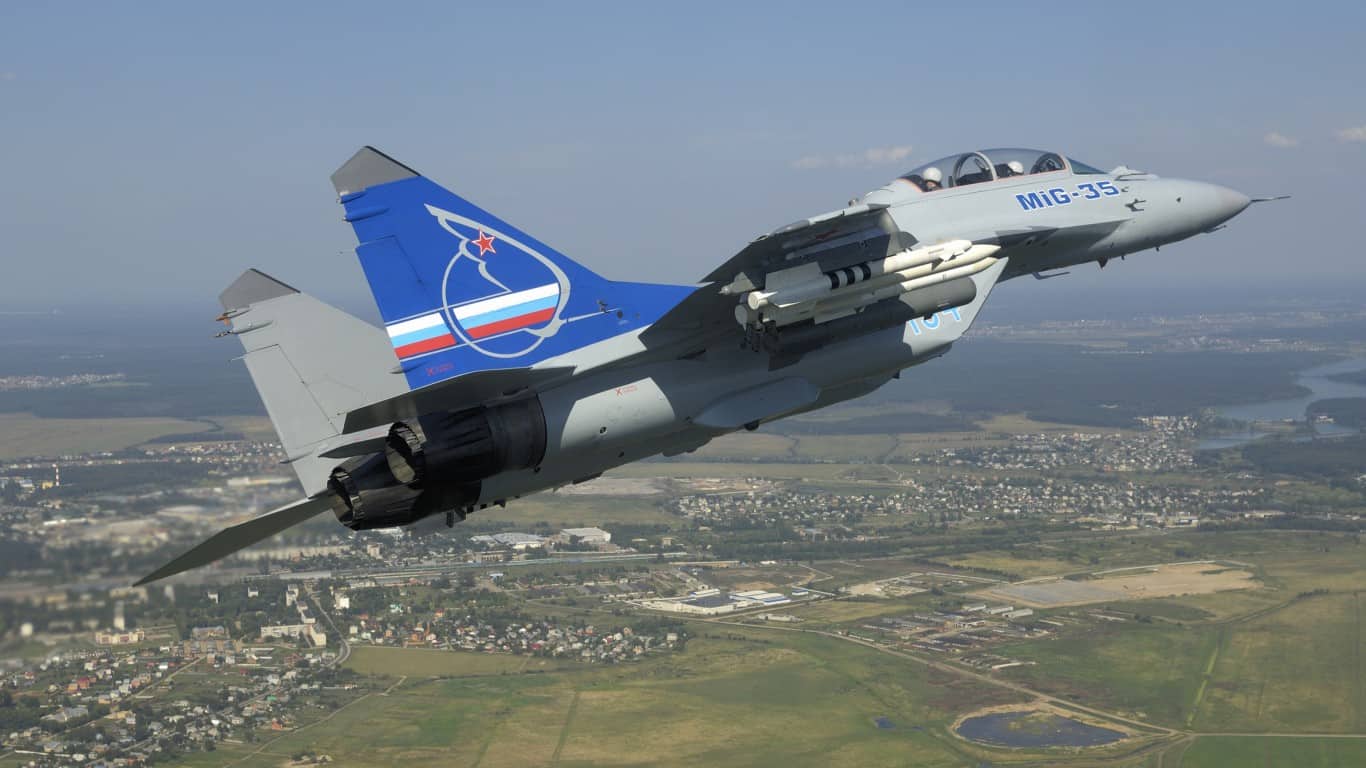

- Type: Lightweight multirole fighter aircraft
- Year introduced: 1984
- Active aircraft: 258
- Top speed: 1,519 mph
- Armament: 30mm GSh-1 internal automatic cannon, Alamo missiles, Adder missiles, rocket pods, conventional drop bombs, guided bombs
The MiG-29/35 Fulcrum makes up the backbone of Russia’s fleet of fighter jets. Introduced in 1984, these jets can hit speeds up to 1,519 mph. They come equipped with a 30mm GSh-1 internal automatic cannon standard, as well as Alamo and Adder missiles, rocket pods, and both conventional and guided bombs. The MiG-35 variant includes advanced avionics, improved radar systems, and can perform multi-role missions like ground strikes and interception.
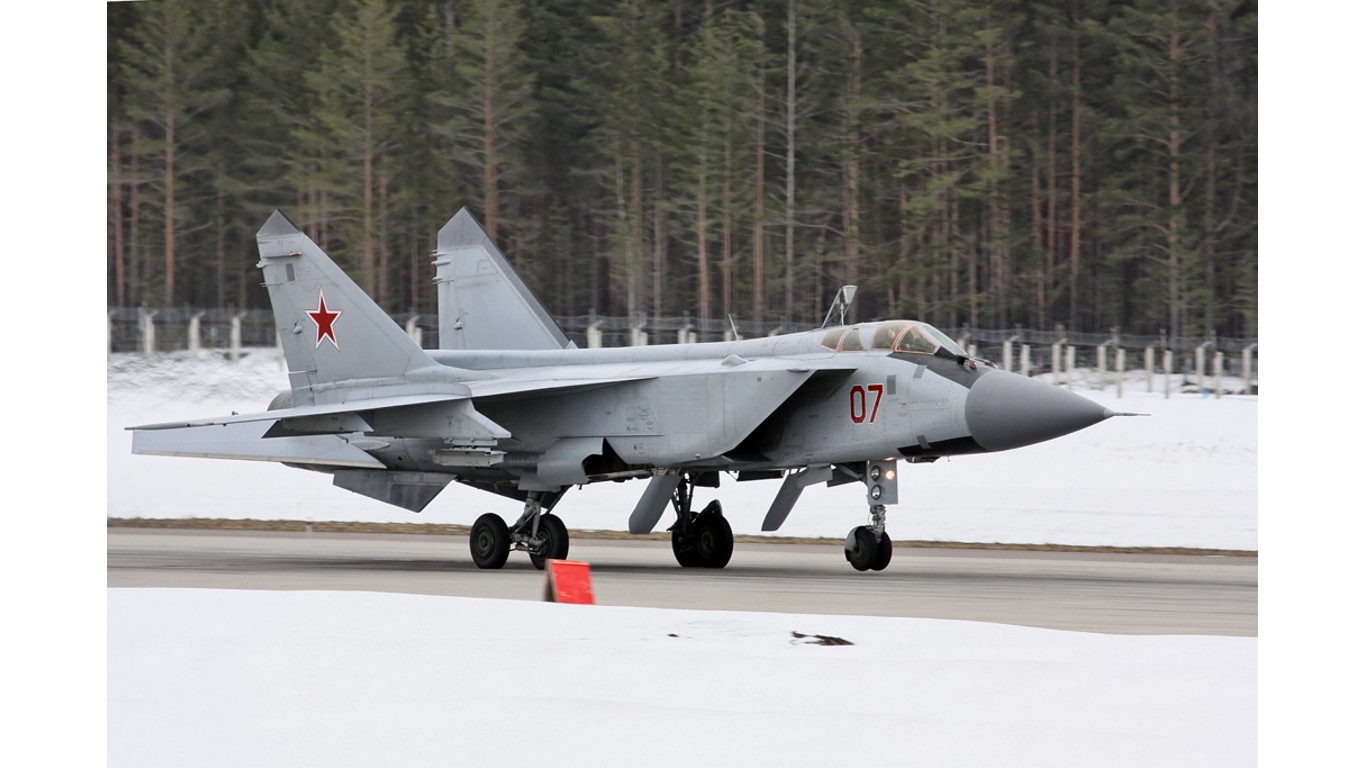
MiG-31 Foxhound
- Type: Interceptor aircraft
- Year introduced: 1979
- Active aircraft: 128
- Top speed: 1,864 mph
- Armament: 23mm GSh-6 internal cannon, Amos missiles, Aphid missiles, Acrid missiles
The MiG-31 Foxhound is one of the fastest fighter jets in the world. Its incredible speed puts it primarily as an interceptor. These jets are designed to defend against enemy bombers or even cruise missiles at long range. The Foxhound can also reach altitudes that most other aircraft can’t, further extending its defensive capabilities.
Su-24 Fencer
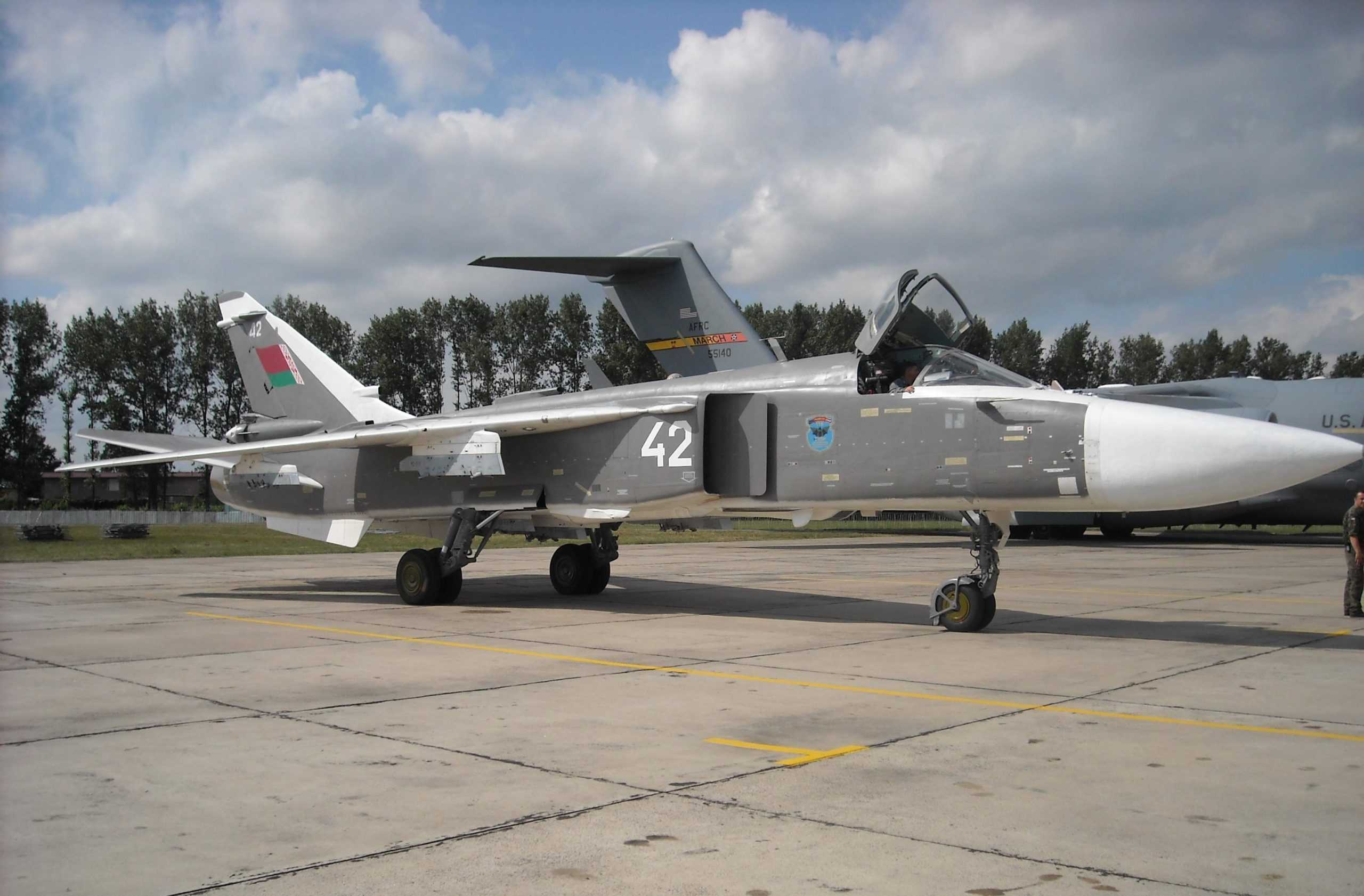

- Type: Long-range strike / attack aircraft
- Year introduced: 1974
- Active aircraft: 300
- Top speed: 1,439 mph
- Armament: 23mm GSh internal six-barrel cannon, Aphid missiles, Archer missiles, Kingbolt missiles, Krypton missiles, rocket pods, conventional drop bombs, guided bombs
The Su-24 Fencer was one of the first Soviet aircraft that came with an all-weather radar and terrain-following capabilities, allowing it to fly at low altitudes to evade enemy defenses. It was introduced in 1974 as a long-range strike aircraft, but it can perform a variety of other roles.
Su-25 Grach Frogfoot
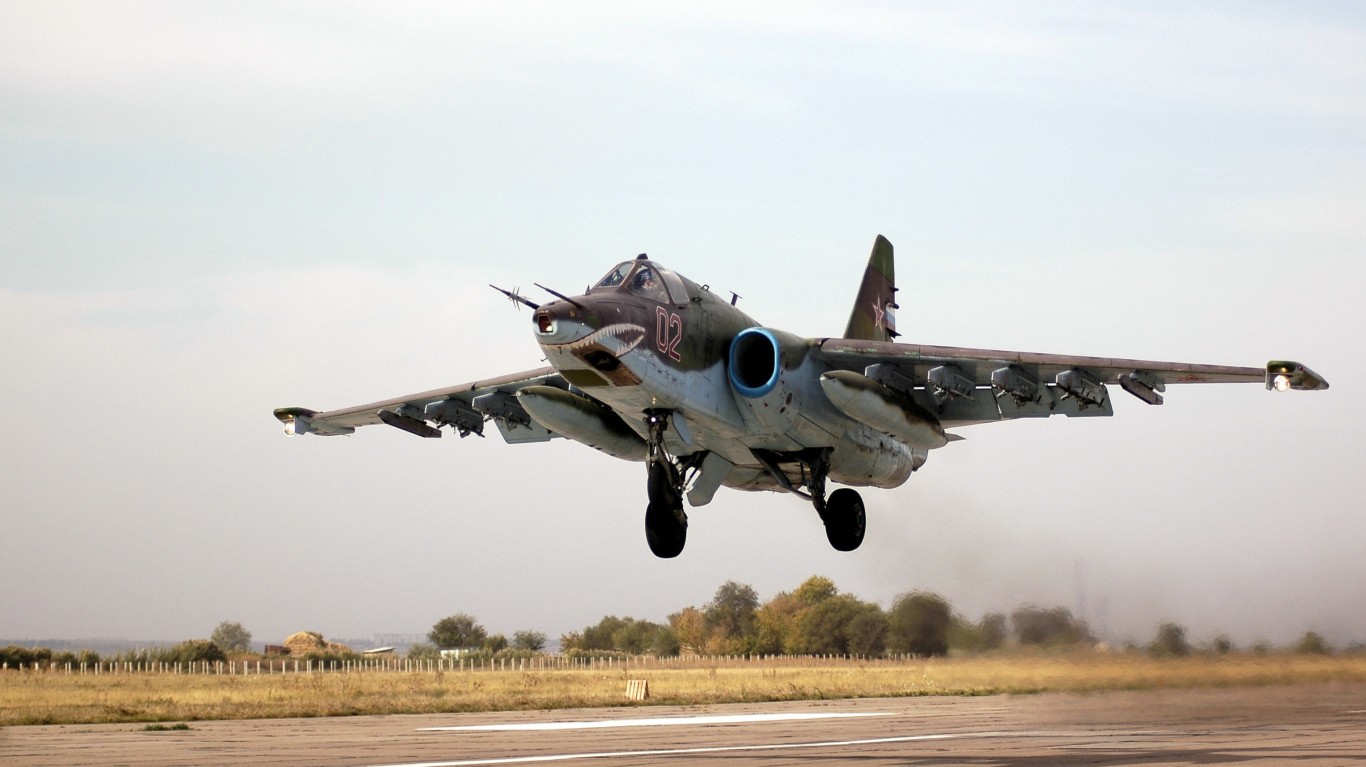

- Type: Close-air support / ground attack aircraft
- Year introduced: 1981
- Active aircraft: 176
- Top speed: 590 mph
- Armament: 30mm GSh- internal cannon, rocket pods, guided munitions, conventional drop bombs, air-to-surface missiles, air-to-air missiles
Recognized by the NATO reporting name “Frogfoot,” the Su-25 is a dedicated close-air support and ground attack aircraft. Although these jets have a relatively slow top speed of 590 mph, they can equip a wide array of armament including a 30mm GSh internal cannon, rocket pods, guided munitions, conventional bombs, air-to-surface missiles, and air-to-air missiles. There are currently 176 of these aircraft in active service.
Su-27 Flanker
- Type: Multi-role air superiority fighter
- Year introduced: 1985
- Active aircraft: 409
- Top speed: 1,553 mph
- Armament: 30mm GSh internal cannon, air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface missiles, conventional drop bombs, cluster bombs, anti-ship missiles, anti-radar missiles
Introduced in 1985, the Su-27 Flanker is an air-superiority fighter with a top speed over 1,550 mph. These come outfitted with a 30mm GSh internal cannon and a wide variety of munitions, including air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface missiles, conventional bombs, cluster bombs, anti-ship missiles, and anti-radar missiles. These jets were originally designed to counter the American F-15 Eagle, which has led to a long-standing rivalry between these two aircraft.
Su-34 Fullback
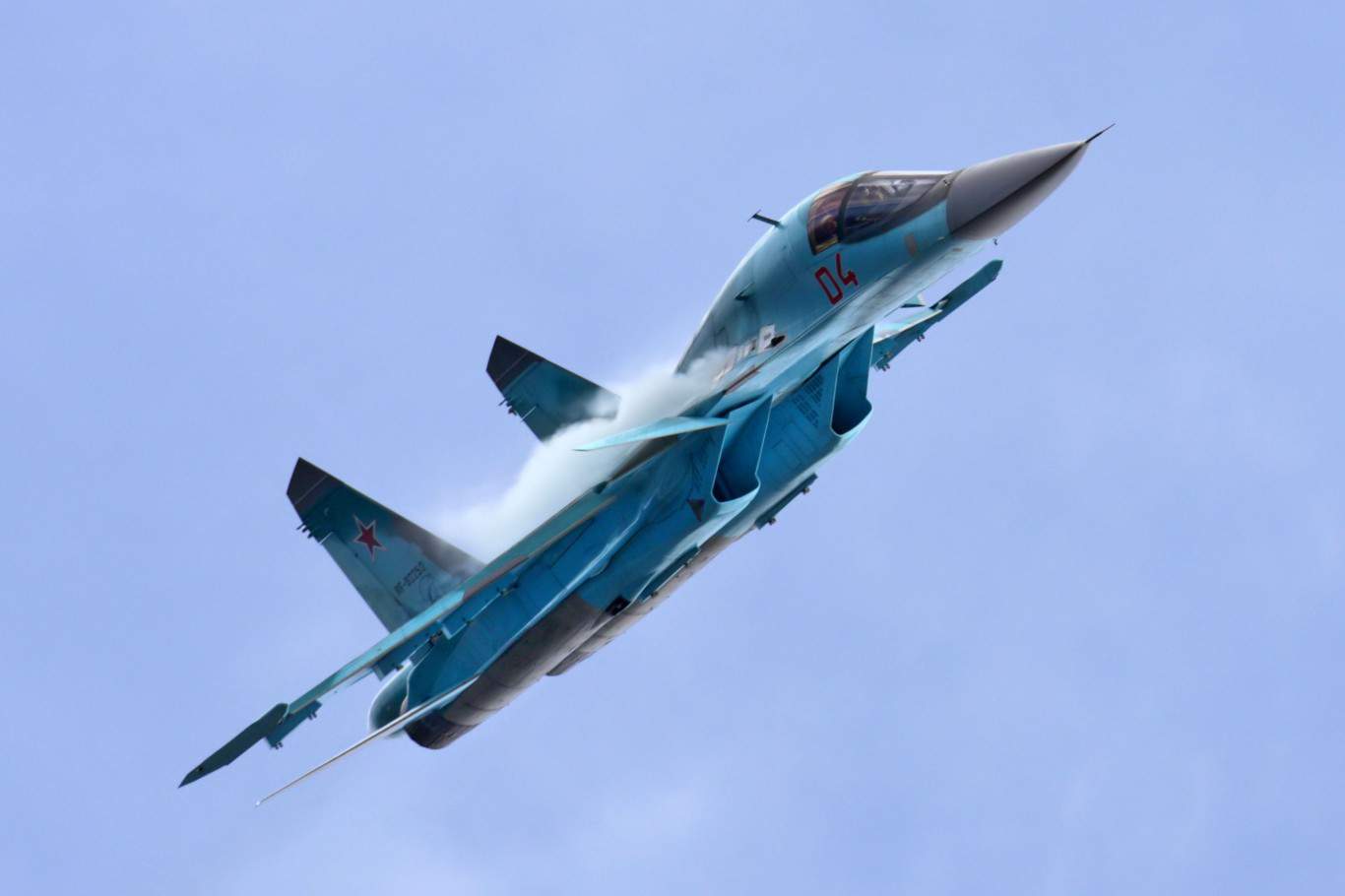

- Type: Strike fighter aircraft
- Year introduced: 2014
- Active aircraft: 134
- Top speed: 1,367 mph
- Armament: 30mm GSh internal cannon, Archer missiles, Moskit missiles, air-to-ground missiles, air-to-air missiles, guided munitions, rocket pods
Introduced in 2014, the Su-34 Fullback is one of the newest strike fighter aircraft to enter the Russian Air Force. There are 134 of these aircraft in service, and they can hit top speeds of nearly 1,400 mph.
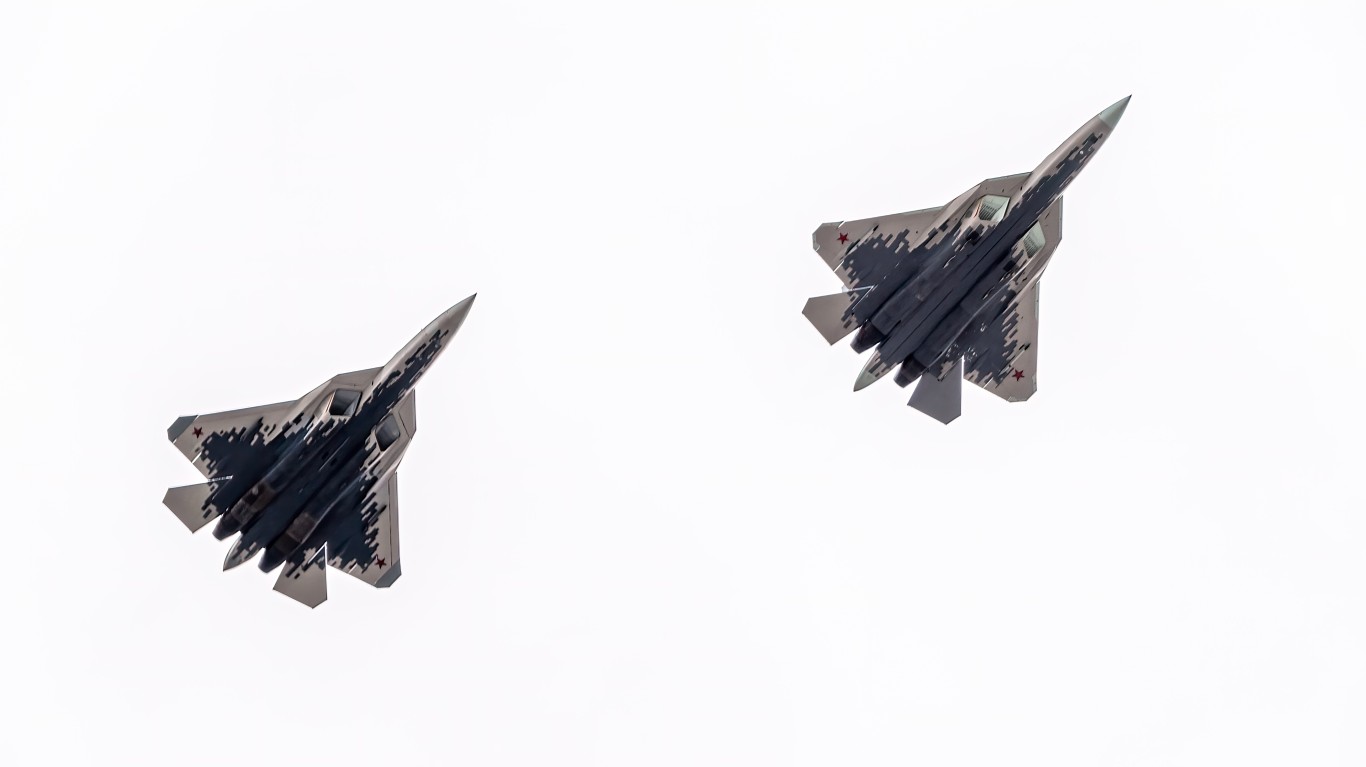
Su-57 Felon

- Type: Multi-role stealth aircraft
- Year introduced: 2019
- Active aircraft: 14
- Top speed: 1,616 mph
- Armament: 30mm GSh internal cannon, air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface missiles, guided bombs
The Su-57 Felon is the newest iteration of Sukhoi fighter jets. These fifth-generation fighters feature advanced stealth technology and avionics. With a top speed of 1,616 mph, these jets are capable of supercruise, which allow them to fly at supersonic speeds without afterburners. There are only 14 of these aircraft in service now, but more are on the way.
Tu-134 Crusty
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1967
- Active aircraft: 6
- Top speed: 590 mph
- Armament: N/A
The Tu-134 Crusty, introduced in 1967, is a transport aircraft originally developed as a short-range passenger jet but it was later adapted for military transport and VIP missions.
Tu-142 Bear
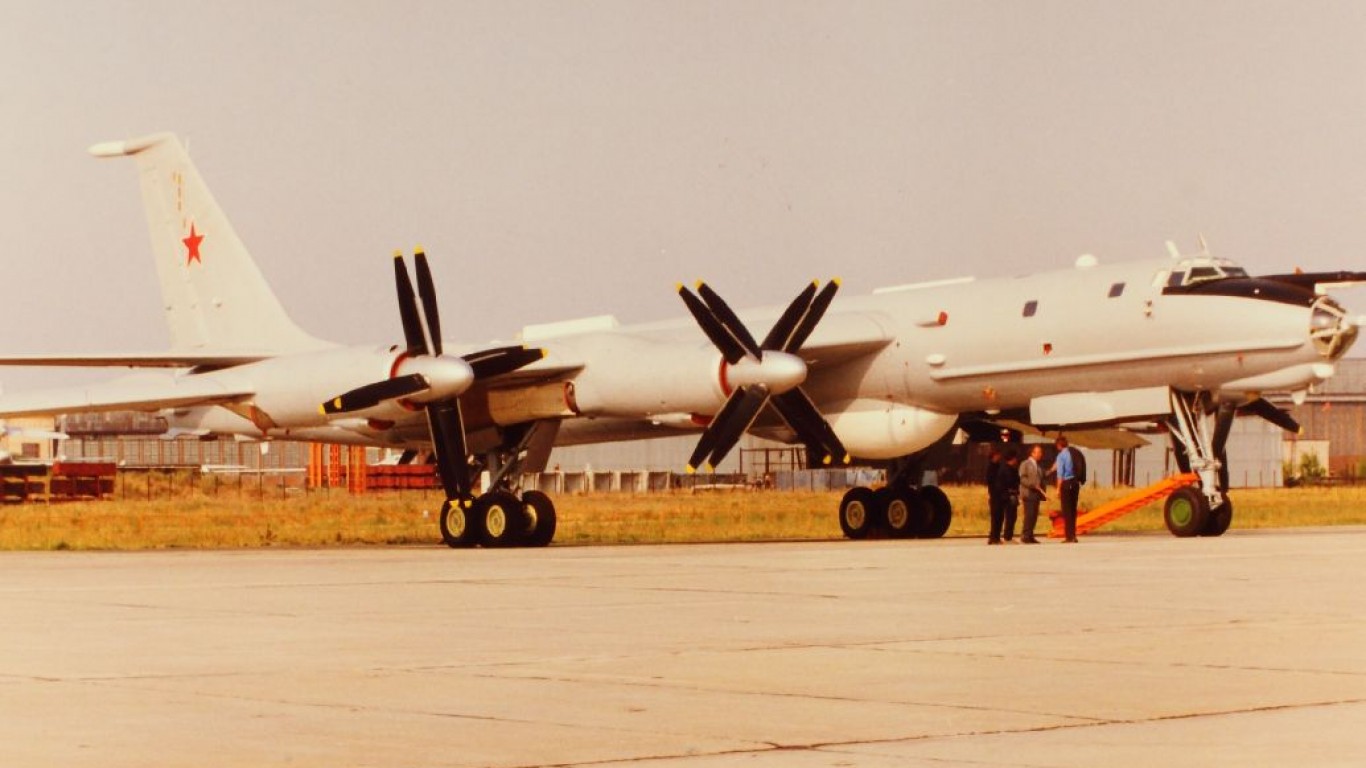

- Type: Anti-submarine bomber aircraft
- Year introduced: 1972
- Active aircraft: 32
- Top speed: 575 mph
- Armament: 23mm automatic cannon, torpedoes, naval mines, cruise missiles, anti-ship missiles
Introduced in 1972, the Tu-142 Bear is a long-range anti-submarine warfare and maritime patrol aircraft developed from the original Tu-95. These aircraft have a top speed of 575 mph and previously held the world record for the fastest turboprop aircraft.
Tu-154 Careless
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Year introduced: 1972
- Active aircraft: 4
- Top speed: 590 mph
- Armament: N/A
The Tu-154 Careless was introduced in 1972 as a three-engine transport aircraft primarily used for civilian passenger flights but it was later adapted for military transport roles. Currently on 4 are in service of the Russian military.
Tu-160 Blackjack
- Type: Strategic heavy bomber aircraft
- Year introduced: 1989
- Active aircraft: 15
- Top speed: 1,243 mph
- Armament: Kent cruise missiles, Kickback nuclear missiles, conventional drop bombs, air-to-surface missiles
With a top speed of 1,243 mph, the Tu-160 Blackjack is one of the fastest strategic heavy bombers on the planet. It is also recognized as the largest and heaviest combat aircraft ever built. It’s heavy duty payload reflects this. It was nicknamed the “White Swan” for its sleek, all-white appearance.
Tupolev Tu-214
- Type: Airborne command post
- Year introduced: 1996
- Active aircraft: 4
- Top speed: 559 mph
- Armament: N/A
The Tupolev Tu-214 is an airborne command post designed to provide mobile command and control capabilities for military operations. It has a top speed of 559 mph and is equipped with advanced communications and radar systems. Introduced in 1996, there are only 4 of these aircraft currently in service.
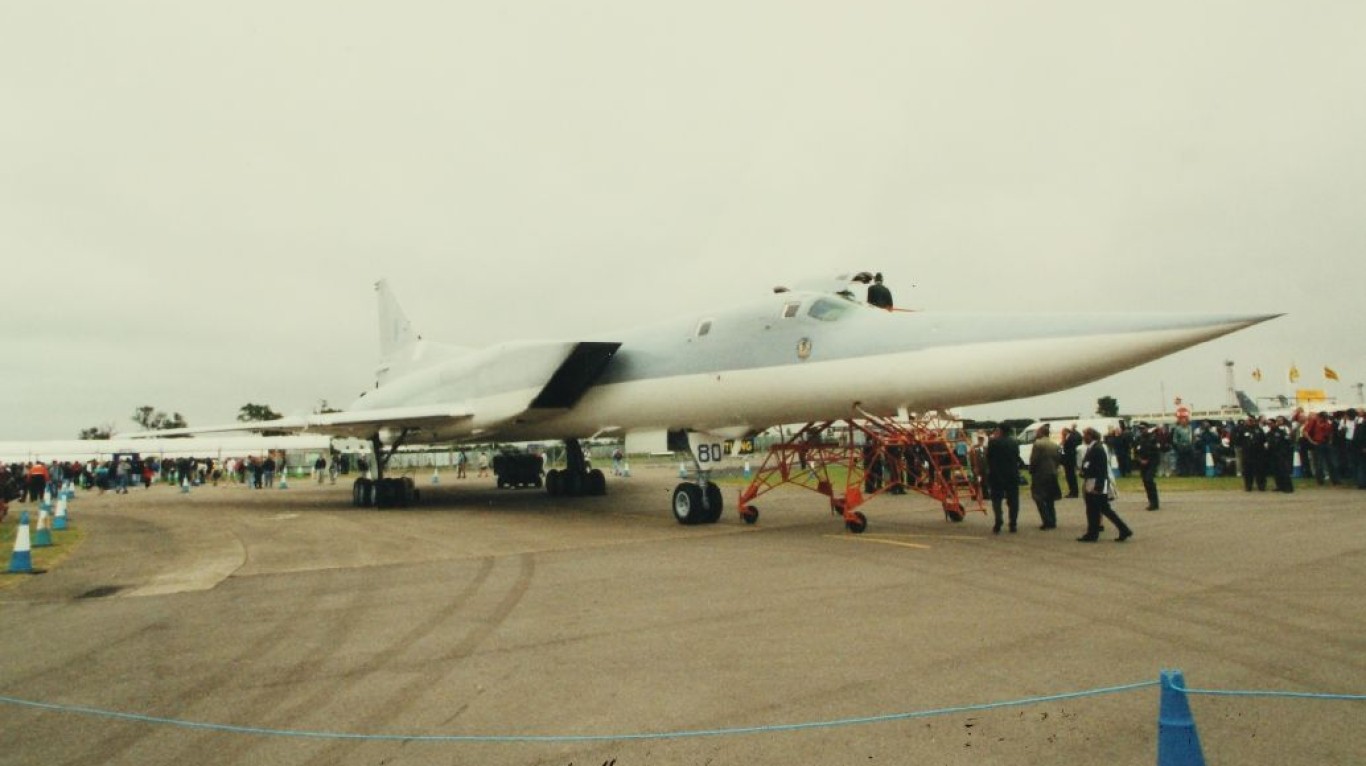
Tu-22M Backfire
- Type: Strategic maritime bomber
- Year introduced: 1972
- Active aircraft: 58
- Top speed: 1,243 mph
- Armament: 23mm GSh tail-mounted cannon, air-to-surface missiles, anti-ship missiles, conventional drop bombs, laser-guided bombs, cruise missiles
Introduced in 1972, the Tu-22M Backfire is a strategic maritime bomber designed for long-range strike missions against naval and land-based targets. There are currently 58 of these aircraft in active service.
Tu-95 Bear
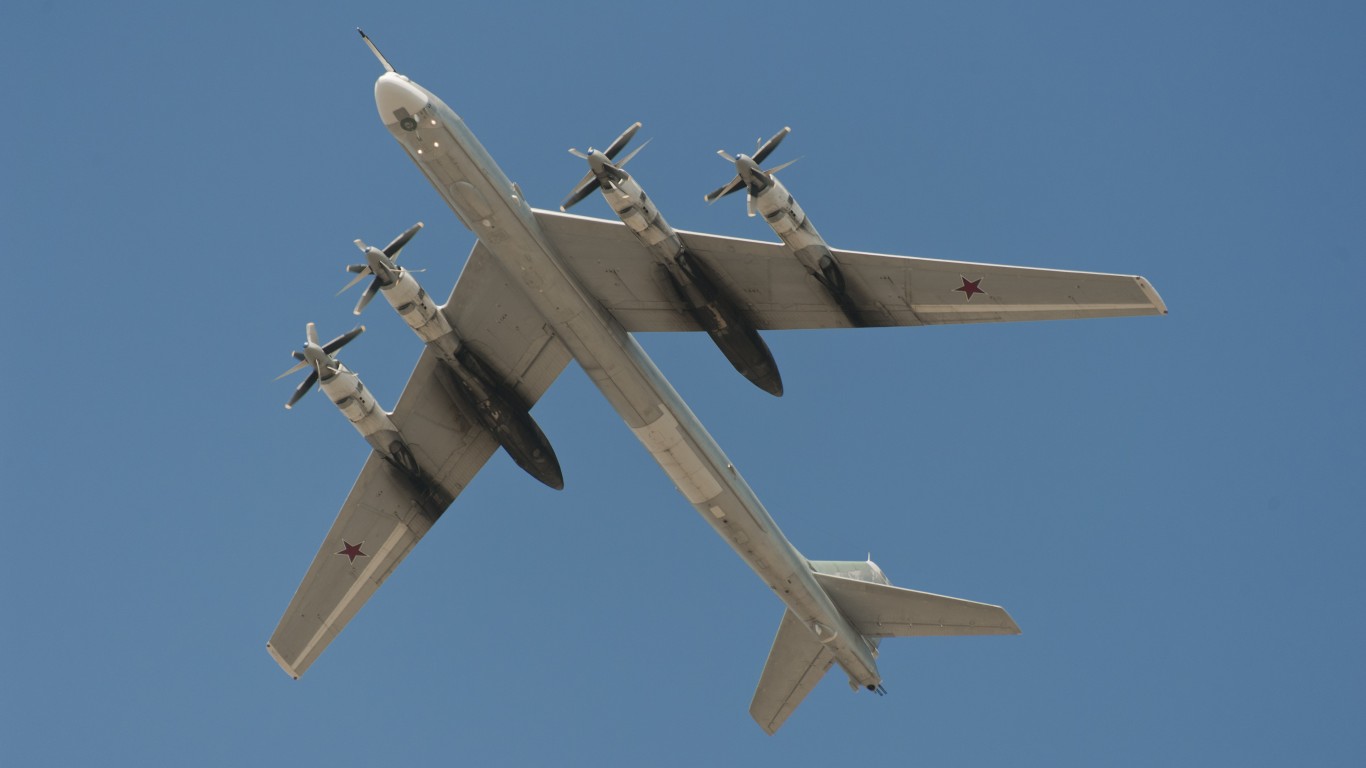

- Type: Strategic reconnaissance / heavy bomber aircraft
- Year introduced: 1956
- Active aircraft: 47
- Top speed: 531 mph
- Armament: 23mm cannons, air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface missiles, anti-ship missiles, precision guided munitions, conventional drop bombs
The Tu-95 Bear was introduced in 1956, and it would go on to influence the Tu-142 Bear. It was introduced in 1956 and is one of the longest serving aircraft in the Russian military with 47 currently in service.
Get Ready To Retire (Sponsored)
Start by taking a quick retirement quiz from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes, or less.
Each advisor has been vetted by SmartAsset and is held to a fiduciary standard to act in your best interests.
Here’s how it works:
1. Answer SmartAsset advisor match quiz
2. Review your pre-screened matches at your leisure. Check out the advisors’ profiles.
3. Speak with advisors at no cost to you. Have an introductory call on the phone or introduction in person and choose whom to work with in the future
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.