Military
This Powerful WWII Campaign Brought 250,000 Axis Soldiers to Their Knees

Published:

The North African Campaign of World War II, spanned from 1940 to 1943, was a pivotal theatre of war that tilted the balance of power in favor of the Allies. This theatre involved a series of battles across the desert expanses of Libya, Egypt, and Tunisia, as well as some in East Africa.
In terms of the belligerents, this campaign can be defined as a struggle between the Axis powers, led by German General Erwin Rommel’s Afrika Korps, and the Allied forces, initially under the command of British generals and later joined by American and Free French forces.
The campaign began in earnest during the summer of 1940, when Italian forces from Libya launched an invasion of Egypt, which was then a British protectorate. However, there would be a back and forth between the Allies and Axis over the next two years. The tide did not truly turn in favor of the Allies until mid-1942 in the First Battle of El Alamein when they halted the advance of Axis powers into Egypt. (These two countries had the most casualties in World War II, and it’s not even close.)
Also the North African Campaign saw the emergence of Erwin Rommel, a German tank commander considered one of the greatest military commanders of the 20th century. He earned the nickname the “Desert Fox” through is strategic brilliance and tactical application of tanks. Rommel’s knack for rapid, surprise attacks and his adept use of the desert terrain allowed him to outmaneuver enemy forces repeatedly.
The North African Campaign was important to the overall war for a few reasons. It ultimately secured the Mediterranean for the Allies and then protected Middle Eastern oil resources that were vital for the Allied war effort. At the same time, this campaign developed the experience, cooperation, and coordination among Allied forces, setting the stage for the later invasions of Italy and France.
24/7 Wall St. is diving into the North African Campaign and noting some of the most pivotal events and battles that occurred over the course of it. To map out the timeline of the North African theatre in World War II, 24/7 Wall St. reviewed World War II Database, an online archive of World War II data. We ordered these events chronologically and added some context as to why they played a pivotal role in shaping the outcome of the war.

Exploring the history of World War II is important not only to understand one of the most pivotal periods in modern history but also to grasp the profound impact that this global conflict had on the world at large. Ultimately, World War II reshaped boundaries, alliances, and ideologies in ways that still influence global relations and conflicts today. The outcome of World War II effectively made the world order that we know today.

The Malta Campaign during World War II was a prolonged military operation surrounding the strategic island of Malta, as Allied forces defended it against Axis attempts to bombard from June 1940 to December 1942.

The British attacks on the French fleet in 1940, known as Operation Catapult, were attacks by the British to prevent French ships from falling into German hands after France’s surrender.
The Invasion of British Somaliland in August 1940 was a quick military operation where Italian forces from East Africa attacked and occupied the British protectorate of Somaliland.
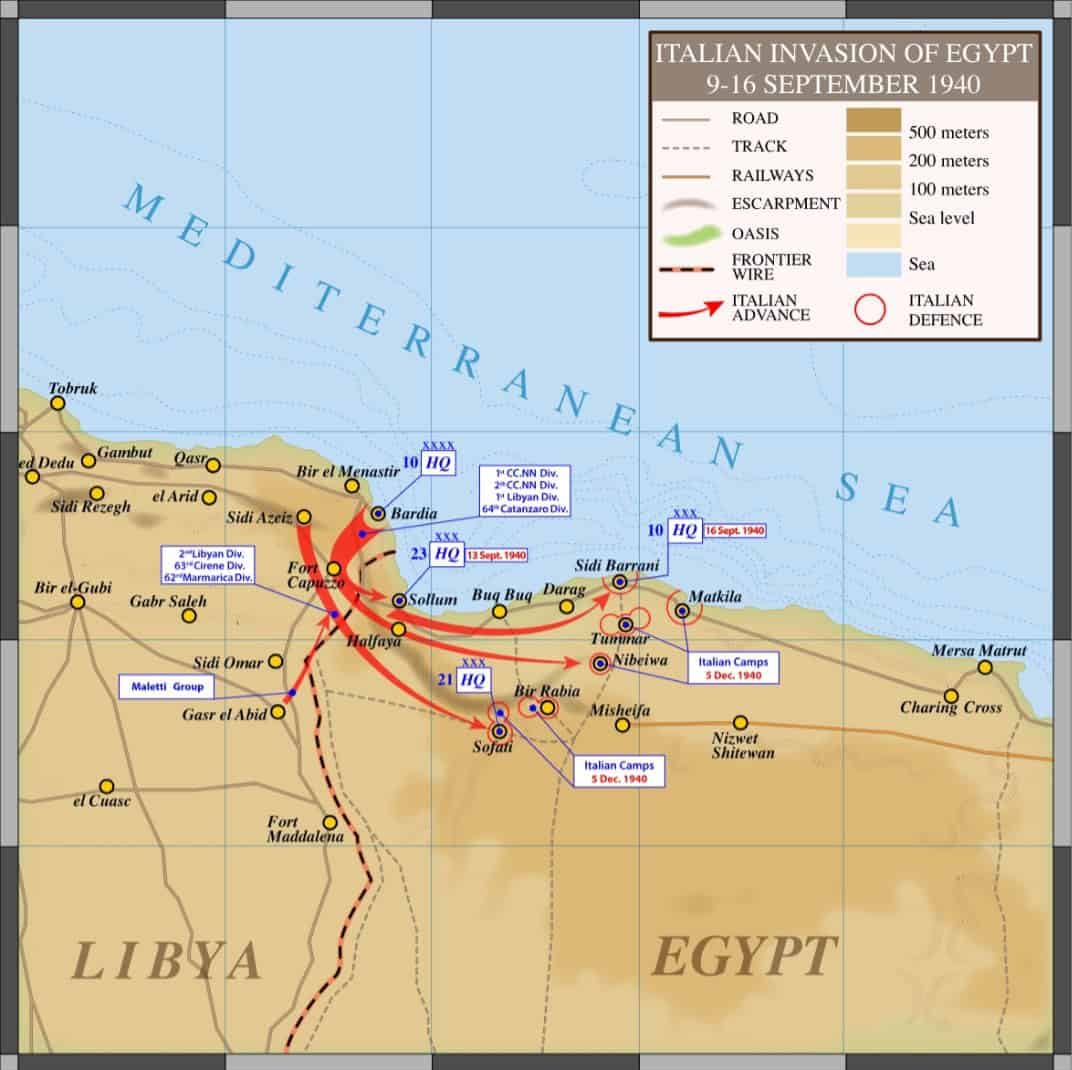
The Invasion of Egypt marked the beginning of the Italian offensive into British-held Egypt during World War II.

The Battle of Gabon was part of the broader Free French campaign to rally Vichy French territories to the Allies.
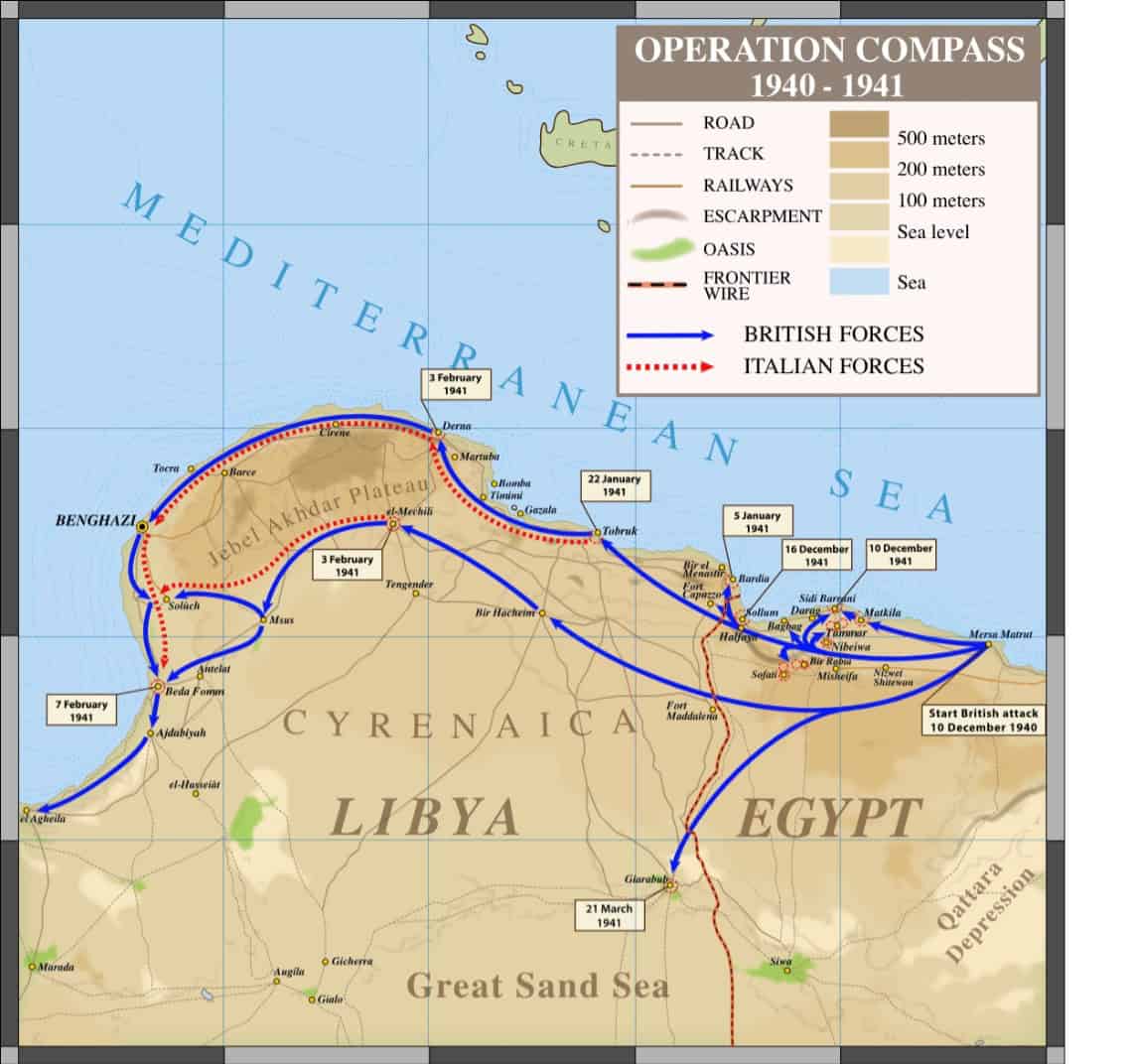
Operation Compass was a major Allied military operation in the Western Desert Campaign during World War II. It was the first large-scale successful offensive by the Allies against the Italian forces in North Africa.

The Battle of Kufra occurred when Free French and British forces launched an operation to seize the Italian-held oasis of Kufra in southeastern Libya in early 1941.
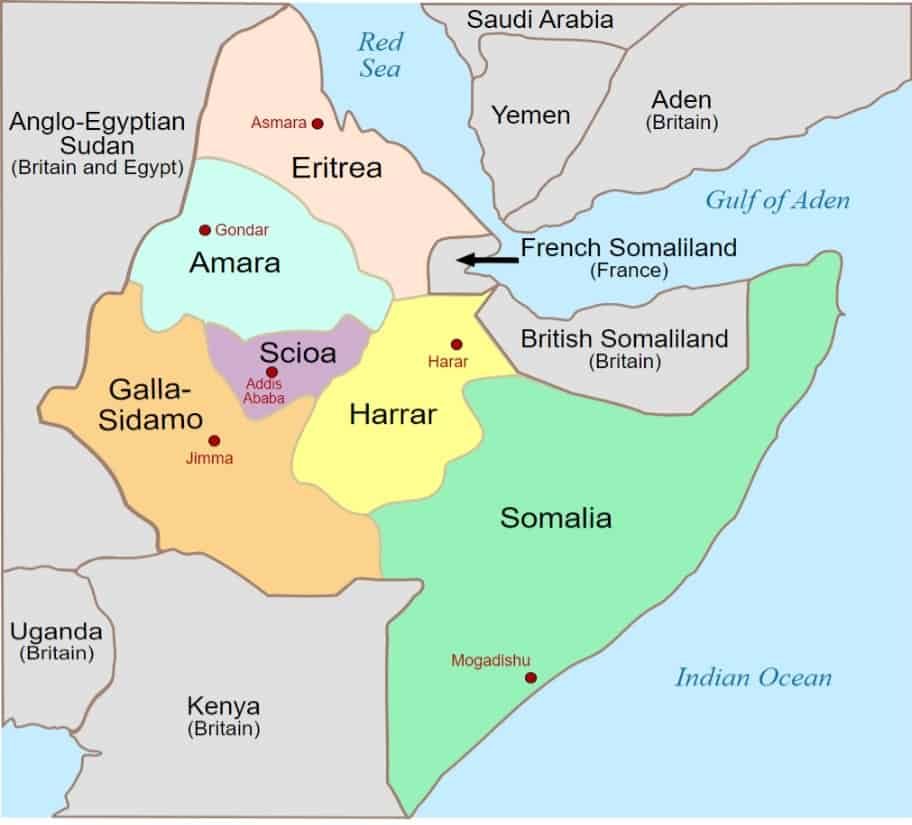
The Invasion of Italian East Africa was an Allied campaign aimed at removing Italy’s hold of East Africa.
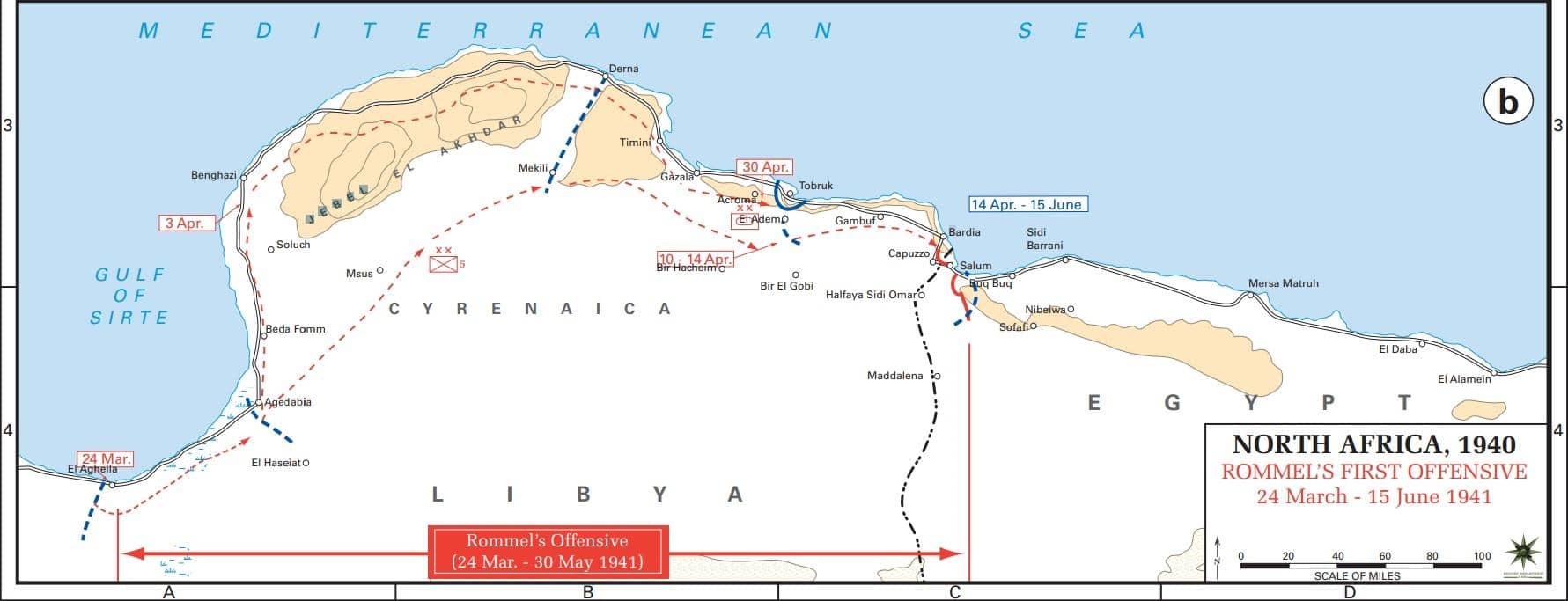
Operation Sonnenblume was a German initiative to reinforce Italian forces in North Africa. This operation saw the arrival of the Afrika Korps, led by General Erwin Rommel, which shifted the balance of power in favor of Axis nations.

The Battle of Giarabub saw Australian forces overrun the Italian garrison at the remote oasis of Giarabub in Libya.
The Siege of Tobruk was a standoff where Allied forces, primarily Australians, held the Libyan port of Tobruk against a prolonged Axis siege.
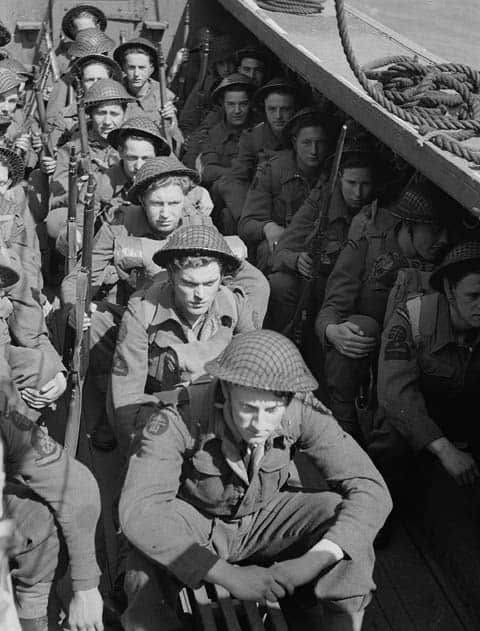

The Bardia Raid was a quick and aggressive British commando operation targeting the Italian-held town of Bardia in Libya. The raid was targeting Axis communications and supply lines, but it was not entirely successful.
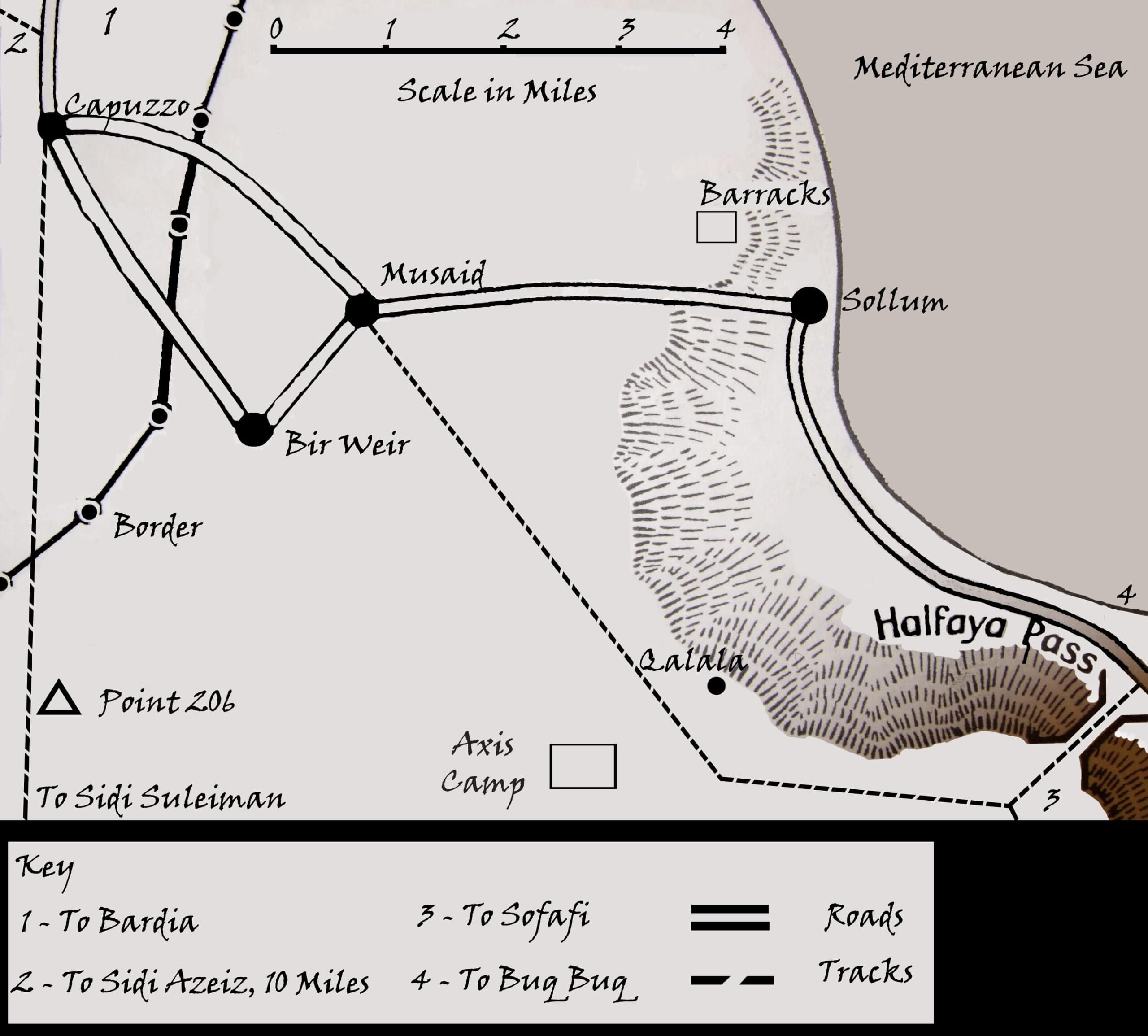
Operation Brevity was a short-lived British offensive. It was designed as a limited attack to secure specific strongpoints and disrupt Axis positions near the Egypt-Libya border.
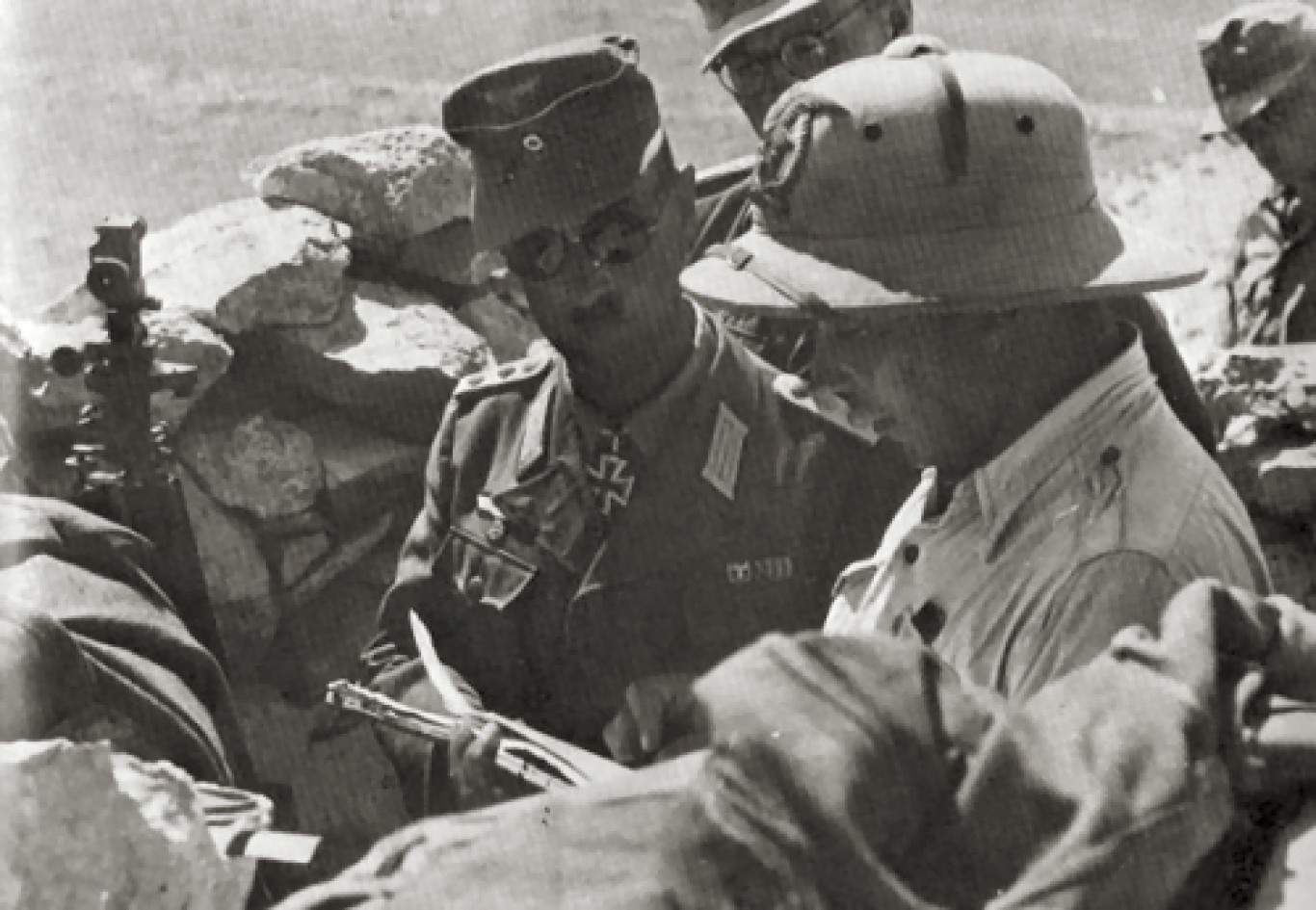

Operation Battleaxe was a British offensive intended to lift the Siege of Tobruk and push back Axis forces in North Africa. British forces failed to achieve their objective and this led to an extensive reevaluation of Allied strategies throughout the region.
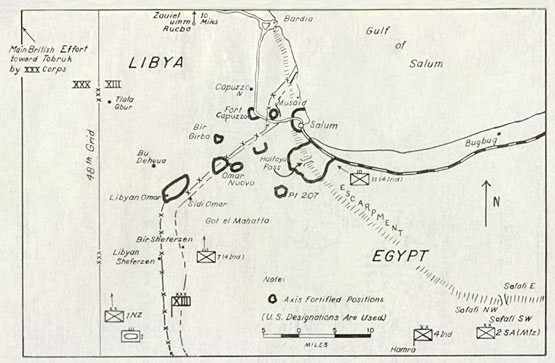
Operation Crusader was a sizable Allied military campaign aimed again at relieving the besieged forces at Tobruk. This operation was ultimately successful in relieving Tobruk and yielded a temporary strategic advantage for the Allies.
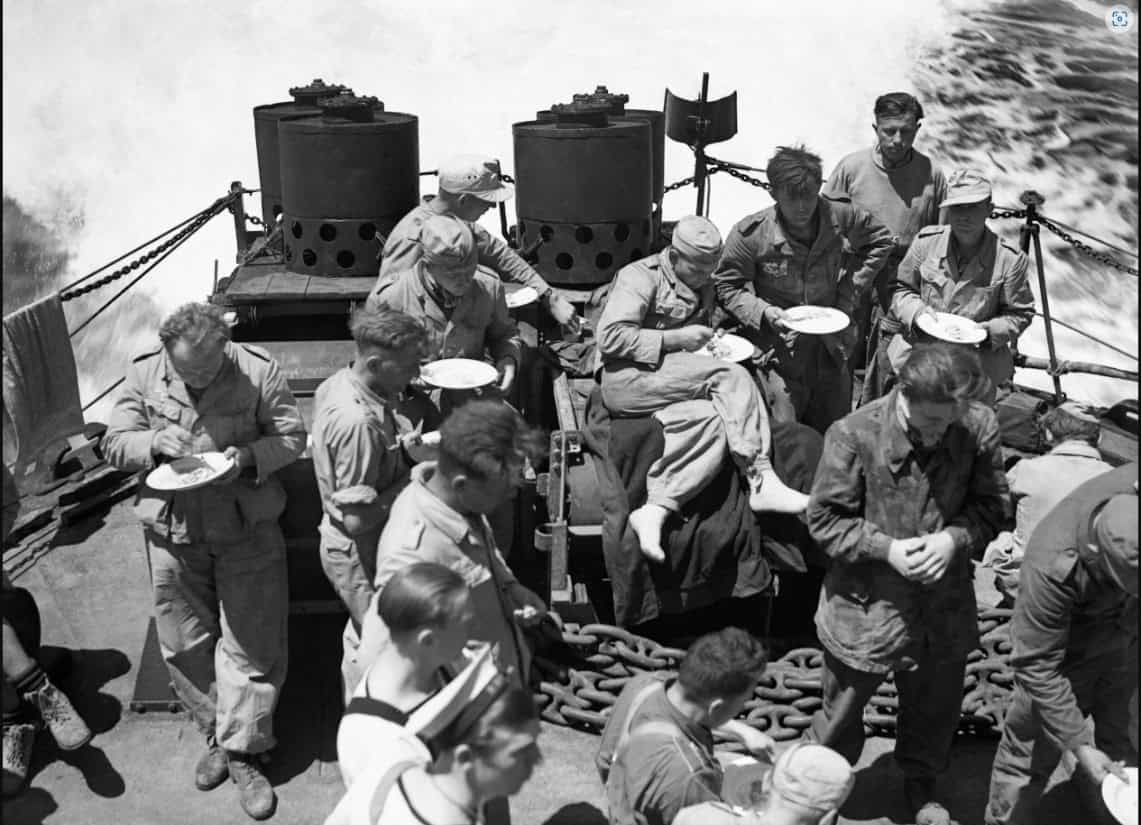

The Battle of Cape Bon took place off the coast of Tunisia in the Mediterranean Sea. British forces intercepted and decisively defeated a small Italian squadron.

The Underwater Raid of Alexandria was an operation executed by Italian naval commandos using manned torpedoes. This attack targeted the British Mediterranean fleet in Alexandria. The commandos managed to successfully place explosives on two battleships, HMS Queen Elizabeth and HMS Valiant, dealing significant damage to each.
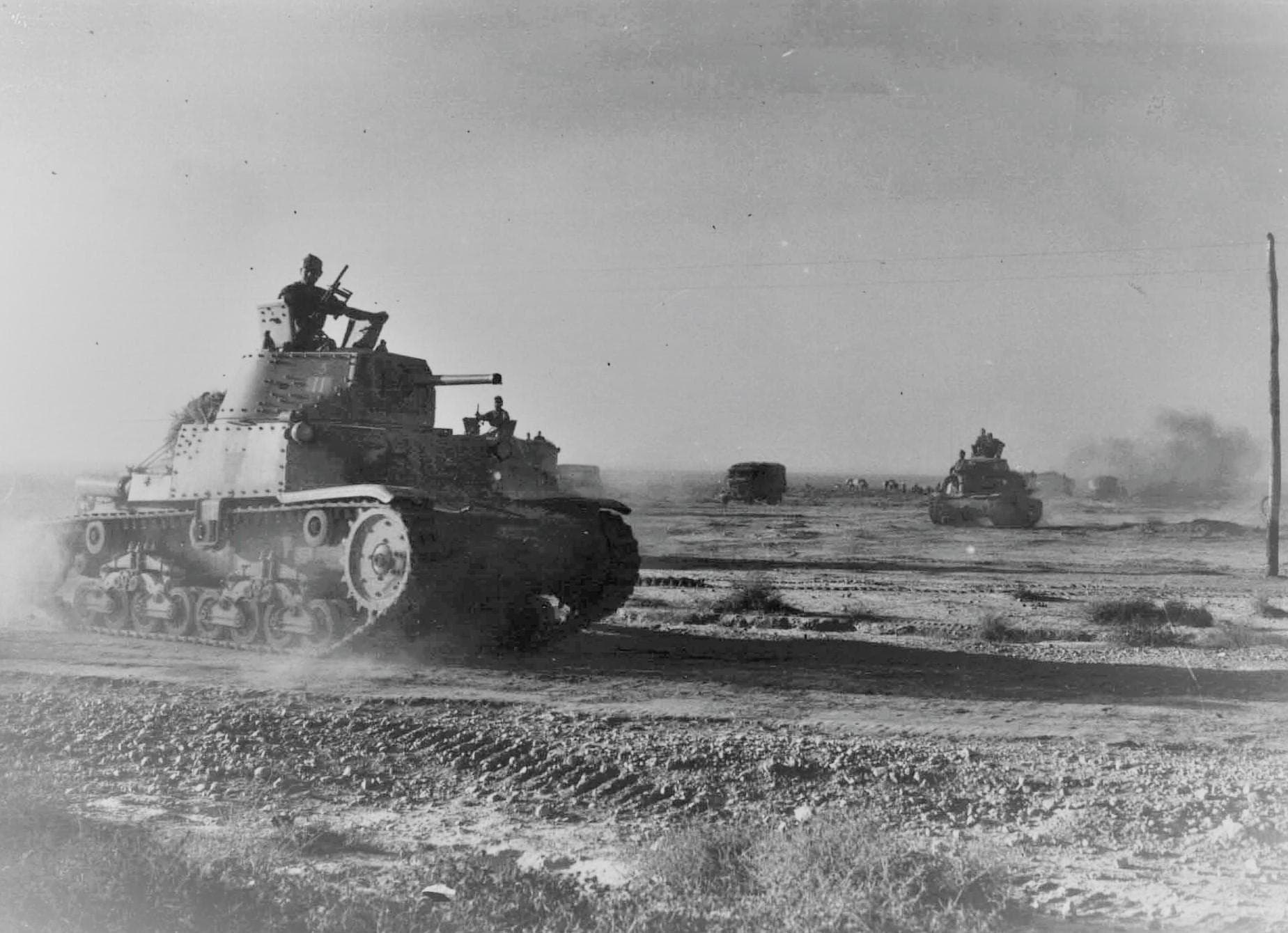

The Battle of Gazala was a major engagement between the Axis forces led by Field Marshal Erwin Rommel and Allied troops in the Gazala line near Tobruk.
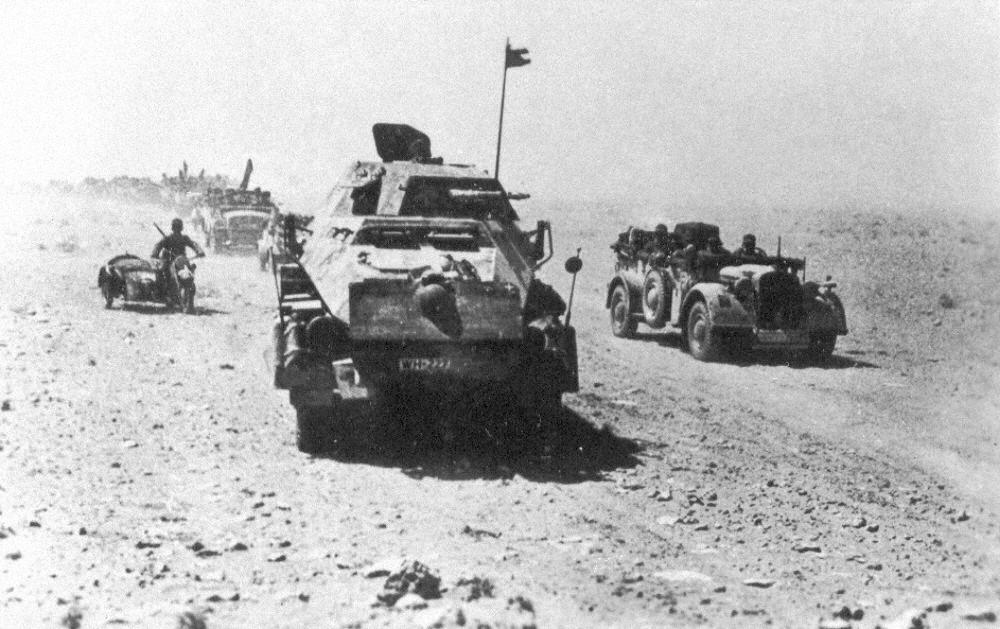

The Battle of Mersa Matruh was a continuation of the Axis push into Egypt following their success at the Battle of Gazala.
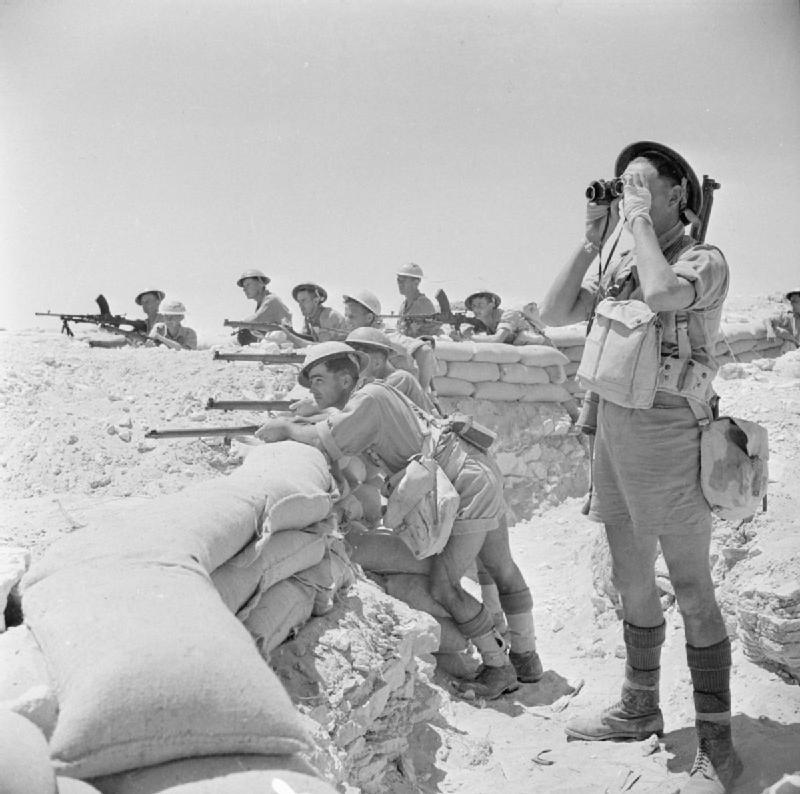

The First Battle of El Alamein was a turning point in the North African campaign. After the retreat from Mersa Matruh, the British Army made a stand at El Alamein and halted the advance of the Axis Powers towards the Suez Canal.

The Battle of Alam el Halfa occurred just south of El Alamein showcasing the newly appointed British commander, General Bernard Montgomery, facing off against Erwin Rommel’s Panzer Army Africa. This was a very strategic victory for the Allies, effectively ending Rommel’s ambitions at capturing the Suez Canal.
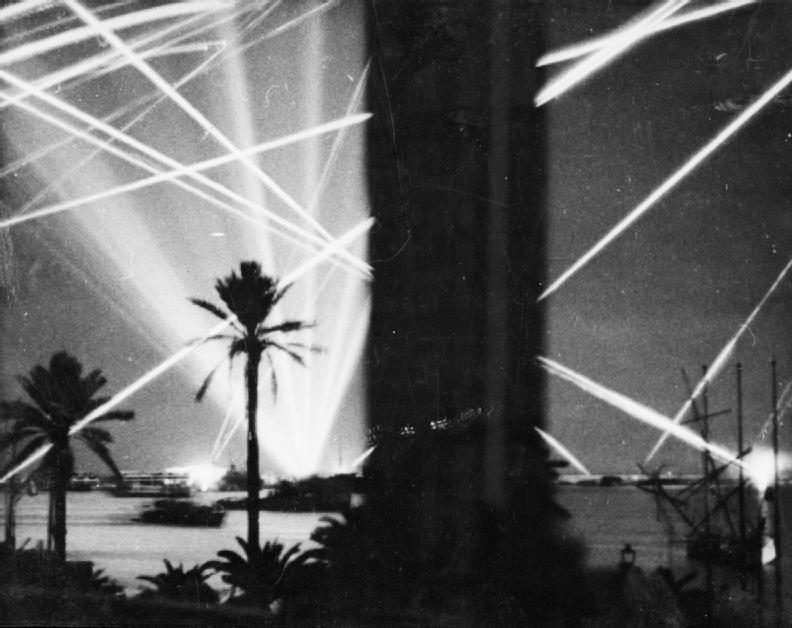

The Raids in Libya were a series of aggressive reconnaissance and raiding operations by the British against German and Italian forces. These raids targeted enemy airfields, supply depots, and communication lines.
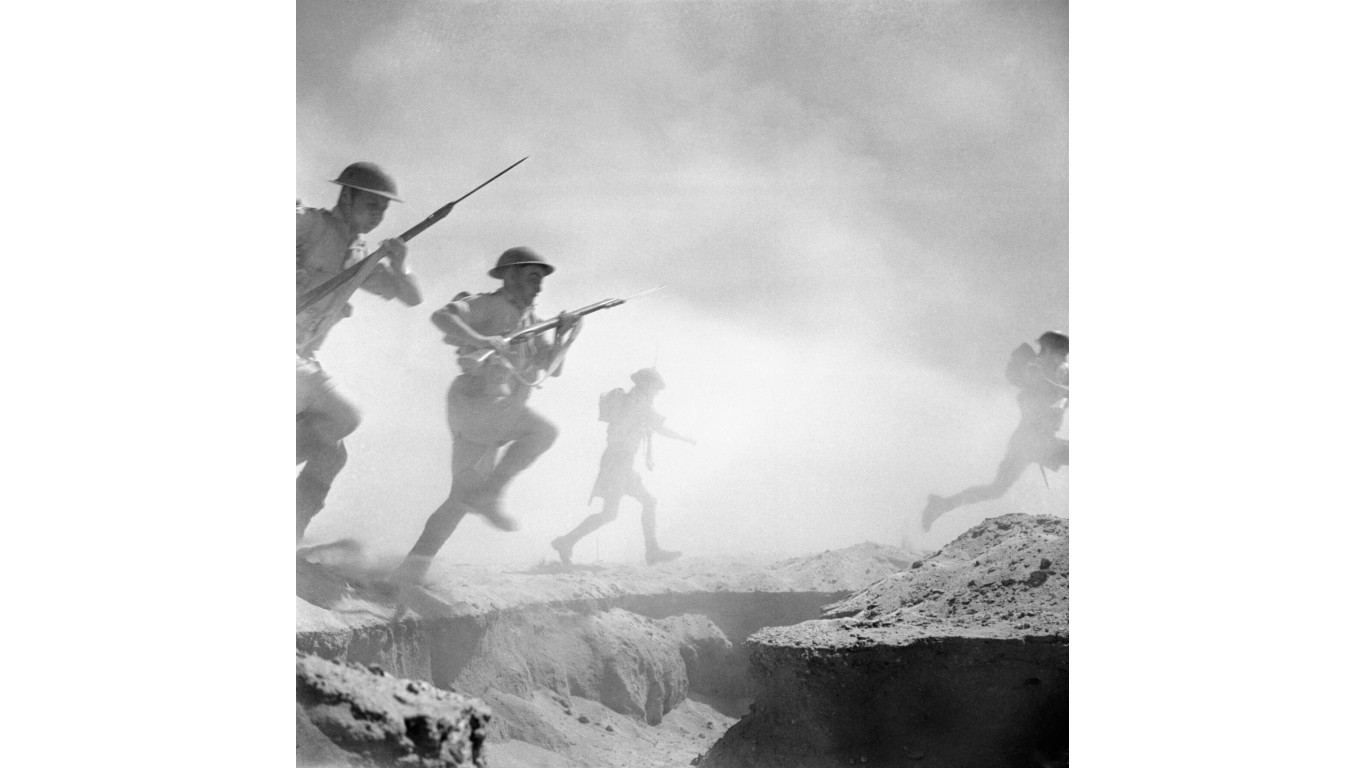

The Second Battle of El Alamein was one of the most decisive confrontations of World War II. Allied Forces led by Montgomery and Axis Forces led by Rommel clashed again at El Alamein decisively halting the Axis push into Egypt and leading to their retreat across Libya and Tunisia. This would ultimately set up for the Allied push in Operation Torch.
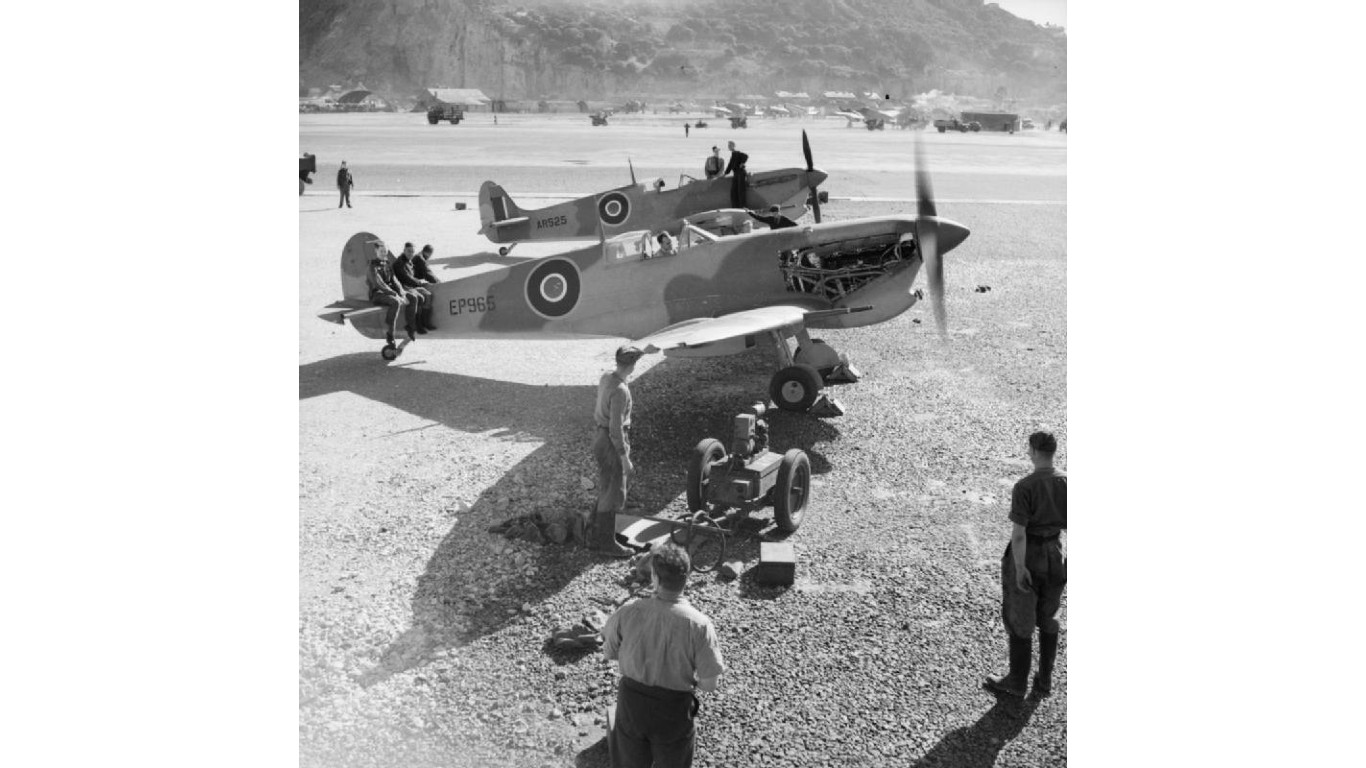

Operation Torch, led by British and American forces, was the first major Allied offensive of the Western theatre during World War II. It marked the beginning of the Allied invasion of Axis-held North Africa.
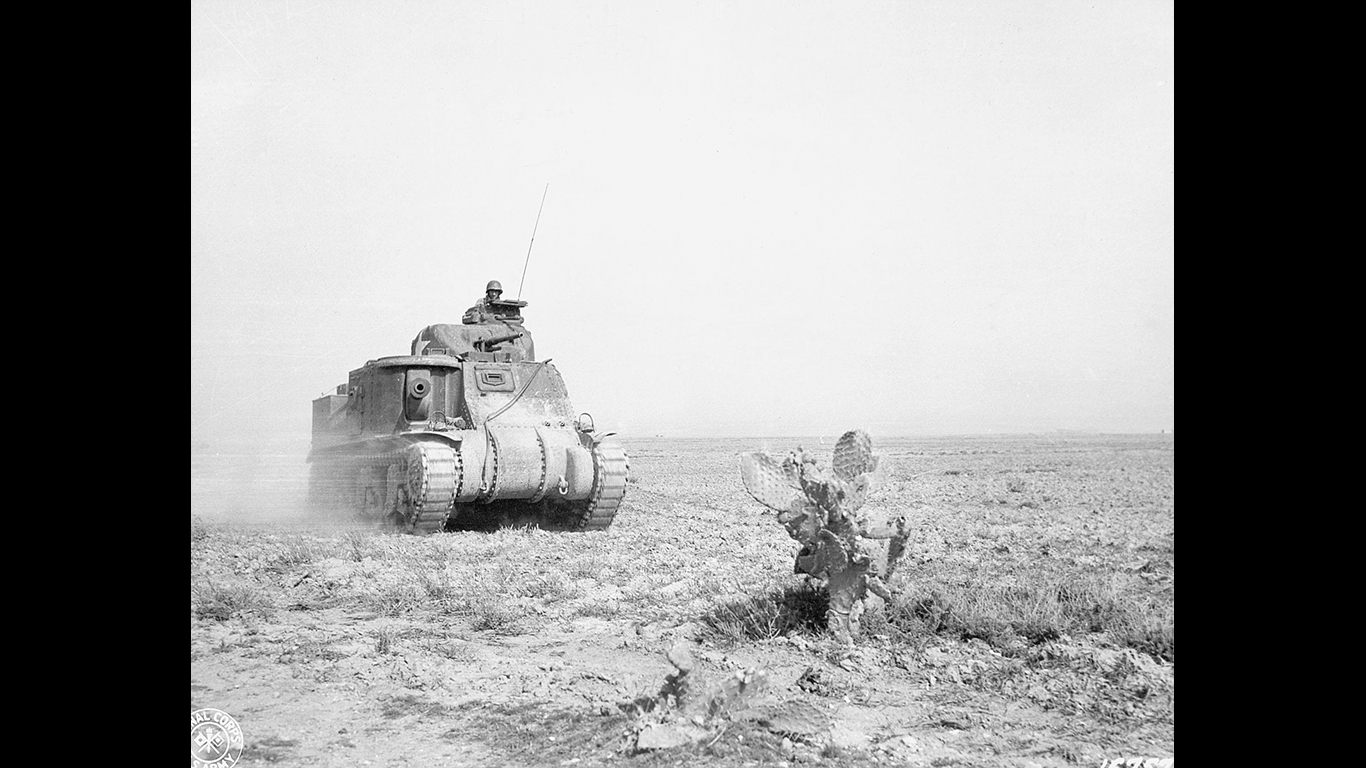

The Advance into Tunisia was an important step in the Allied North African campaign in the wake of the success of Operation Torch. This operation aimed to take control of Tunisia and ultimately secure control over the entire North African coast, and then use this as a staging grounds for moving into Southern Europe.
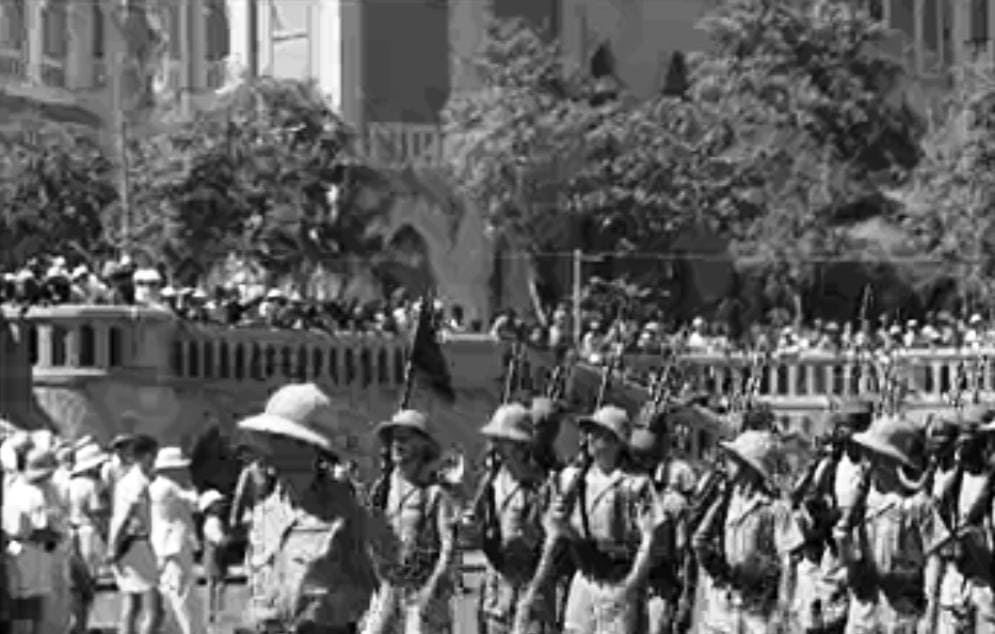

The Invasion of French Somaliland was part of the Allied effort to expel Axis powers in the Horn of Africa.
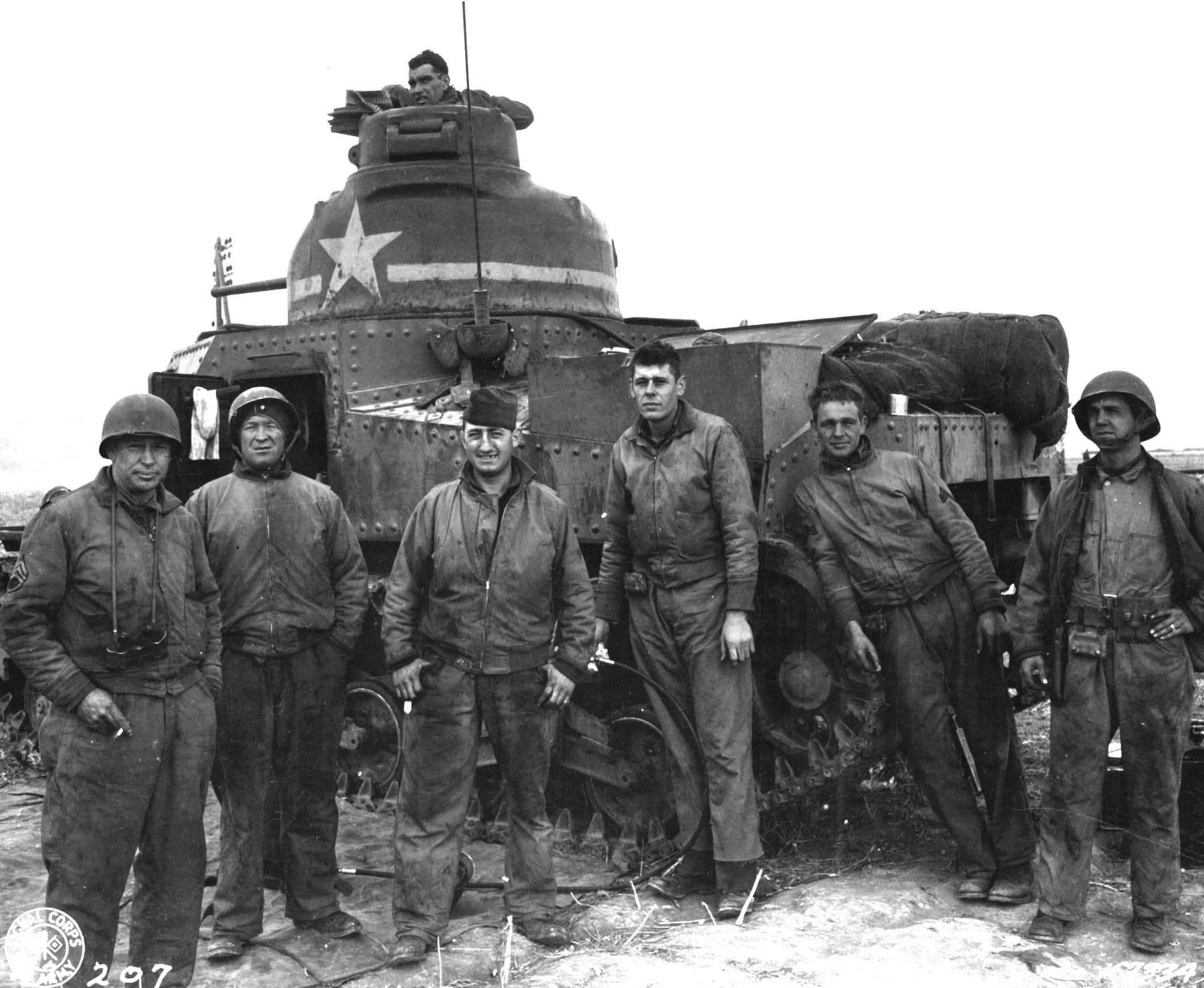

The Battle of Faïd Pass and Sidi Bouzid were important engagements in the Tunisian Campaign. These battles were early Axis counterattacks to set back the Allies in their campaign to control Northern Africa.
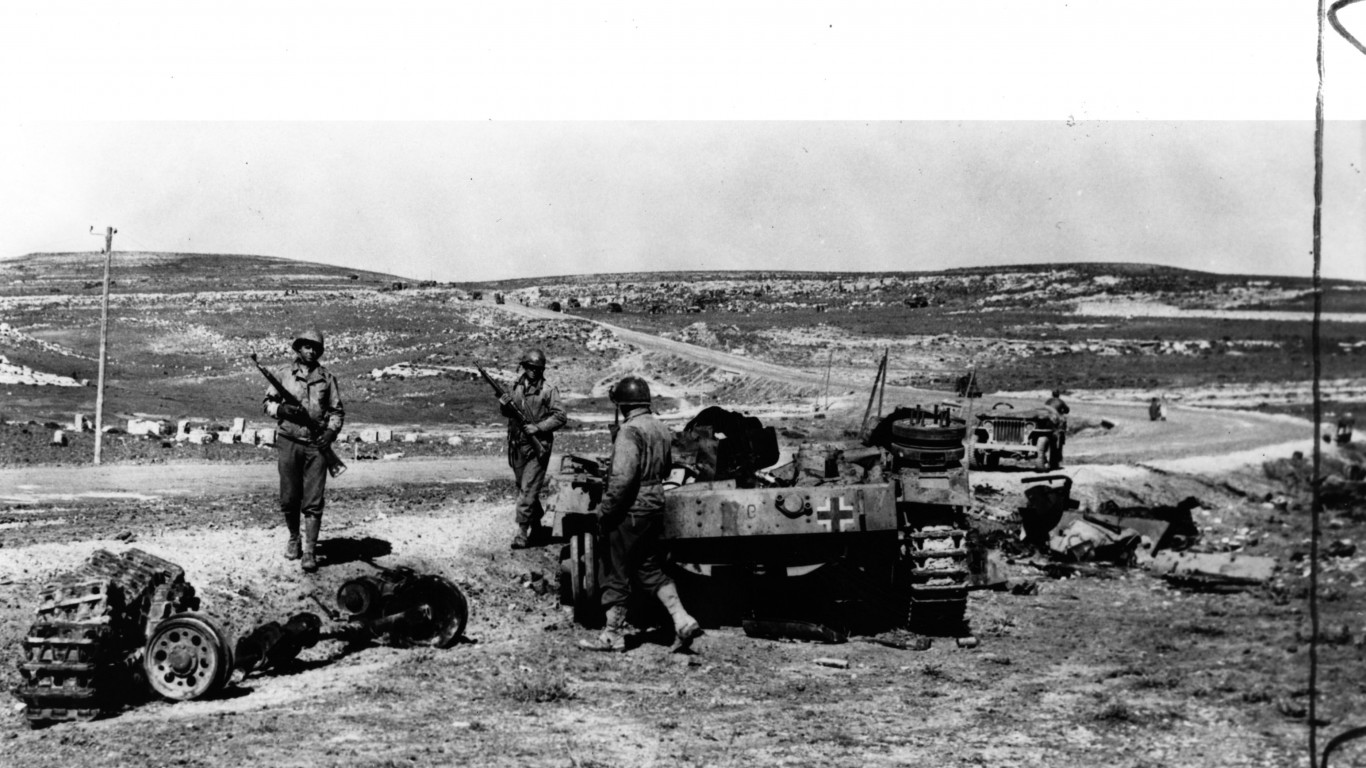

The Battle of Kasserine Pass was the first major engagement between American and Axis forces in the Tunisian Campaign, marking an important test for the relatively inexperienced U.S. troops.
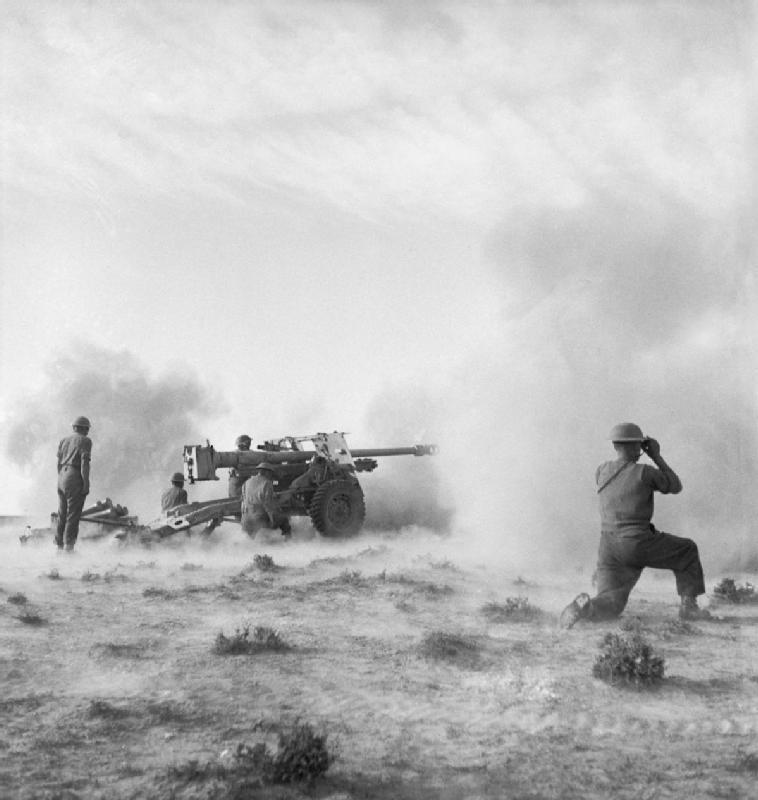

The Battle of Medenine was an Allied defensive engagement during the Tunisian Campaign. This battle occurred when Axis forces, led by Rommel, launched an attack against Allied positions.

Operations Pugilist and Supercharge II were Allied offensives during the Tunisian Campaign.
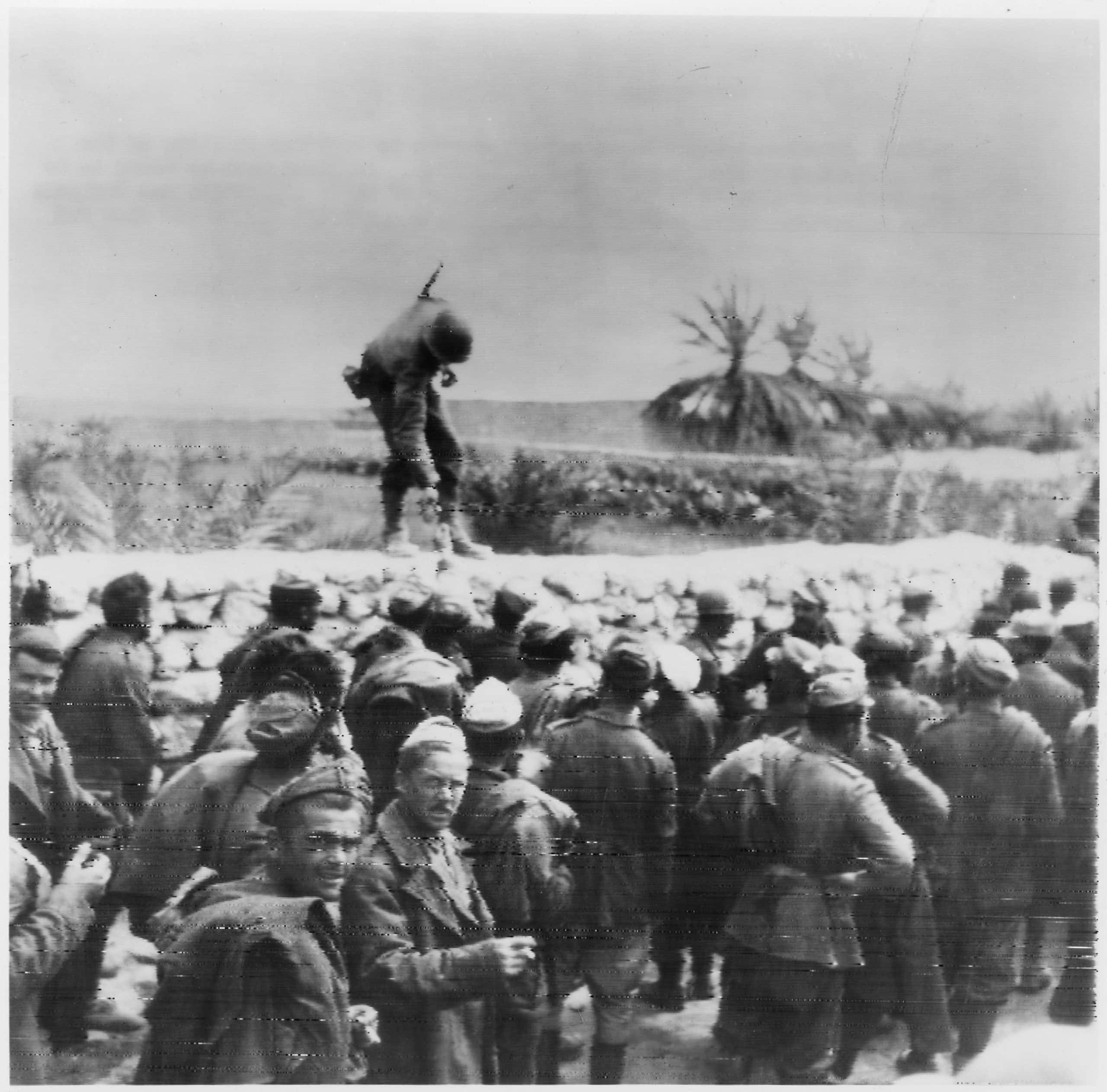

The Battle of El Guettar was the first time U.S. forces successfully defeated German armored units in combat as part of the Tunisian Campaign.
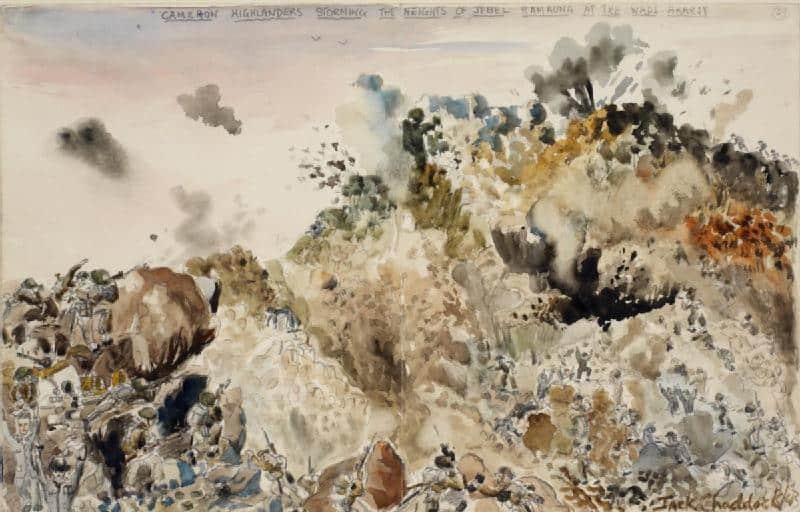

The Battle of Wadi Akarit was part of the Allies’ final push against Axis forces in Tunisia. The Allied victory effectively broke the last major defensive line before Tunis and paving the way for the final stages of the campaign in North Africa.

The conclusion of the Desert War saw the complete encirclement and defeat of Axis forces in Tunisia, culminating in the surrender of over 250,000 German and Italian soldiers. This was one of the largest Axis surrenders of the war.
Start by taking a quick retirement quiz from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes, or less.
Each advisor has been vetted by SmartAsset and is held to a fiduciary standard to act in your best interests.
Here’s how it works:
1. Answer SmartAsset advisor match quiz
2. Review your pre-screened matches at your leisure. Check out the advisors’ profiles.
3. Speak with advisors at no cost to you. Have an introductory call on the phone or introduction in person and choose whom to work with in the future
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.