
During the Cold War, the superpowers signed a number of arms control agreements that helped build trust and limit the scope of their competition. Generally, they agreed to ban nuclear weapons from areas where deploying them would be expensive and difficult and to limit weapons that could give the other side a destabilizing advantage. In the current geopolitical climate, more arms control treaties are not likely, but with a friendlier government in Moscow in the future, and with China emerging as a growing multi-dimensional threat, we might see more of these to regulate new areas of competition, such as cyberspace.
Key Points

- The United States and the Soviet Union signed numerous arms control treaties to limit the scope, danger, and expense of their competition.
- Future arms control treaties are possible but unlikely in the present tense geopolitical climate.
- Check out: 2 Dividend Legends To Hold Forever and Discover “The Next NVIDIA
1. Antarctic Treaty (1959)

- Banned military activity, mining, and detonating nuclear devices in Antarctica
- Establishes the continent as a scientific reserve with findings to be shared internationally.
2. Hot Line Treaty (1963)

- The U.S. and USSR agreed to establish a direct communication link to help them deescalate fast-moving crises.
- This agreement was signed one year after the Cuban Missile Crisis.
3. Limited Test Ban Treaty (1963)

- Signed by John F. Kennedy and Nikita Khrushchev.
- Stopped testing nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, space, or under water.
- Weapons could be tested underground as long as the debris did not cross the border to another country’s territory.
4. Outer Space Treaty (1967)

- Signed by Lyndon B. Johnson and Alexei Kosygin
- Agreed not to deploy weapons of mass destruction in space, on the Moon or other celestial bodies, or in orbit around the planet.
5. Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (1968)
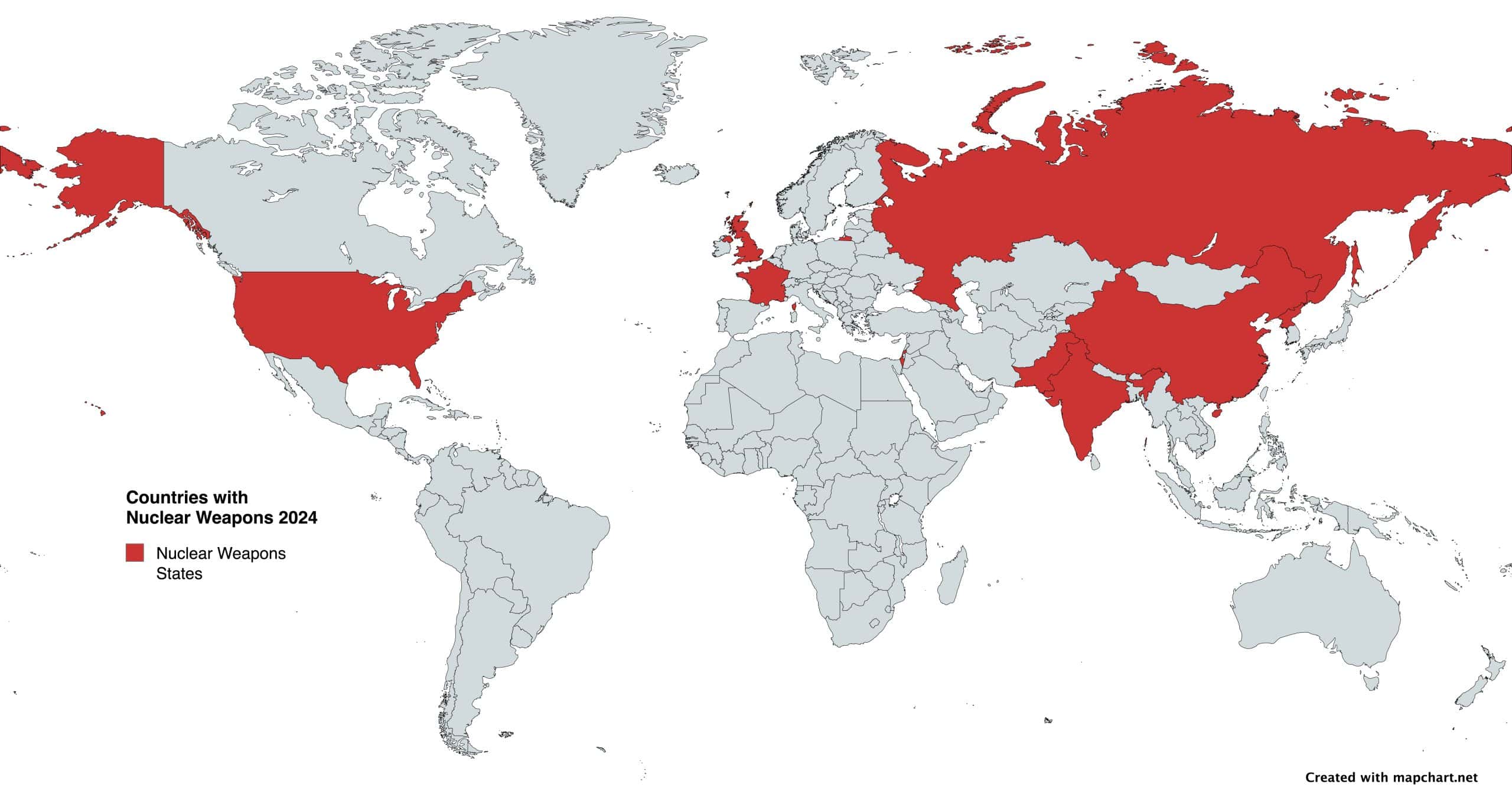
- Countries without nuclear weapons pledged not to get them; those with nuclear weapons pledged to get rid of them eventually.
- Non-nuclear weapons countries are still allowed to have nuclear reactors for peaceful purposes such as research and electricity generation.
- Countries must declare their facilities to the International Atomic Energy Agency, meet safety standards, and submit to international inspections.
6. Seabed Arms Control Treaty (1971)

- Signed by Richard Nixon and Alexei Kosygin
- Under the terms of this treaty, neither country will put weapons of mass destruction on the seabed any further out than 12 miles from their coast.
7. Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty I (1972)

- Signed by Richard Nixon and Leonid Brezhnev
- Placed limits on deployment of new ICBMs and submarine-launched missiles.
- Limited how many anti-ballistic missile systems each country could have.
8. Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty (1972)

- Restricted the development of anti-ballistic missiles.
- The United States withdrew from the treaty in 2002. It wanted to develop stronger ABM defenses against newer, more unstable nuclear powers like North Korea.
9. Biological Weapons Convention (1972)

- Signed by Richard Nixon and Leonid Brezhnev
- Forbade the development, production, and stockpiling of biological weapons.
10. Threshold Test Ban Treaty (1974)

- Signed by Gerald Ford and Leonid Brezhnev.
- Prohibited tests of nuclear weapons of more than 150 kilotons. This is 10 times larger than the bomb dropped on Hiroshima.
11. Peaceful Nuclear Explosions Treaty (1976)

- Signed by Gerald Ford and Leonid Brezhnev
- Allows nuclear explosions to be used for construction, mining, or similar peaceful purposes.
- Some examples both countries considered included excavating land for canals or creating underground storage caverns.
12. Environmental Modification Convention (1977)

- Signed by Jimmy Carter and Leonid Brezhnev.
- This treaty committed each side not to modify the environment for military purposes.
- Some examples could include trying to change the weather, such as seeding clouds to cause them to drop all their moisture before reaching the other country, or finding ways to cause earthquakes.
13. Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty II (1979)

- SALT II was signed by Jimmy Carter and Leonid Brezhnev.
- It limited the numbers of long-range missiles and heavy bombers each side could deploy.
- The U.S. Senate refused to ratify the treaty because of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. However, both sides followed it anyway for several years.
14. Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (1980)

- Placed restrictions on the use of landmines, incendiary weapons, and others that indiscriminately harm civilians.
- Required that signatories clean up unexploded ordnance they were responsible for.
- The treaty is flexible so that countries can adopt some parts of it and not others.
15. Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (1987)

- The INF treaty was signed by Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev
- It resulted in both sides destroying all ground-launched missiles with a range of 500-5,000 km, globally.
- This was the first arms control agreement that wiped out a whole class of nuclear weapons.
- The U.S. withdrew in 2019 in protest of the Russian deployment of a new missile that violated the treaty.
16. Ballistic Missile Launch Notification Agreement (1988)

- Bill Clinton and Boris Yeltsin signed this agreement.
- It requires the U.S. and USSR to notify one another at least 24 hours in advance if they intended to test-launch an ICBM or submarine-launched ballistic missile.
17. Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (1990)
- Signed by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev.
- Restricted the deployment level in Europe of tanks, aircraft, and artillery to reduce tensions between NATO and the Warsaw Pact.
- At the time, the Soviet Union was keen to lessen tensions with the West while it tried to implement radical political and economic reforms.
18. Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (1991)

- START I was signed by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev.
- This treaty replaced the expired SALT treaties. It limited the number of offensive missiles each side could deploy.
- It was in force from 1994-2009 and resulted in the elimination of thousands of warheads.
19. Open Skies Treaty (1992)

- Signed by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev.
- Under the terms of this agreement, NATO and Russia agreed to allow unarmed reconnaissance flights over their territory.
- The U.S. withdrew from it in 2020.
20. Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty II (1993)

- Signed by George H.W. Bush and Boris Yeltsin
- START II limited each side to deploying 3,000-3,500 nuclear warheads. It also put limits on delivery systems, like heavy bombers and strategic missiles.
- The U.S. signed this treaty but the Senate did not ratify it due to concerns about the complex situation after the collapse of the USSR.
- Russia withdrew from the treaty in 2002.
21. Chemical Weapons Convention (1993)

- Signed by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev.
- The treaty prohibits producing, stockpiling, or using chemical weapons. Countries currently owning them were expected to destroy them.
- Nearly every country has signed the treaty.
- The U.S. has destroyed about 97% of its stockpile. Russia also is destroying its remaining weapons.
- Syria and North Korea are the only two countries that still have significant stockpiles of chemical weapons.
22. Treaty of Pelindaba (1996)
- This treaty declares Africa to be a nuclear-weapons-free zone.
- The U.S. and other signatories are committed not to deploy or test nuclear weapons in Africa.
23. Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (1996)

- This treaty would ban all nuclear weapons testing.
- Instead of testing nuclear explosions, nuclear powers can simulate their effects with computer models and use large conventional explosions to test the performance of components of nuclear weapons.
- The U.S. signed the treaty but the Senate did not ratify it.
24. Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (2002)

- Signed by George W. Bush and Vladimir Putin
- Reduced the number of nuclear warheads for each country to 1,700-2,200.
- It did not include any limitations on delivery systems, unlike some previous arms control agreements.
25. International Code of Conduct Against Ballistic Missile Proliferation (2002)

- This agreement attempts to prevent countries from getting ballistic missiles that could be used for weapons of mass destruction.
- It requires international cooperation to monitor missile proliferation.
26. International Convention for the Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism (2005)

- This United Nations treaty criminalizes planning, threatening, or executing nuclear terrorism. This provides a stronger international legal foundation for prosecuting such crimes.
- It involves not only the use of nuclear weapons by terrorist actors, but also attacks on nuclear reactors and other facilities with the intent to disperse radiation and sow terror.
27. New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (2010)

- Signed by Barack Obama and Dmitry Medvedev
- Reduced the levels of U.S. and Russian nuclear warheads to 1,550 apiece.
- Prior to the treaty the U.S. had 2,200 warheads and Russia had 2,700.
It’s Your Money, Your Future—Own It (sponsor)
Retirement can be daunting, but it doesn’t need to be.
Imagine having an expert in your corner to help you with your financial goals. Someone to help you determine if you’re ahead, behind, or right on track. With SmartAsset, that’s not just a dream—it’s reality. This free tool connects you with pre-screened financial advisors who work in your best interests. It’s quick, it’s easy, so take the leap today and start planning smarter!
Don’t waste another minute; get started right here and help your retirement dreams become a retirement reality.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
