Special Report
20 Most Common Problems Behind a Check Engine Light

Published:
Last Updated:

Car owners are familiar with that dreaded feeling when the “check engine” indicator lights up on the dashboard display. It could be a minor issue, such as a loose gas cap, but it could also be something serious, like cylinder misfires that can do costly damage to the engine if left unattended. Engine problems can also decrease mileage efficiency and allow excess fuel vapors to escape into the atmosphere — even if you’re driving one of the most eco-friendly cars on the market.
The check engine light, also known as the malfunction indicator lamp, is the result of an industry standard that began with the 1996 model year, according to automotive information provider Edmunds. Since then, new vehicles have been equipped with a universal on-board diagnostics system (OBD-II), accessed with a code reader which a mechanic plugs into a connector usually located near the base of the steering column. The code reader collects sensor-generated alphanumeric “trouble codes” that can identify numerous problems.
The way the check engine light works varies by vehicle. It can flash or stay illuminated. In some cases, the light changes from yellow to red or orange to indicate a more serious mechanical problem.
Click here to see the 20 most common reasons for a check engine light.
Some cars also include a general maintenance reminder light in addition to the check engine warning. Refer to your manual to learn what these indicators mean — especially if you drive one of the new cars that are most likely to break down.
To determine the 20 most common reasons for a check engine light 24/7 Wall St. reviewed 2021 data from FIXD.com, which aggregates data from 18 million vehicles that detected and cleared engine codes from the FIXD OBD-II sensor in 2020. Vehicle repair data was obtained from CarMD’s 2021 Vehicle Health Index which lists the 10 most common classes of check-engine-light-related repairs in 2020, as well as the average cost to make the repair.

1. P0300
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0300 indicates that at least two engine cylinders are misfiring, which can seriously damage the engine or catalytic converter. Cylinder misfires, when an insufficient amount of fuel is burned in a cylinder, are often due to worn-out spark plugs or spark plug wires or a faulty ignition coil.
[in-text-ad]

2. P0301
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0301 is similar to P0300, but indicates a misfire in cylinder No. 1 rather than in two or more cylinders. Both issues cause the engine to run rough and operate with lower power, and can cause serious and expensive damage if left unrepaired for too long.

3. P0302
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0302 indicates that the cylinder No. 2 is misfiring. You risk serious and costly engine damage by ignoring this problem.

4. P0303
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0303 indicates a misfire in the cylinder No. 3. Any misfiring causes serious and expensive damage if left unrepaired for too long.
[in-text-ad-2]

5. P0304
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0304 indicates a misfiring in the cylinder No. 4. An unrepaired cylinder misfire will eventually lead to costly engine failure.

6. P0305
> Vehicle repair: Replace ignition coil(s) and spark plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0305 indicates the cylinder No. 5 is misfiring. Ignoring any cylinder misfire codes can lead to catastrophic engine damage.
[in-text-ad]
7. P0306
> Vehicle repair: Replace Ignition Coil(s) and Spark Plug(s)
> Average repair cost: $390
P0306 indicates cylinder No. 6 is misfiring. Cylinder misfire can cause serious engine damage.
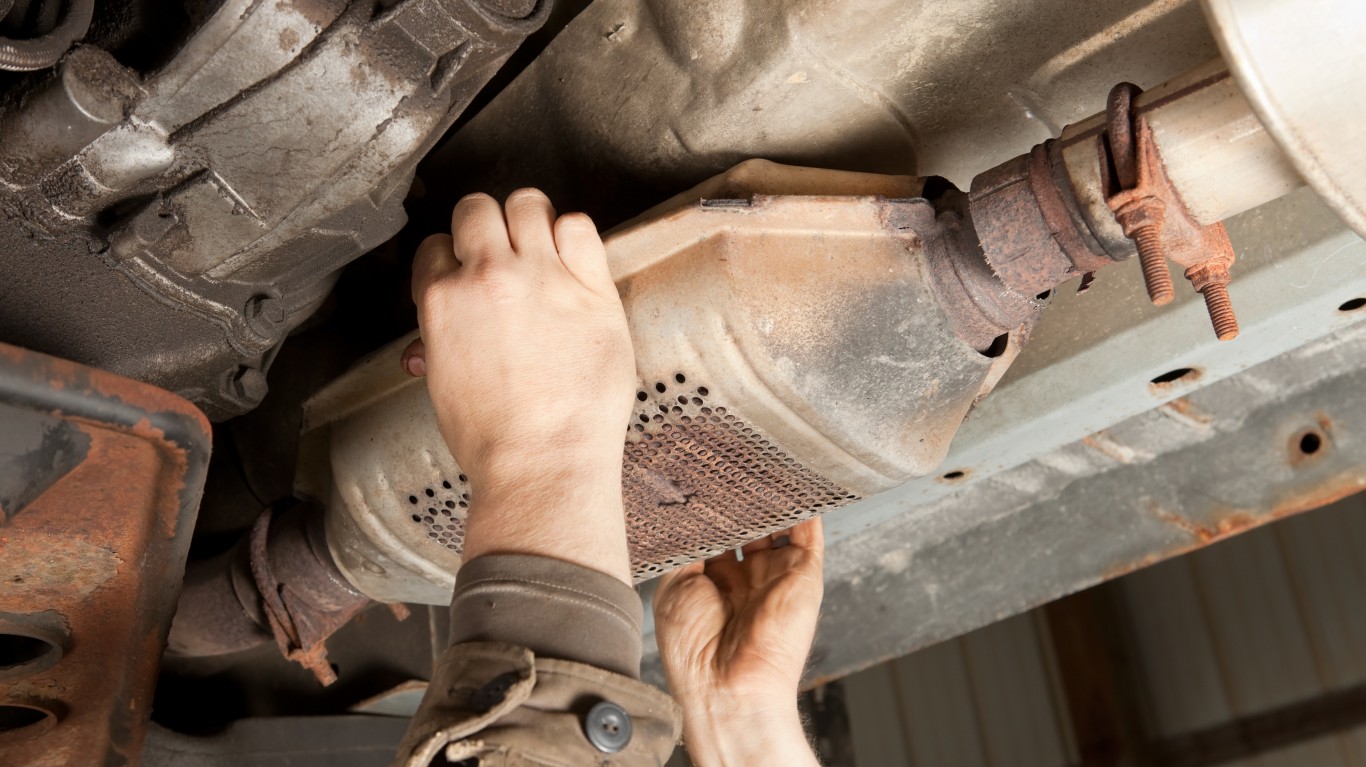

8. P0420
> Vehicle repair: Replace catalytic converter(s) with new OE catalytic converter(s)
> Average repair cost: $1,400
P0420 points to the catalytic converter — the emissions-control device(s) located near the exhaust manifold. Catalytic converters typically do not malfunction unless other problems, like a failed spark plug or exhaust valve, have gone unfixed. The code could also indicate other issues, including damaged oxygen sensors, leaking fuel injectors, or cylinder misfires.
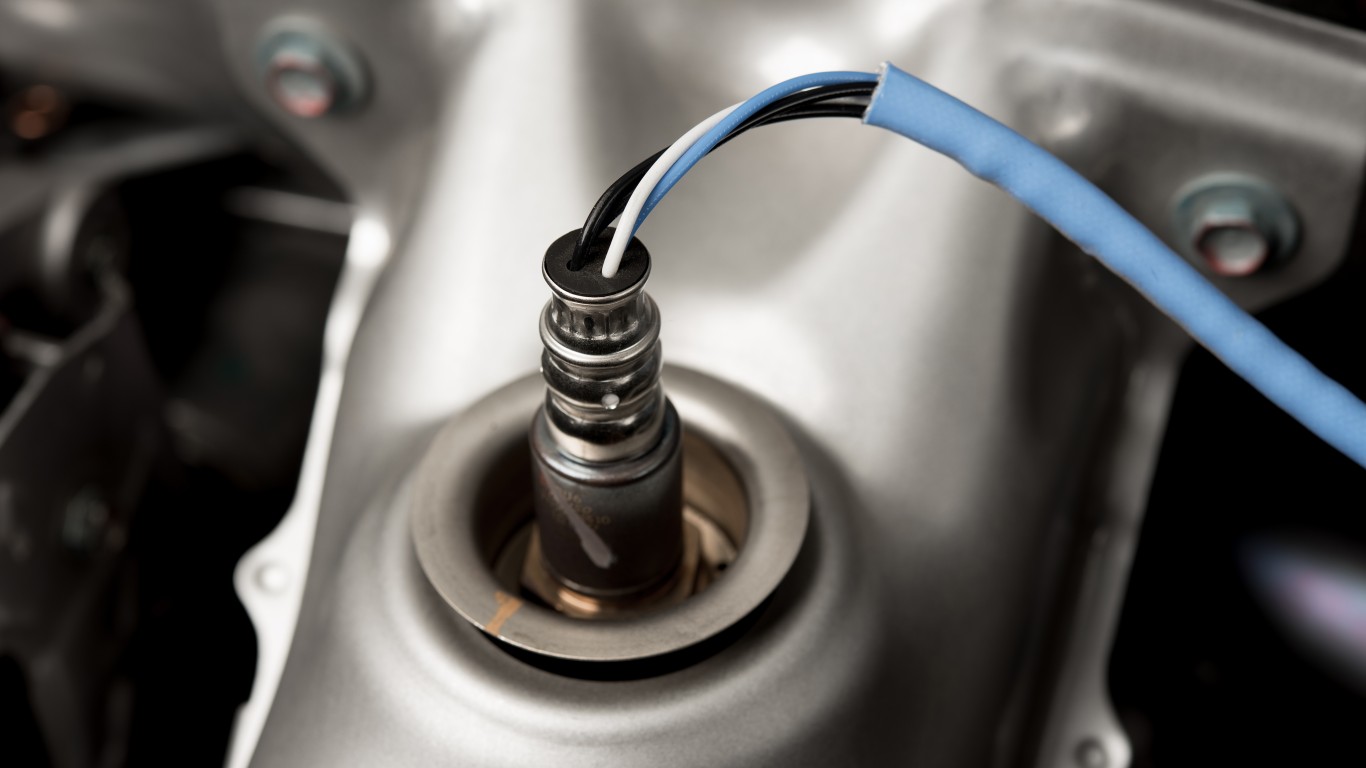

9. P0430
> Vehicle repair: Replace oxygen sensor(s) (O2S)
> Average repair cost: $250
P0430 is similar to P0420, in that both focus on issues with the catalytic converter, an emissions control device. The difference is that P0430 identifies an issue with one of the oxygen sensors on the device. If the problem is a faulty oxygen sensor, then the repair job costs less than replacing the entire catalytic converter.
[in-text-ad-2]

10. P0171
> Vehicle repair: Replace oxygen sensor(s) (O2S)
> Average repair cost: $250
P0171 indicates a problem with the vehicle’s ability to maintain an optimal fuel-to-air ratio, which could mean either too little fuel or too much air. This can cause a lack of power to the engine, engine misfiring or “coughing,” or a rough idle.
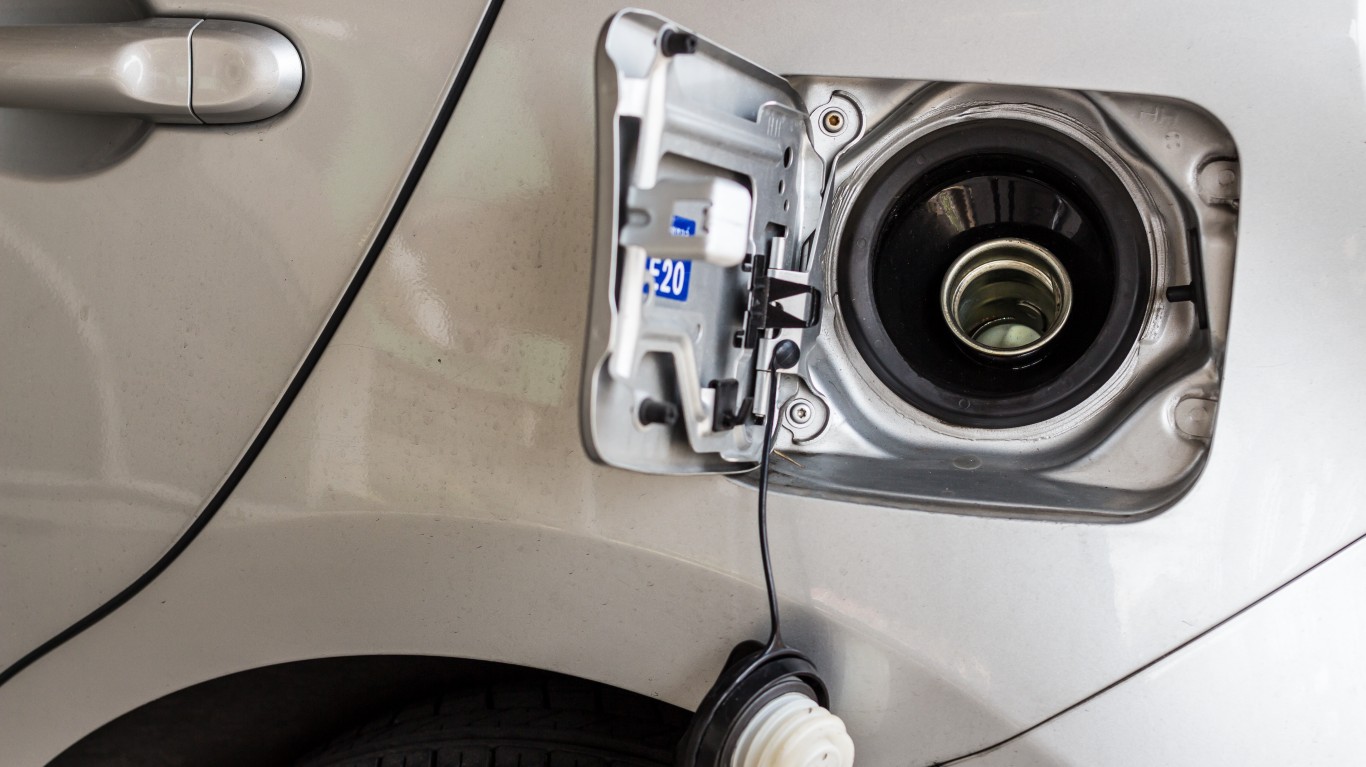

11. P0455
> Vehicle repair: Replace evaporative emissions (EVAP) purge control valve
> Average repair cost: $150
P0455 signals a large leak in the evaporative emissions control systems (EVAP), which prevent fuel vapors from being released into the atmosphere by storing them in a canister of charcoal pellets and then sending them into the engine air intake manifold using a purge control valve. This problem could also be caused by a faulty gas cap.
[in-text-ad]
12. P0456
> Vehicle repair: Replace evaporative emissions (EVAP) purge solenoid
> Average repair cost: $150
P0456 is similar to P0455, but indicates a small fuel vapor leak (0.20″ in diameter or less) rather than a large one in the evaporative emission control systems (EVAP).

13. P0442
> Vehicle repair: Replace evaporative emissions (EVAP) purge solenoid
> Average repair cost: $150
P0442 is similar to P0455 and P0456, indicating a fuel-vapor leak in the evaporative emission control (EVAP) system. P0442 appears when your vehicle has a leak measuring between .020″ to .040″ in diameter.

14. P0441
> Vehicle repair: Replace Evaporative Emissions (EVAP) Purge Solenoid
> Average repair cost: $148.81
This is another code indicating a problem with the evaporative emission control (EVAP) system.
[in-text-ad-2]
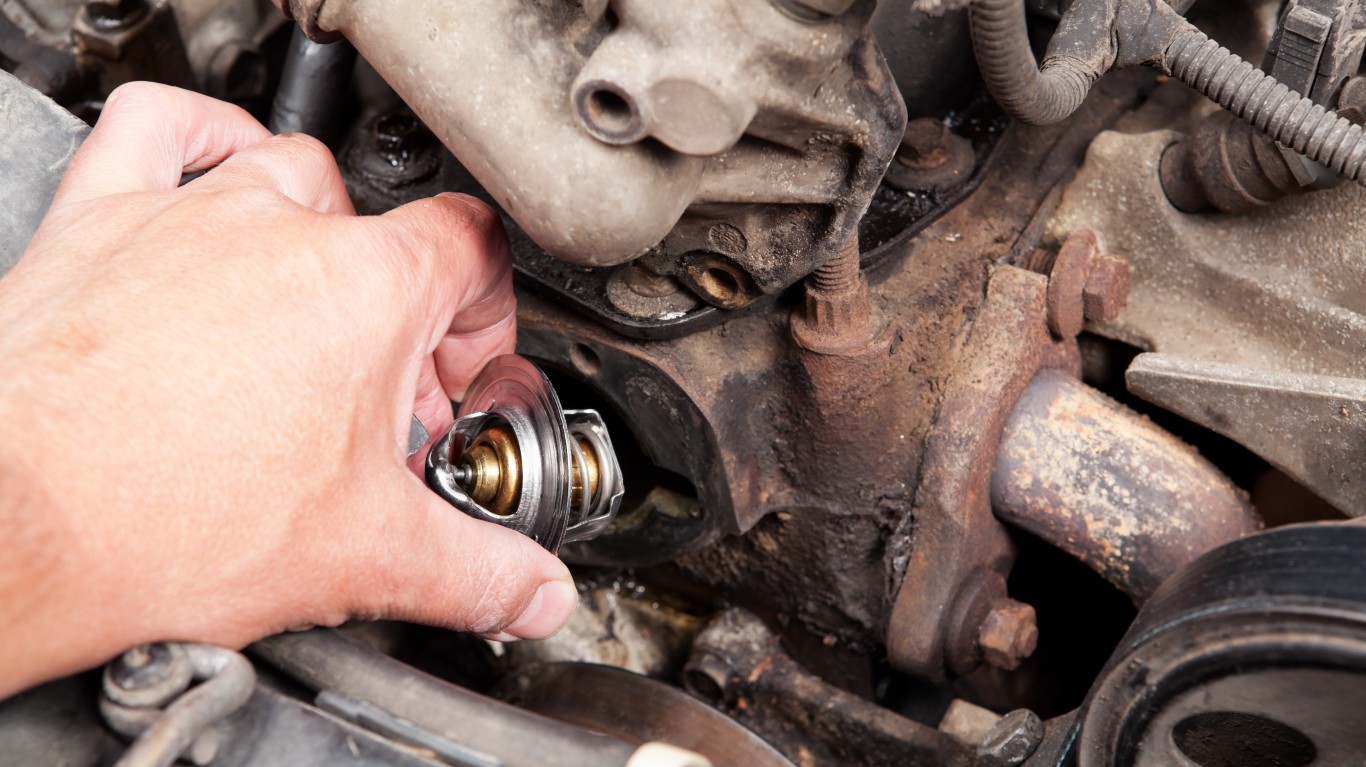

15. P0128
> Vehicle repair: Replace thermostat
> Average repair cost: $240
P0128 suggests your vehicle is not reaching or maintaining its ideal operating temperature. This problem is minor, but can adversely impact fuel economy and cause higher levels of harmful emissions.
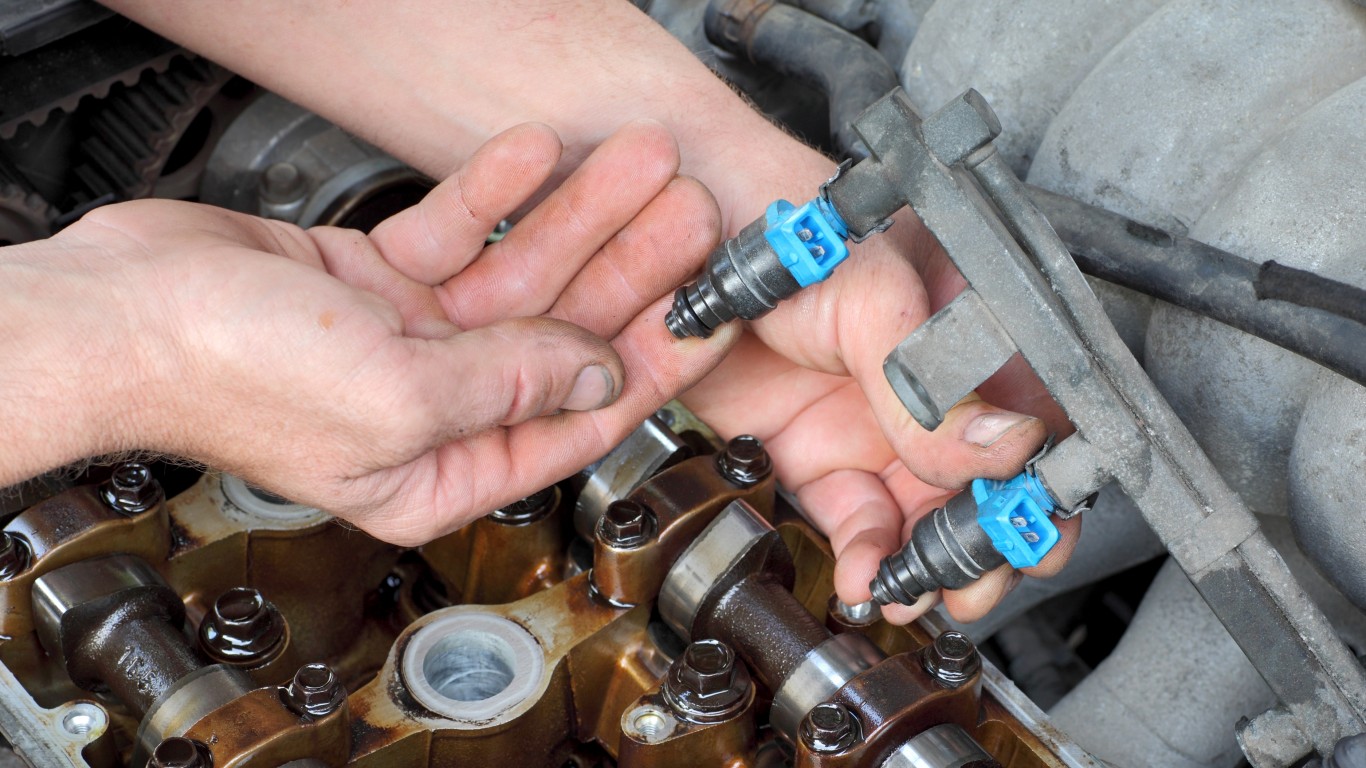

16. P0174
> Vehicle repair: Replace fuel injector(s)
> Average repair cost: $450
P0174 indicates a fuel-air ratio problem in one of the banks of cylinders. Improper fuel-air ratios can eventually cause serious engine damage. Symptoms include lack of power, higher fuel consumption, and a hesitation/surge in acceleration.
[in-text-ad]

17. P1000
> Vehicle repair: N/A
> Average repair cost: N/A
P1000 is a manufacturer-specific trouble code, used mostly by Ford, Jaguar, and Mazda, though some other brands also utilize it. It indicates that the vehicle’s engine control computer did not complete a self-diagnostic cycle related to emissions control. The code doesn’t indicate why the cycle wasn’t completed. This is a minor issue.
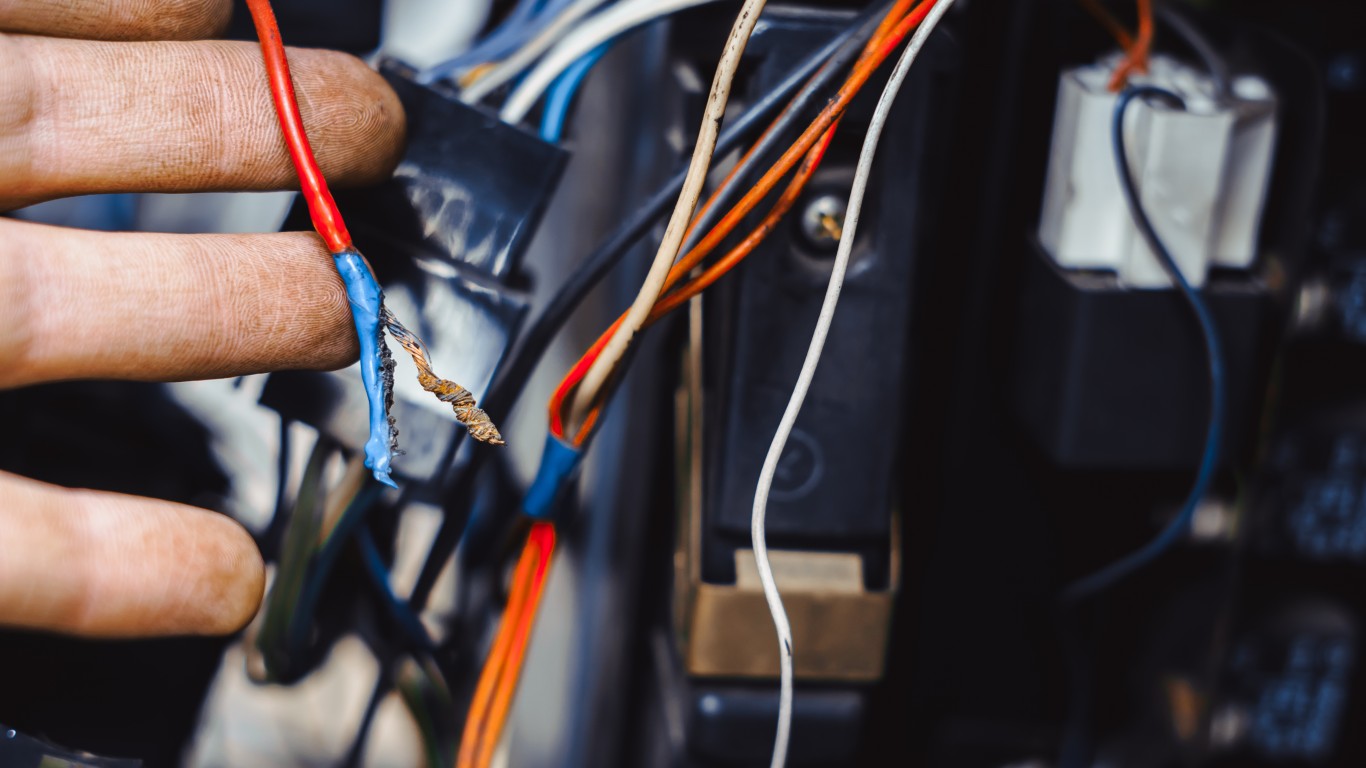

18. P0113
> Vehicle repair: N/A
> Average repair cost: N/A
P0113 indicates a problem with the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor that regulates the correct amount of spark and fuel injected into the cylinders based on outdoor temperatures. A common problem is simply loose wiring, but it could also indicate a faulty IAT sensor.

19. P0446
> Vehicle repair: Inspect for Loose Fuel Cap and Tighten or Replace as Necessary
> Average repair cost: $25
P0446 indicates that the vehicle’s evaporative emission control (EVAP) system is not working properly due to a short circuit in the control of the vent control valve. This causes a failure to maintain proper pressure that can lead to a decrease in fuel economy and a fuel smell.
[in-text-ad-2]
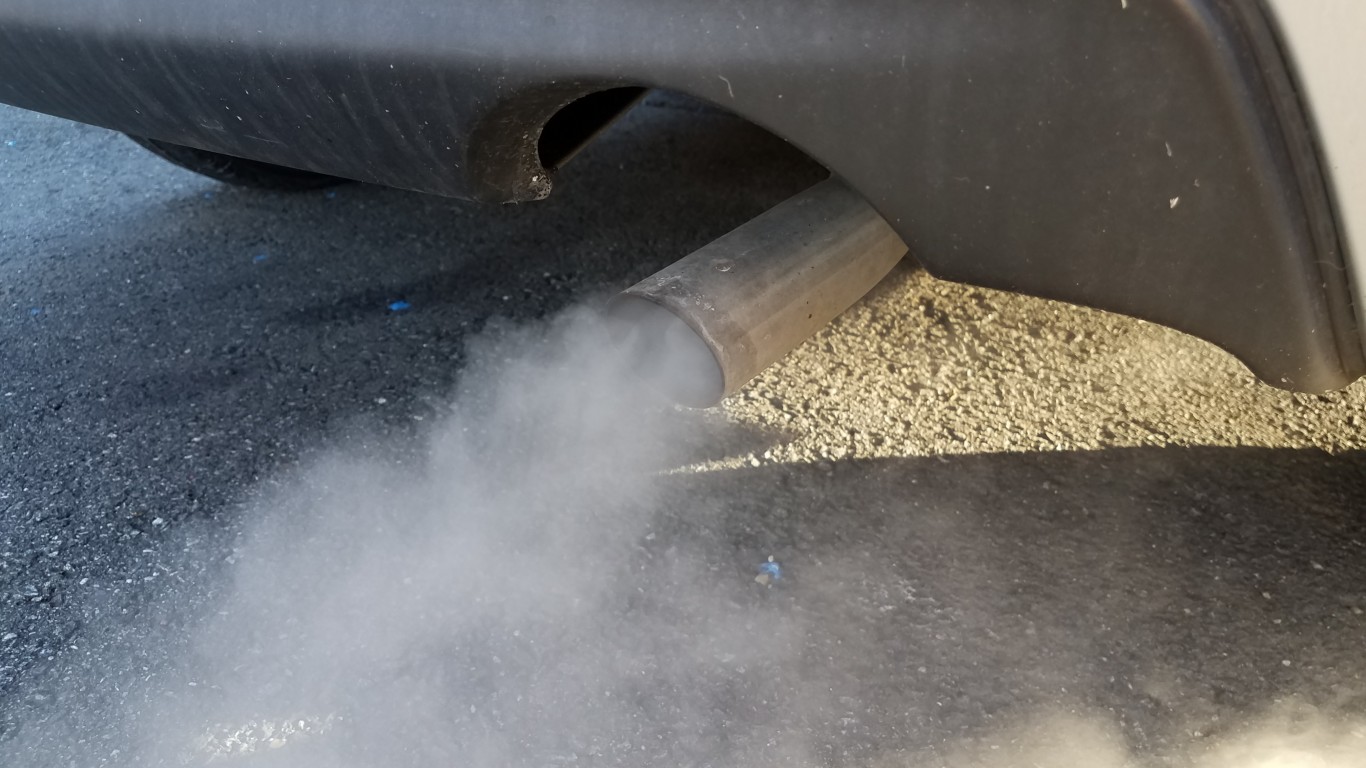

20. P0102
> Vehicle repair: Replace Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
> Average repair cost: $340
P0102 indicates a problem with the engine’s air intake related to low voltage output from air flow controllers, reducing engine performance. Symptoms include a rough running engine, black smoke from the tailpipe, or stalling. Inadequate air intake over the long-term can eventually lead to more serious engine trouble down the road.
Finding a qualified financial advisor doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to 3 fiduciary financial advisors in your area in 5 minutes. Each advisor has been vetted by SmartAsset and is held to a fiduciary standard to act in your best interests. If you’re ready to be matched with local advisors that can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.