An empire comprises many territories ruled by one centralized governing body, often an emperor or other monarch. As long as humans have had aspirations to rule, there have been empires. Some date back more than 4,500 years, almost to the end of the Stone Age.
Some empires are short-lived, while others endure for centuries. Even those that disappear within a few hundred years can make a significant impact, imparting lasting influence on the arts, science, government, commerce, farming techniques, tradesmen crafts, religion, and urban development, among other human endeavors.
To determine the longest-lived empires in history, 24/7 Tempo reviewed numerous articles, encyclopedia entries, and historical and archeological websites, among the Britannica, World History, HistoryFiles, New World Encyclopedia, and Maps of India.
In many instances, it is impossible to determine a precise founding date for an empire, either because there are no trustworthy historical records or because some empires come into being slowly, beginning with minor dynasties that may turn into empires. It is also sometimes difficult to pinpoint the exact end of a declining empire unless it was conquered definitively. The date ranges given, then, are often approximate, and may be contested. (These are ancient civilizations destroyed by natural disasters.)
Whatever their lifespan, running an empire was a difficult task. Some managed to hold farflung possessions by allowing varying degrees of autonomy. That was one of the factors that allowed the Holy Roman Empire to last as long as it did. Other empires, such as the Saudeleur Dynasty in what is now Pohnpei island, in the Federated States of Micronesia in the South Pacific, imposed a strong centralized government. (These are the 50 most powerful leaders of all time.)
This list includes some of the most famous empires in human history – the Roman, the Ottoman, the Byzantine, and the British among them. Less well-known but no less interesting are the three empires that fought for supremacy in Korea for decades – the Goryeo, Paekche, and Silla kingdoms.
Click here to see the longest-lived empires in history
Among the many African-based empires on the list is Abyssinia (Ethiopian Empire), which succeeded in fending off European colonization. One of the longest-lasting empires in South America was the Wari civilization that lasted for 500 years and preceded the arrival of the Spanish by half a millenium.

50. Gurjara-Pratihara Dynasty
> Dates: 725-1027
> Span: 302 years
The Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty ruled a large portion of medieval Northern India. It reached its height of influence in the late 9th and early 10th centuries.
[in-text-ad]

49. Kingdom of Judah
> Dates: 922-586 B.C.
> Span: 336 years
The Kingdom of Judah was created from the territories of the tribes of Judah, Simon, and Benjamin after the United Kingdom of Israel was split in two following the death of Solomon around 922 B.C. It was named after Judah, son of Jacob. The area was estimated to encompass 3,435 square miles. Judah is sometimes called the Southern Kingdom to distinguish it from the Northern Kingdom, formed after the two states divided.

48. British Empire
> Dates: 1588-1997
> Span: 409 years
Though it was at its height from the late 16th through early 18th centuries, with colonies or other possessions on every continent, the British Empire is sometimes said to have begun with the English colonization of Ireland in the latter 12th century. Brittanica, on the other hand, pegs its birth to the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588, establishing Britain as a major sea power able to compete for trade and colonies around the world. The last British colony of any size or importance, Hong Kong, was returned to the Chinese in 1997, effectively marking the empire’s end.
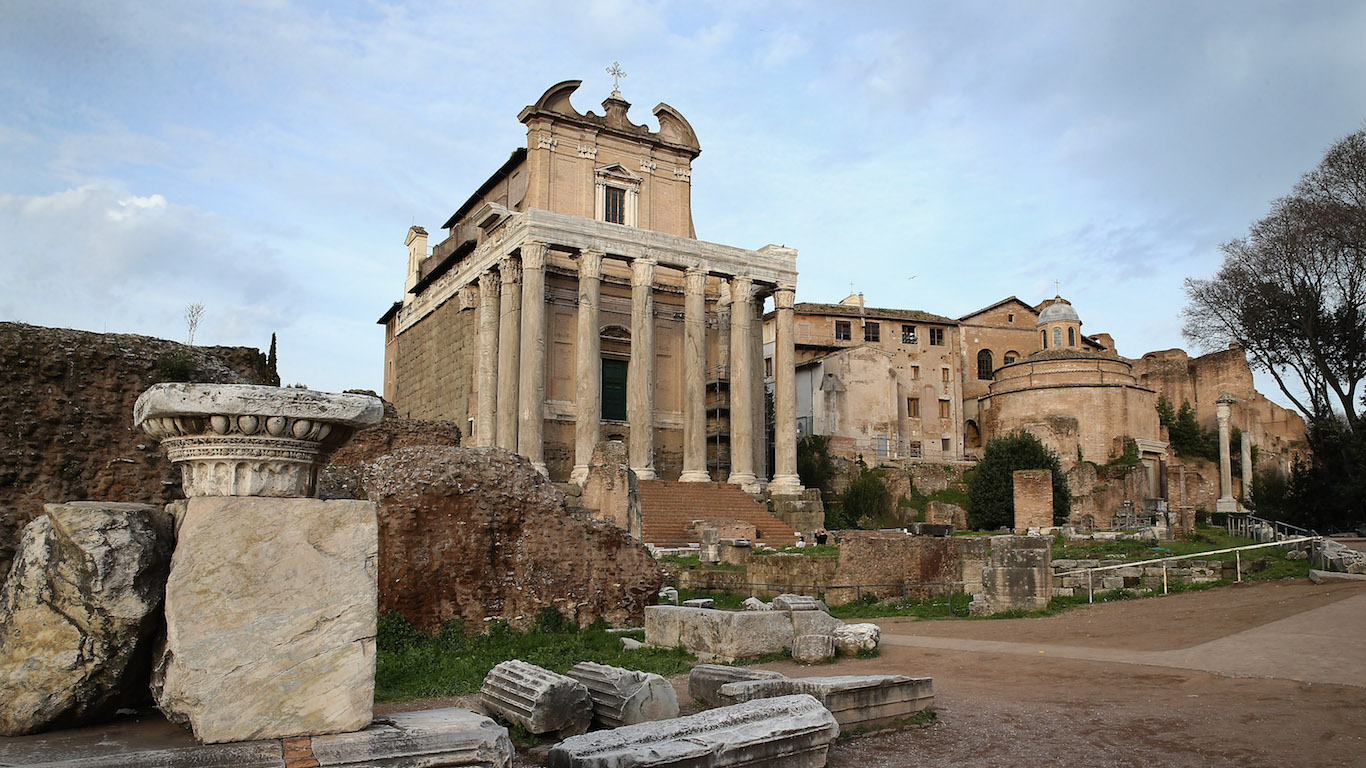

47. Roman Empire
> Dates: 27 B.C.-395
> Span: 422 years
It’s hardly one of the longest-lived empires in history, but the Roman Empire exerted immense and lasting influence all over Europe and beyond, leaving its traces in language, agriculture, art and architecture, law, religion, and more. Though the Romans were a formidable regional power in earlier centuries, the empire itself began when the Roman Senate recognized Octavian â the assassinated Julius Caesar’s adopted son â as emperor. At its height, it held sway over most of Europe, from England to Ukraine, as well as the North African coast and parts of Asia Minor and the Middle East. The empire ended with its division into two halves in 395. The western part quickly disintegrated, while the eastern portion lasted more than a thousand more years as the Byzantine Empire (see No. 7).
[in-text-ad-2]

46. Oyo Empire
> Dates: 1400-1838
> Span: 438 years
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba kingdom, occupying what are now parts of Benin and Nigeria. It prospered from the 17th to the 19th century, with much of its prosperity stemming from the slave trade -so extensive that its part of Africa became known as the “Slave Coast.”
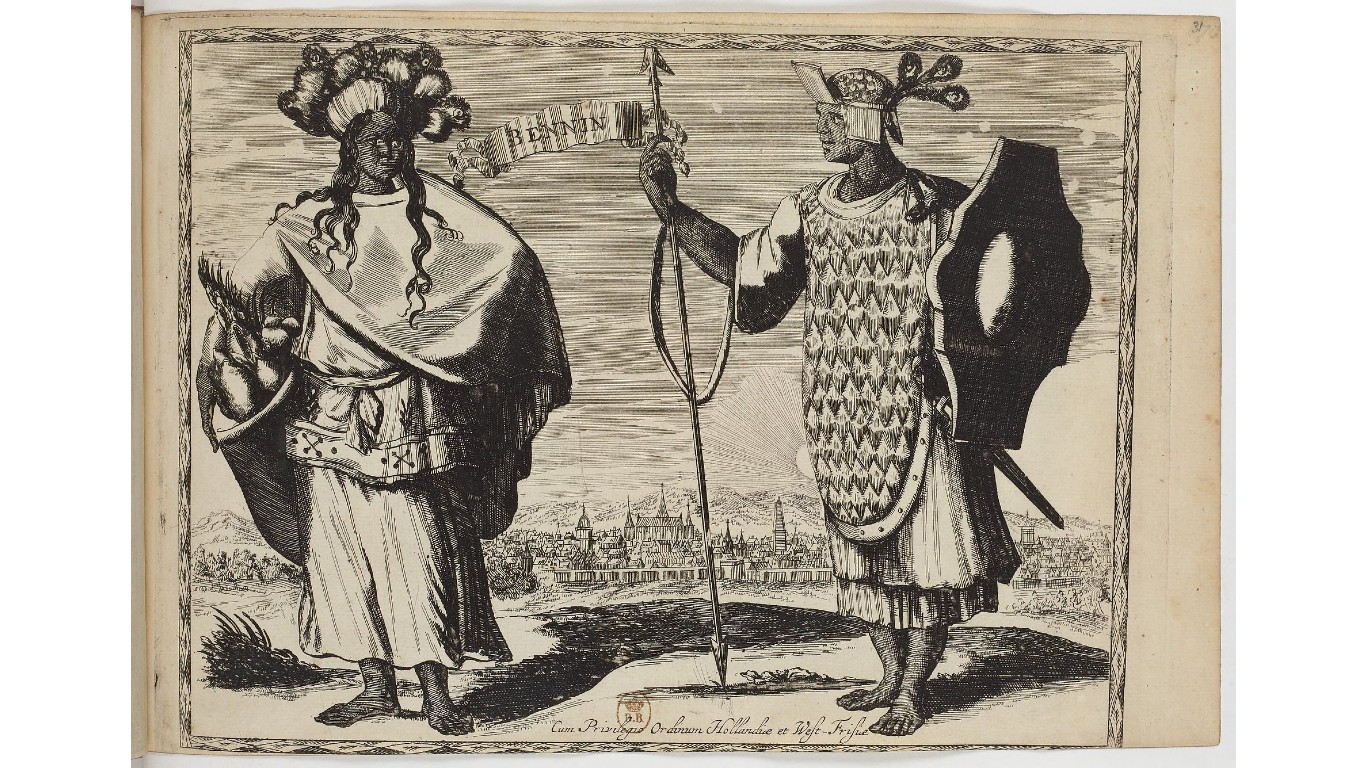

45. Benin Empire
> Dates: 1440-1897
> Span: 457 years
The Benin Empire, located in modern-day southwestern Nigeria, was one of the longest-lasting indigenous empires in African history. Created by the Edo people, it benefited greatly through its trade with the Portuguese. It has no relation to the contemporary African nation of Benin.
[in-text-ad]
44. Parthian Empire
> Dates: 247 B.C.-224
> Span: 471 years
The Parthian Empire had its origins with Seleucus I, one of Alexander the Great’s generals. The empire extended from the Mediterranean to India and China. The vastness of their empire exposed the Parthians to many cultures.
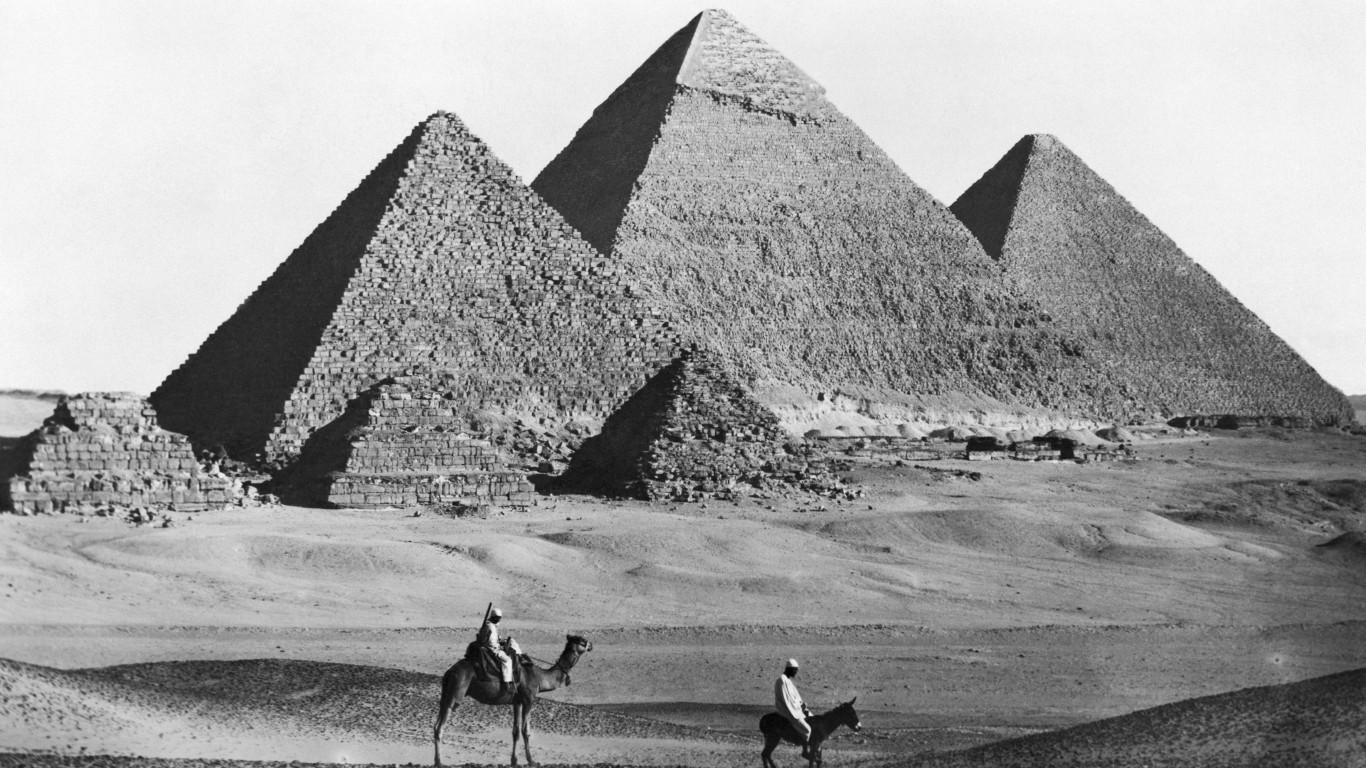

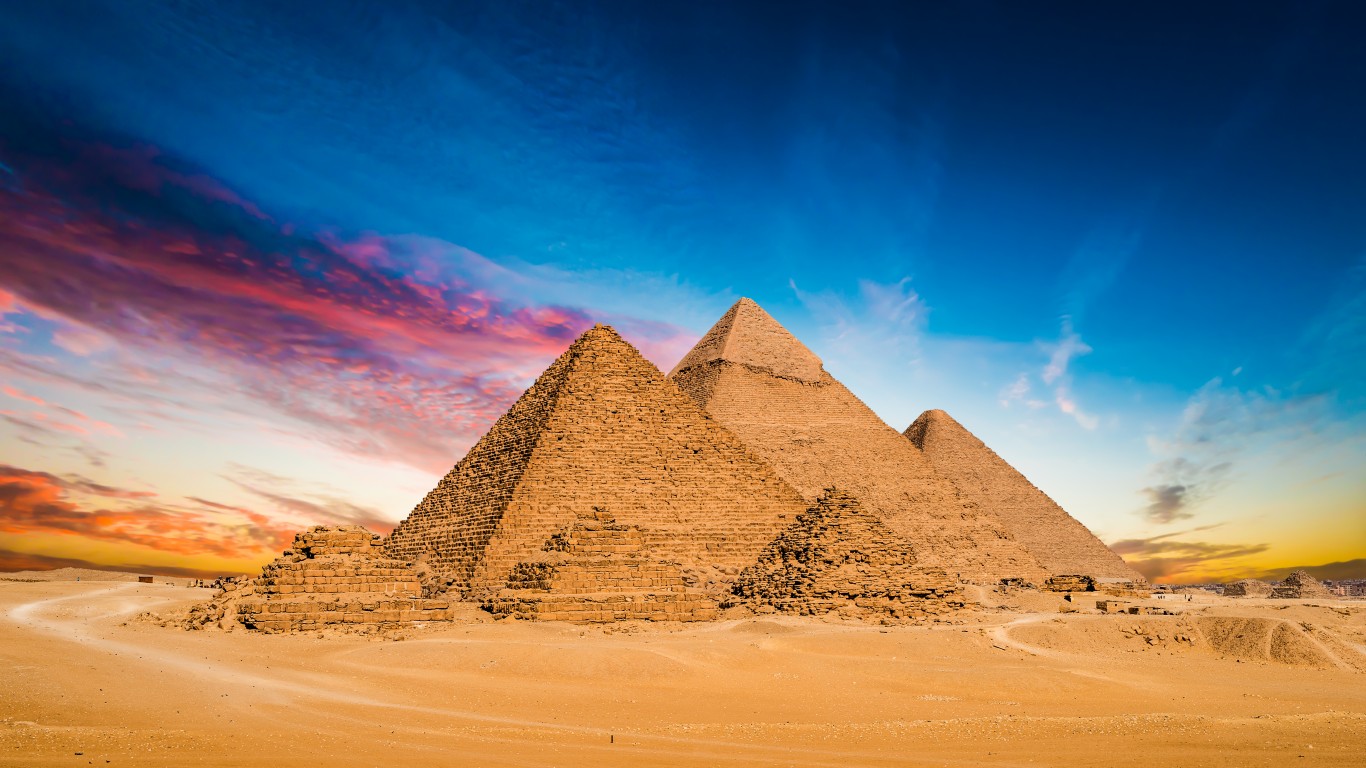
43. Egyptian Empire
> Dates: 1550-1077 B.C.
> Span: 473 years
The Egyptian Empire appeared during the period of the New Kingdom ( 1570-1069 B.C.). It extended from modern-day Syria in the north to Sudan in the south, Jordan in the east, and Libya in the west.

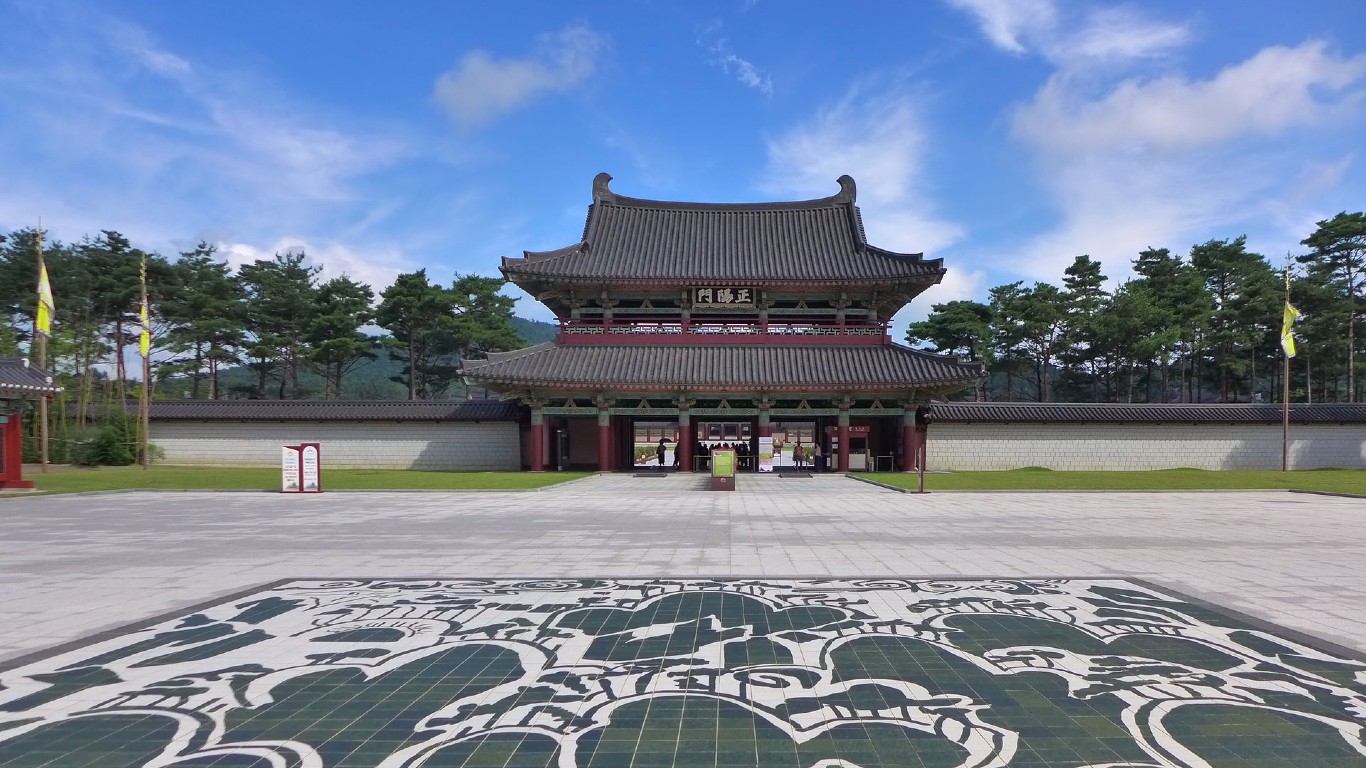
42. Goryeo
> Dates: 918-1392
> Span: 474 years
Korea derives its name from the dynastic kingdom of Goryeo, also is known as Koryŏ. The country was unified by a notable army general, Wang Geon, who named the nation Goryeo. The kingdom became known for its printing, architecture, and ceramics.
[in-text-ad-2]
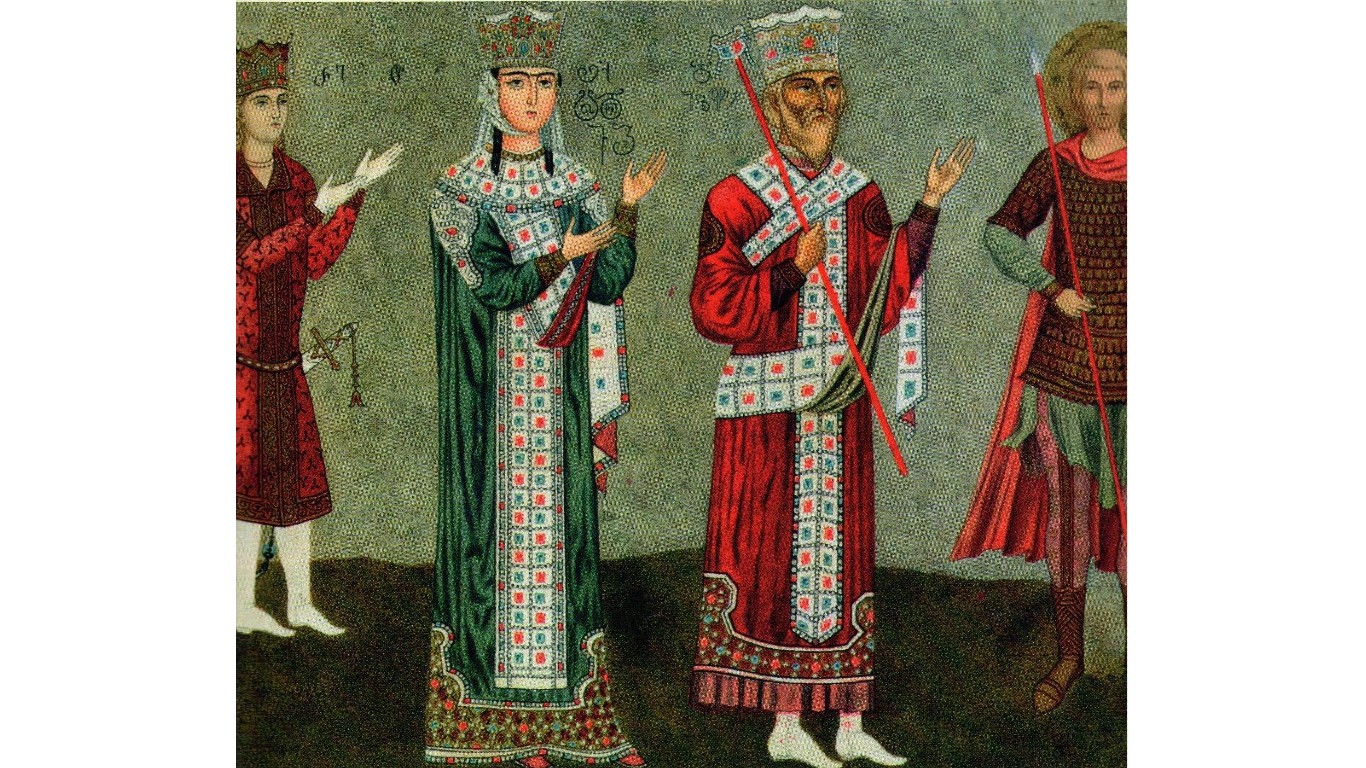

41. Georgian Empire
> Dates: 1008-1490
> Span: 482 years
The Kingdom of Georgia, also known as the Georgian Empire, was a Eurasian monarchy with origins in medieval times, reaching its height between the 11th and 13th centuries. The empire was weakened by invasions by the Mongols and disintegrated from continuous attacks by the Ottoman Empire in the late 15th century.
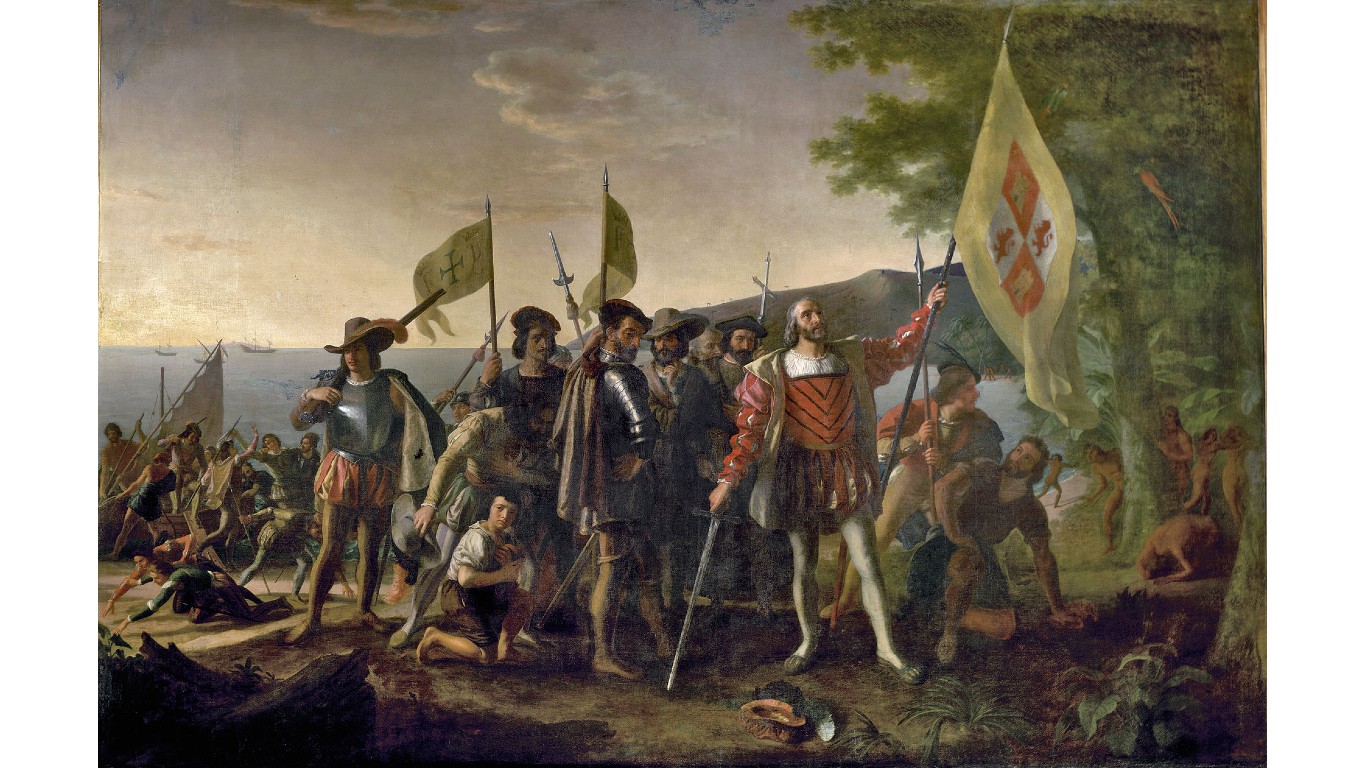

40. Spanish Empire
> Dates: 1492-1976
> Span: 484 years
Spain was at the forefront in the Age of Discovery, extending its dominion across the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, after expelling the Moors and Jews in 1492. The empire’s decline accelerated during the 19th century because of the Napoleonic Wars and the Spanish-American War. It is considered to have lasted until 1975, with the demise of Generalissimo Franco’s dictatorship and the reinstatement of the monarchy.
[in-text-ad]
39. Kachari Kingdom
> Dates: 1336-1832
> Span: 496 years
The Kachari Kingdom, known as Dimasa Kingdom in medieval times, was located in northeastern India. Though the first Kachari king established his rule in the early ninth century, Kachari rulers first established an independent kingdom, based in Assam, in 1336. The British annexed the kingdom in the early 19th century.

38. Bornu Empire
> Dates: 1397-1893
> Span: 496 years
An immediate successor to the earlier Kanem-Bornu Kingdom, which dated from the eighth century, the Bornu Empire encompassed parts of present-day Chad, Nigeria. One of the longest-lasting empires in Africa, it was known for its stability and safe and prosperous cities.
37. Funan
> Dates: 50-550
> Span: 500 years
Funan was the first significant Hindu state in Southeast Asia. The name might come from the Chinese word “pnom,” meaning “mountain.” The empire consisted of parts of present-day Vietnam, Thailand, and Cambodia. The culture was heavily influenced by that of India.
[in-text-ad-2]
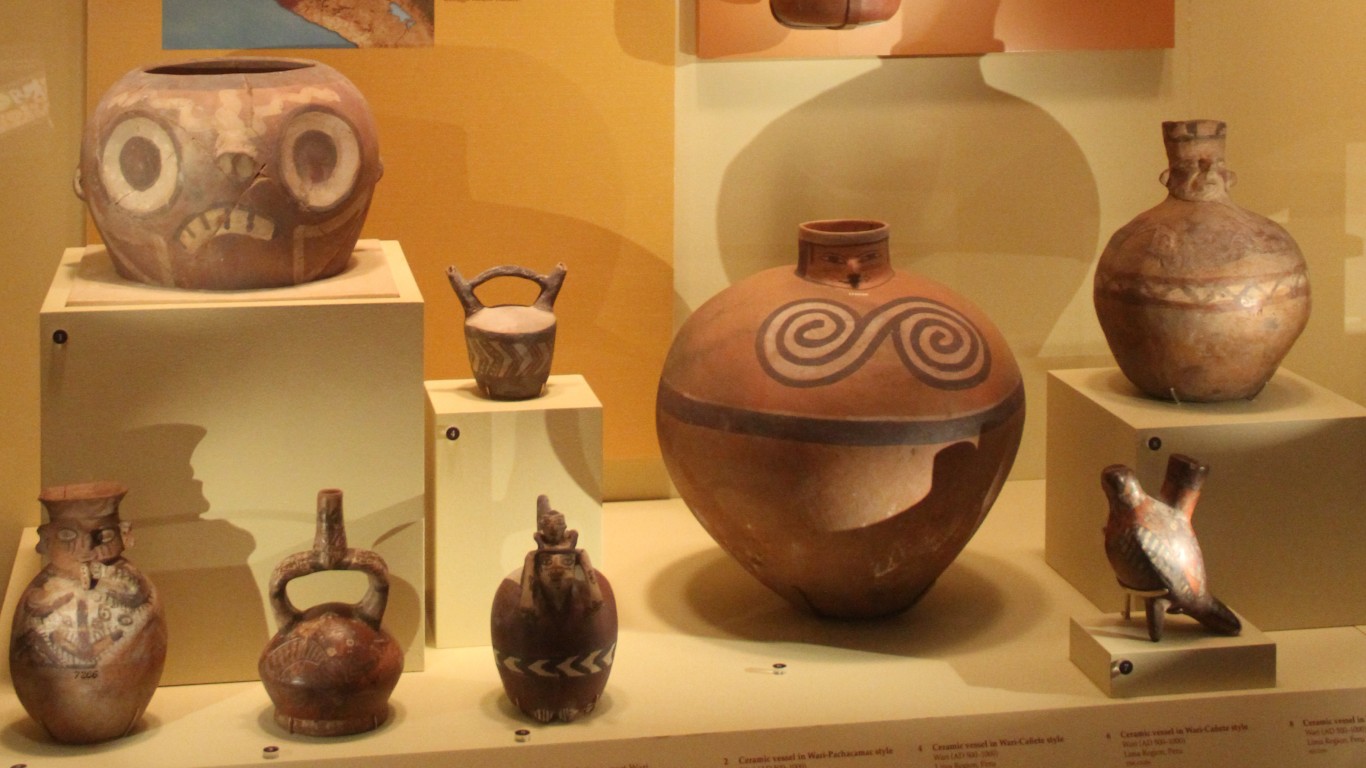

36. Wari Empire
> Dates: 500-1000
> Span: 500 years
One of the longest-lasting empires on this list was in South America. The Wari civilization flourished in the coastal and highland sections of ancient Peru – including parts of modern-day Peru, Chile, and Bolivia – for 600 years. Its sophisticated administrative and road-building skills, as well as its artistic ability, influenced the Inca civilization.
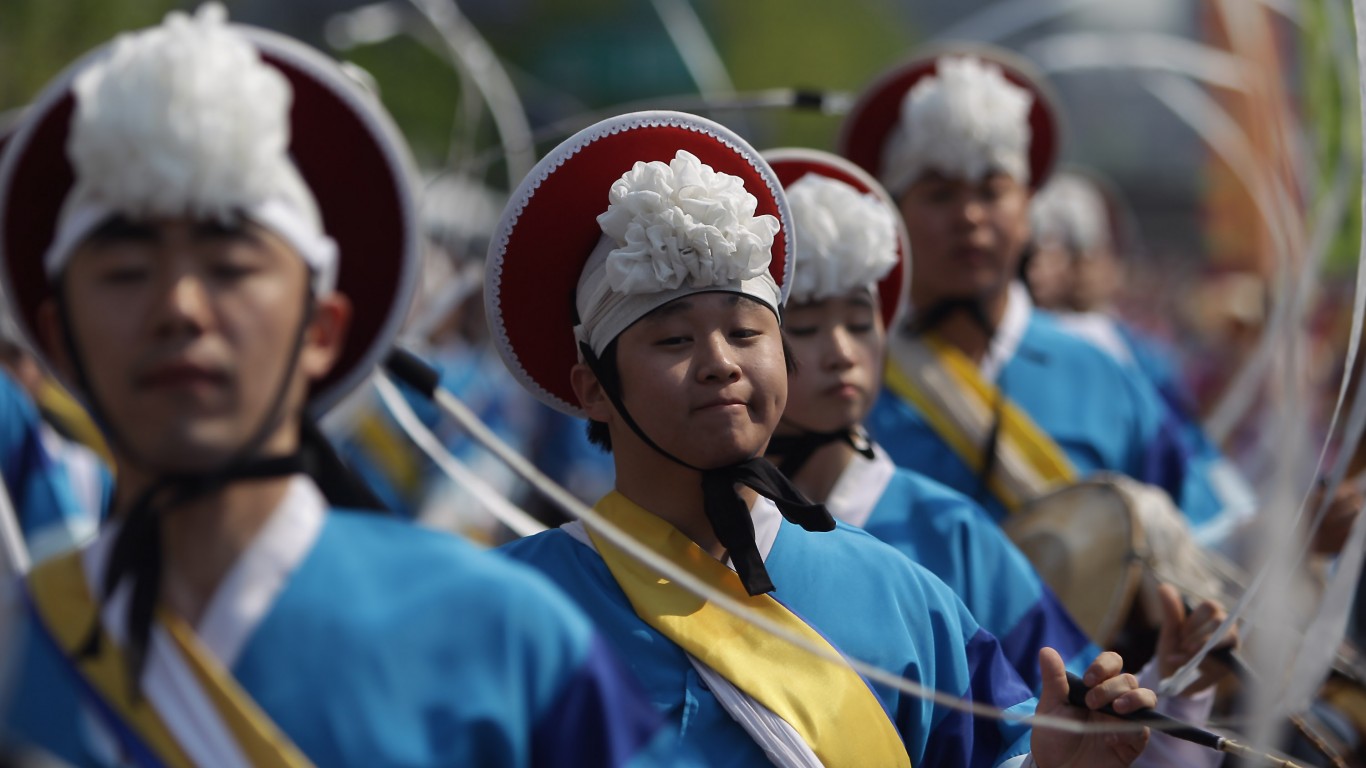

35. Joseon Dynasty
> Dates: 1392-1897
> Span: 505 years
Taejo Lee Sung-gye founded the Joseon (or Chosun) Dynasty in 1392, as a successor to the Goryeo Kingdom. Joseon was the last dynasty in Korea, ending when conflicts with the Chinese and Japanese led the Joseon court to declare the establishment of its successor, the Korean Empire, which endured until the Japanese annexed Korea in 1910.
[in-text-ad]
34. Abbasid Caliphate
> Dates: 750-1258
> Span: 508 years
The Abbasid caliphate was created following the overthrow of the Umayyad caliphate in 750. Unlike the Umayyads, who looked west, the Abbasid caliphate focused on the east, establishing its capital in Baghdad. The caliphate eventually succumbed to the Mongol invasion in 1258.

33. Bruneian Empire
> Dates: 1368-1888
> Span: 520 years
The Bruneian Empire, on the northern coast of Borneo in Southeast Asia, extended through coastal areas of what are now Borneo and the Philippines. It declined in the 17th and 18th centuries and became a British protectorate in the 19th century.
32. Saudeleur Dynasty
> Dates: 1100-1628
> Span: 528 years
The Saudeleur Dynasty unified the people of Pohnpei island, today a part of the Federated States of Micronesia in the South Pacific. Their rule was marked by a strong and sometimes tyrannical centralized form of government.
[in-text-ad-2]
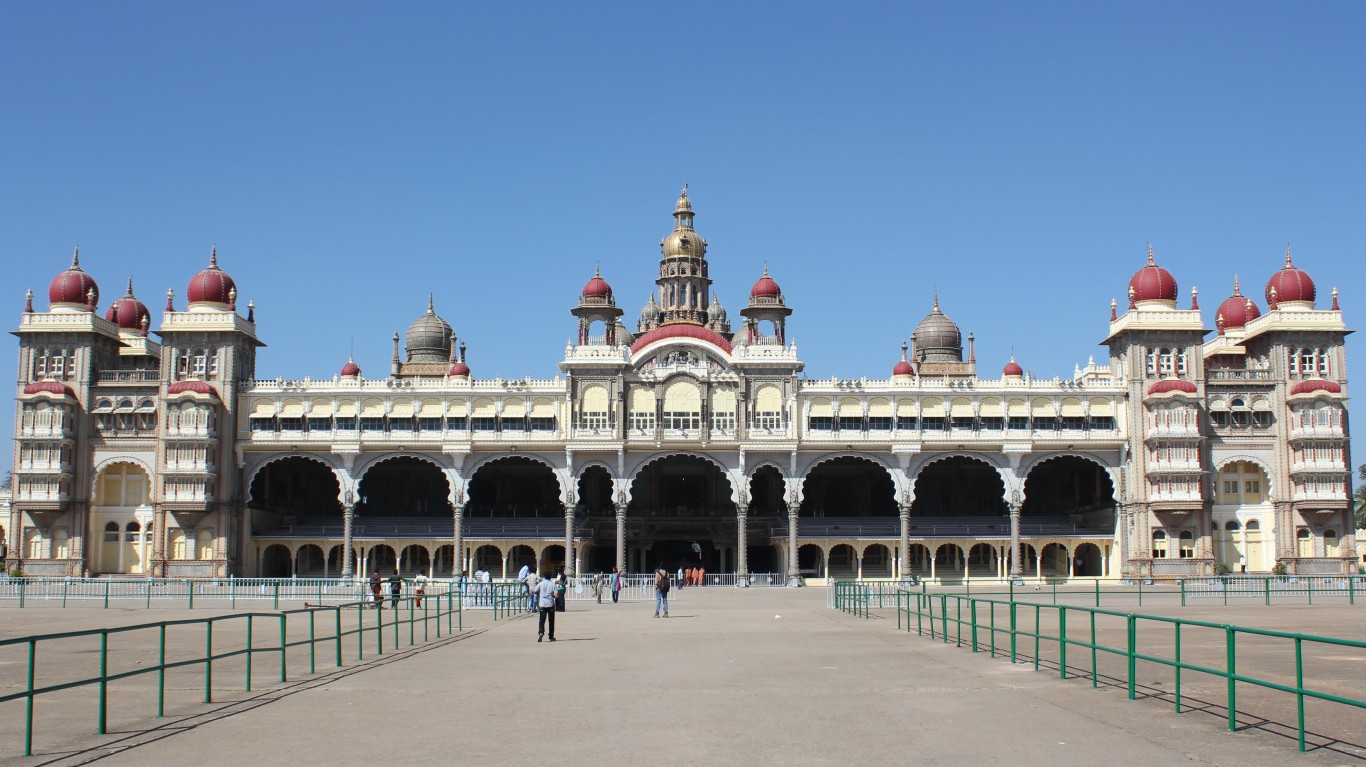
31. Wadiyar Dynasty (Kingdom of Mysore)
> Dates: 1399-1947
> Span: 548 years
The Wadiyars (or Wodeyars), who by tradition trace their ancestry to the god Krishna, ruled the Kingdom of Mysore from its establishment until India won its independence from British rule.

30. Portuguese Empire
> Dates: 1415-1999
> Span: 584 years
Powered by skilled mariners, the Portuguese Empire became the one of the earliest and most extensive of the European colonial empires, with holdings across Africa, Asia, and the Americas. It began in 1415 with the capture of Ceuta in North Africa (today an autonomous city belonging to Spain) and is considered to have lasted until the handover of Macau to China in 1999.
[in-text-ad]
29. Ahom Dynasty
> Dates: 1228-1826
> Span: 598 years
The Ahom Dynasty in what is now the Indian state of Assam was established in the early 13th century by Sukaphaa and it would last more than 600 years. The Ahom people showed local groups how to cultivate wet rice, a technological leap forward. The dynasty became weakened by continuous attacks by the Mughals and then the Burmese before the British took control of the kingdom in the early 19th century.
28. Srivijaya Empire
> Dates: 683-1293
> Span: 610 years
The Srivijaya Empire was a seafaring and commercial kingdom located in present-day Indonesia. The empire established trade relations with India and China and was also a religious center and was a stop for Chinese Buddhist pilgrims going to India. Considered to have lasted in some form until an invasion by the Japanese king in the late 13th century, it was largely forgotten, even in Indonesia, until a French scholar rediscovered its history in the 1920s.
27. Armenian Empire
> Dates: 321 B.C.-428
> Span: 618 years
Though some scholars trace its origins to the Hayasa-Azzi culture, dating back to around 1500 B.C., the ancient Armenian Empire is generally considered to have begun with the birth of the Orontid Dynasty. Because of its geographic location in south Caucasus, the Armenians sometimes struggled with the larger and more ambitious Parthian and Roman empires.
[in-text-ad-2]

26. Ottoman Empire
> Dates: 1299-1922
> Span: 623 years
The Ottoman Empire sprang from a strip of land in present-day Turkey in the 13th century. Powered by a well-trained army, the empire extended its influence over Asia Minor and into the Balkans. It failed to conquer the rest of Europe, and overextension, internal conflicts, and its failure to keep pace with technological and economic changes doomed the empire in the early 20th century.

25. Khmer Empire
> Dates: 802-1431
> Span: 629 years
The Khmer Empire dominated what is now Cambodia, Thailand, Laos, and southern Vietnam for more than 600 years. The Khmer people developed a reputation as skilled and prolific builders of temples, canals, and highways. Their most famous and impressive legacy is the massive 1,000-year-old temple of Angkor Wat, spread over almost 500 acres.
[in-text-ad]
24. Sultanate of Gowa
> Dates: 1300-1945
> Span: 645 years
The Sultanate of Gowa was located in South Sulawesi in what is modern-day Indonesia. Because of its strategic position, it was an important shipping route and trade center. The sultanate was eventually taken over by the Dutch in the 20th century.
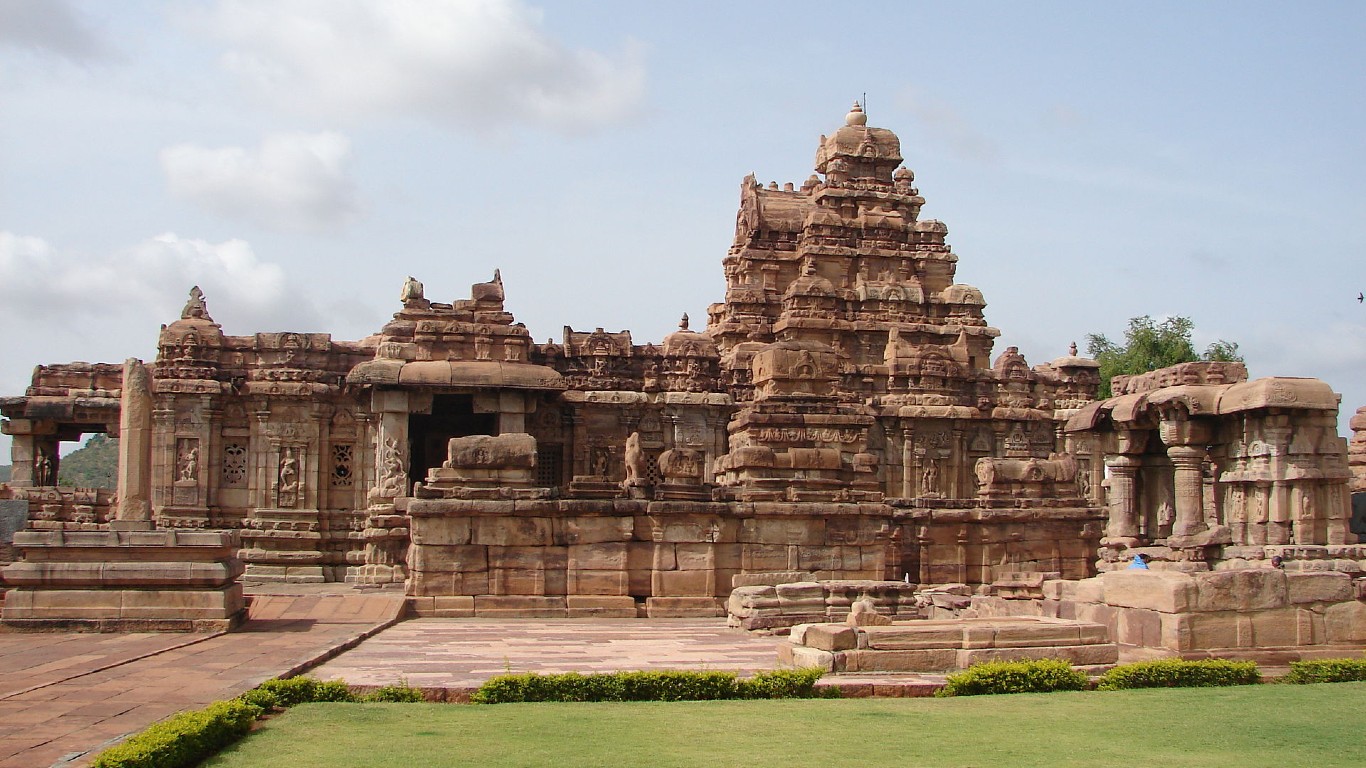
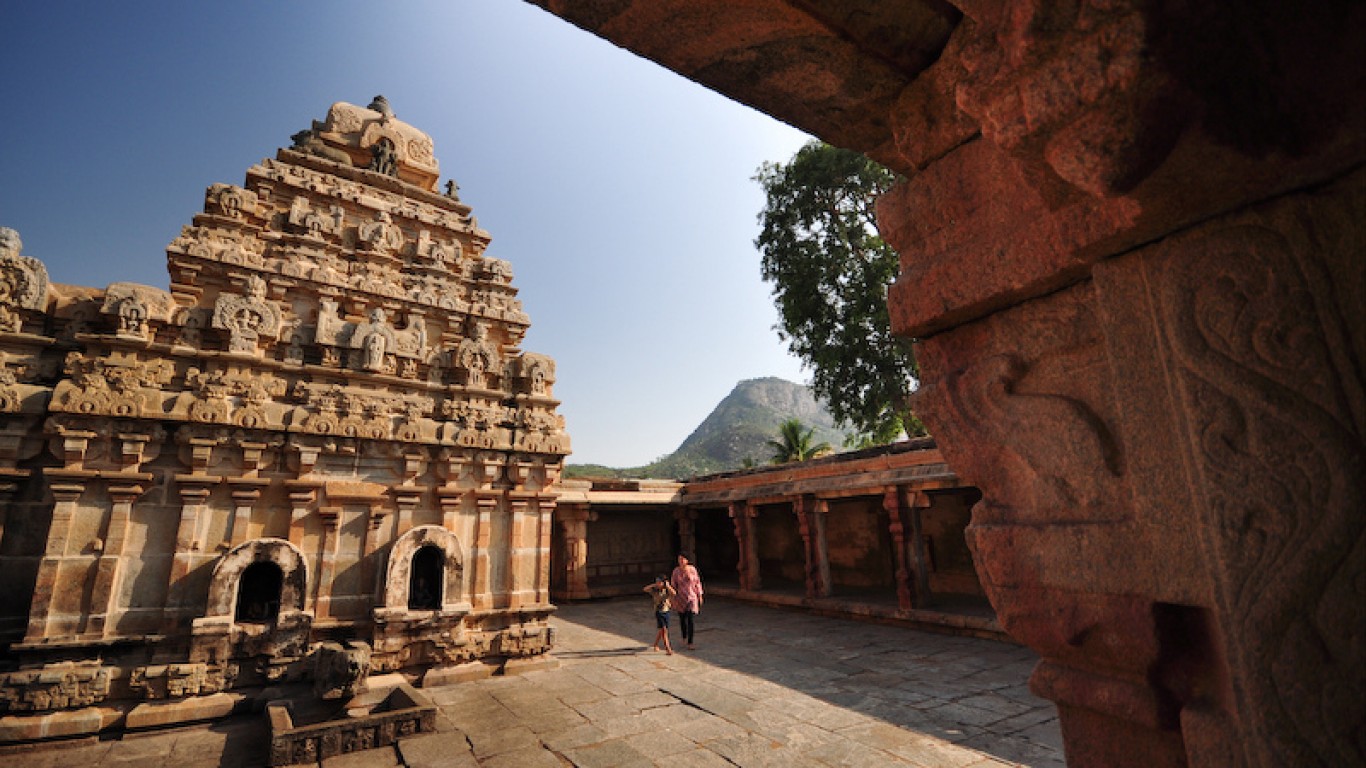
23. Chalukya Dynasty
> Dates: 543-1200
> Span: 657 years
The Chalukya rulers dominated vast expanses of central and southern India for more than 650 years. They ruled as three closely related but distinct dynasties. The Chalukyas incorporated aspects of the cultures of both southern and northern India

22. Carthaginian Empire
> Dates: 814-146 B.C.
> Span: 668 years
History buffs remember Carthage and the great general Hannibal from the Second Punic War with Rome (the Third Punic War, waged more than 30 years after his death led to the demise of Carthage). The Carthaginian Empire was a collection of Phoenician city-states that ringed portions of the Mediterranean encompassing parts of North Africa, modern-day Spain, Sardinia, Corsica, and portions of Sicily.
[in-text-ad-2]
21. Paekche Kingdom
> Dates: 18B.C.-AD660
> Span: 678 years
The Paekche (or Baekje) Kingdom was one of the three major kingdoms that ruled Korea for many centuries. The Paekche dominated the southwestern part of the peninsula. Rivaled by Korea’s other two kingdoms of the era, those of Silla (swee No. 8) and Goguryeo, it was culturally influenced by Japan, its ally.

20. Kingdom of Tondo
> Dates: 900-1587
> Span: 687 years
The Tondo Kingdom, in the Philippines, had its capital north of the Pasig River on the island of Luzon. Tondo was influenced by Hindu and Buddhist cultures from India. It formed diplomatic relations with China in the 14th century, and strong trade and cultural connections between the two developed.
[in-text-ad]

19. Kanem-Bornu Empire
> Dates: 700-1387
> Span: 687 years
The Kanem-Bornu Empire was one of the longest-lasting African empires. At its height, it covered 300,000 square miles in what are now Chad, Niger, northeastern Nigeria, Libya, northern Cameroon, and parts of Sudan. It was founded by the Zaghawa people, who were skilled in iron technology and horsemanship. It was succeeded by the Bornu Empire (see No. 39).

18. Sultanate of Tidore
> Dates: 1274-1967
> Span: 693 years
The Sultanate of Tidore was an Islamic kingdom that ruled eastern Indonesia. Its main rival was the Sultanate of Ternate (see No. 14). Tidore allied itself with Portugal and Spain in the 16th century, remaining independent – though it had to fight off Dutch interference in the 17th and 18th centuries.
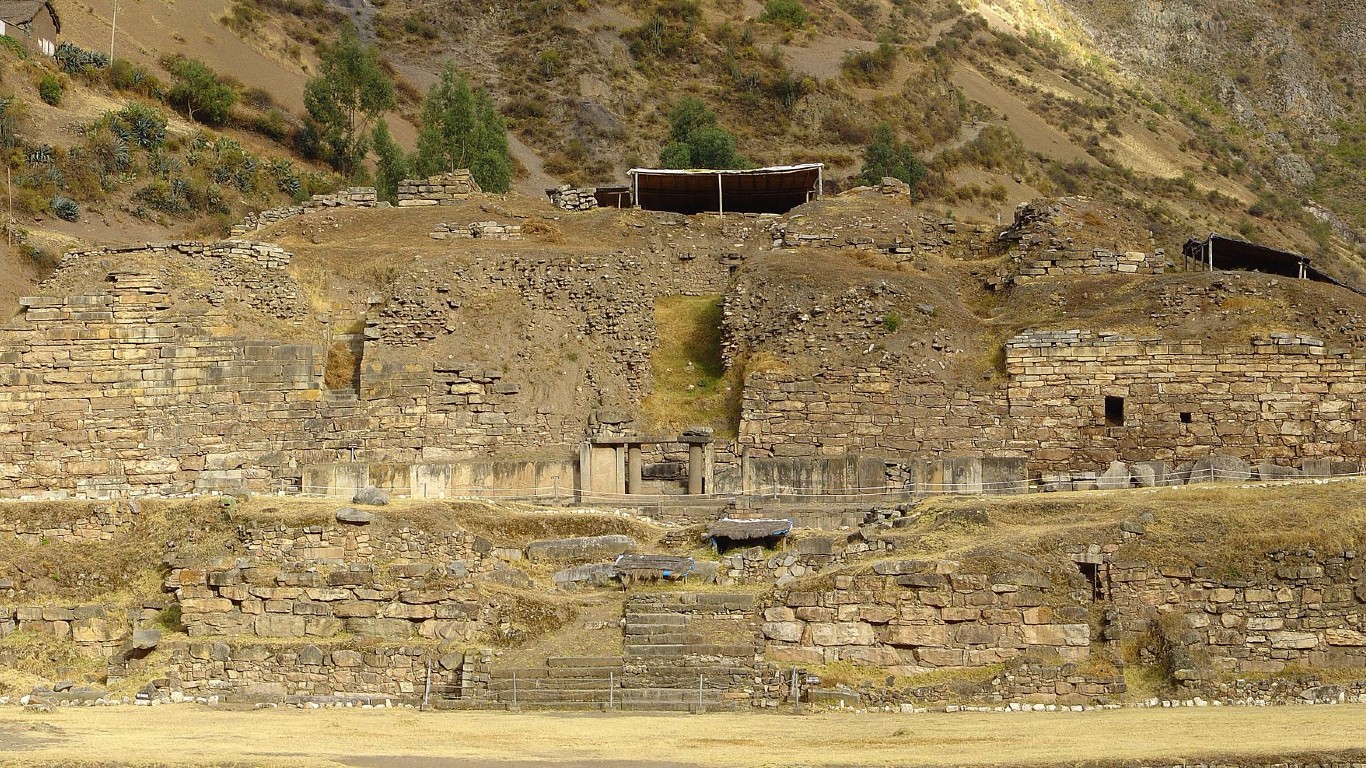
17. Chavín Empire
> Dates: 900-200 B.C.
> Span: 700 years
The pre-Columbian Chavin Empire was located on the coast of Peru. It was a precursor to the empire of the Incas. The empire takes its modern-day name from the settlement of Chavín de Huántar, today a UNESCO World Heritage site, which was occupied as early as 1200 B.C. and which the Chavin people subsequently occupied.
[in-text-ad-2]

16. Republic of Genoa
> Dates: 1096-1797
> Span: 701 years
The city-state of the Republic of Genoa, on the Mediterranean coast in northwestern Italy, near today’s French border, lasted more than 700 years. Genoa gained wealth and power from its maritime tradition – Christopher Columbus is believed to have been Genoese – and gained favor from the Catholic Church by participating in the Crusades. Its political system was dominated by a small group of families.

15. Ethiopian Empire (Kingdom of Abyssinia)
> Dates: 1270-1974
> Span: 704 years
The Ethiopian Empire, or Kingdom of Abyssinia, in what is modern-day Ethiopia, lasted for more than 800 years. It was established by the kings of the Solomonid dynasty, who claimed lineage to King Solomon. It was a Christian kingdom built on trade and conquest. Though it was invaded by Italy in the early 20th century, the kingdom was one of just two African states (along with Liberia) never to be officially colonized by a European power. It endured until the monarchy was overthrown by a coup.
[in-text-ad]
14. Sultanate of Ternate
> Dates: 1258-present
> Span: 763 years (as of 2021)
The Sultanate of Ternate was one of the earliest Muslim kingdoms in Asia. At its height, it encompassed the eastern part of Indonesia and a part of the southern Philippines. Ternate, a rival of another major Indonesian power, the Sultanate of Tidore (see No. 18), was known as a producer of cloves. It exists to this day, as does the dynastic line of its 13-century founder, Baab Mashur Malamo, but it has no political power.
13. Zhou Dynasty
> Dates: 1046-256 B.C.
> Span: 790 years
One of the oldest of the empires on this list, the Zhou Dynasty is also the longest-lasting Chinese dynasty. It is split into two eras: Western Zhou (1046-771 B.C.) and Eastern Zhou (771-256 B.C). The Shang Dynasty preceded the Zhou, and the Zhou adopted the Shang concept of the Mandate of Heaven, the concept that a monarch was divinely appointed. Besides advancements in metallurgy and a flowering of the arts, the dynasty was home to some of China’s most famous thinkers and philosophers, including Confucius and Sun-Tzu.
12. Aksumite Empire
> Dates: 150-940
> Span: 790 years
The Aksumite Empire, in northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, developed a trade network with India and the Mediterranean. The empire benefited from a change in trading routes that favored commerce through the Red Sea. The Aksumites controlled the harbor of Adulis, which became the main port for the export of ivory, incense, gold, and live animals.
[in-text-ad-2]

11. Holy Roman Empire
> Dates: 962-1806
> Span: 844 years
The Holy Roman Empire – Voltaire famously joked that it was neither holy, Roman, nor an empire – was a multi-ethnic domain encompassing many parts of western and central Europe and ruled first by Frankish monarchs and later by German kings. It was a Christian empire (Voltaire notwithstanding) that brought elements of the old Roman Empire into its sphere of influence. It lasted until 1806 when Francis II, the last Holy Roman emperor, abdicated.

10. Tu’i Tonga Empire
> Dates: 950-1865
> Span: 915 years
Centered on the South Pacific island of Tongatapu, the Tu’i Tonga Empire began extending its hegemony throughout Oceania in the 10th century. The peak of its powers ran from 1200 to 1500. Tu’i Tonga was the name given to the empire’s ruler, and the empire dissolved when the title was abolished in 1865.
[in-text-ad]

9. Ghana Empire
> Dates: 300-1240
> Span: 940 years
Despite its name, the Ghana Empire is not linked with present-day Ghana. It was located in parts of what are now southern Mauritania and Mali, with the Sahara desert to the north and rainforests to the south. Buoyed by rich deposits of iron, gold, and copper and access to the Niger and Senegal Rivers, the empire grew rich. Competing trade routes to the east and a weakened central government led to its decline.

8. Silla Kingdom
> Dates: 57 B.C.-935
> Span: 992 years
The Silla Kingdom was another Korea-based empire. It originated in southeastern Korea and eventually conquered the whole peninsula. The empire was known for its centralized government and strict hierarchical society. It also is famous for its splendid gold crowns.
7. Byzantine Empire
> Dates: 395-1453
> Span: 1058 years
The Byzantine Empire was founded by Constantine I, who established Constantinople as his capital after the Roman Empire split into western and eastern (Byzantine) halves. The Byzantine Empire included territory in Italy, Greece, the Balkans, Asia Minor, and North Africa. It was influenced by Greek and Roman culture but was infused with Middle Eastern culture as well. The empire fell in 1453 when the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II conquered Constantinople.
[in-text-ad-2]

6. Republic of Venice
> Dates: 697-1797
> Span: 1100 years
Today’s Venice may be a tourist magnet, but it was a force to be reckoned with in medieval times. Also known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice, the city-state exercised influence that stretched south into the Italian peninsula and over Mediterranean and Aegean islands such as Cyprus and Crete. It fought and traded with Muslims and the Republic of Genoa. One of its most famous residents was Marco Polo.
5. Kingdom of Kush
> Dates: 1070 B.C.-350
> Span: 1420 years
The Kingdom of Kush was located in Nubia in northern Africa, a region considered to have been one of the cradles of civilization. The area was under Egyptian rule between 1150 and 1070 B.C., at which time the Kushite kingdom was founded. Kush began to decline because of overuse of land and it fell following attacks from Egypt and the Aksumites.
[in-text-ad]
4. Chera dynasty
> Dates: 430 B.C.-1102
> Span: 1532 years
The Chera dynasty was one of three ancient Tamil dynasties, and Chea held sway over South India for more than 1,500 years. They were prodigious traders, exchanging goods with people from Egypt, Rome, Greece, Phoenicia, Arabia, Mesopotamia and Persia.
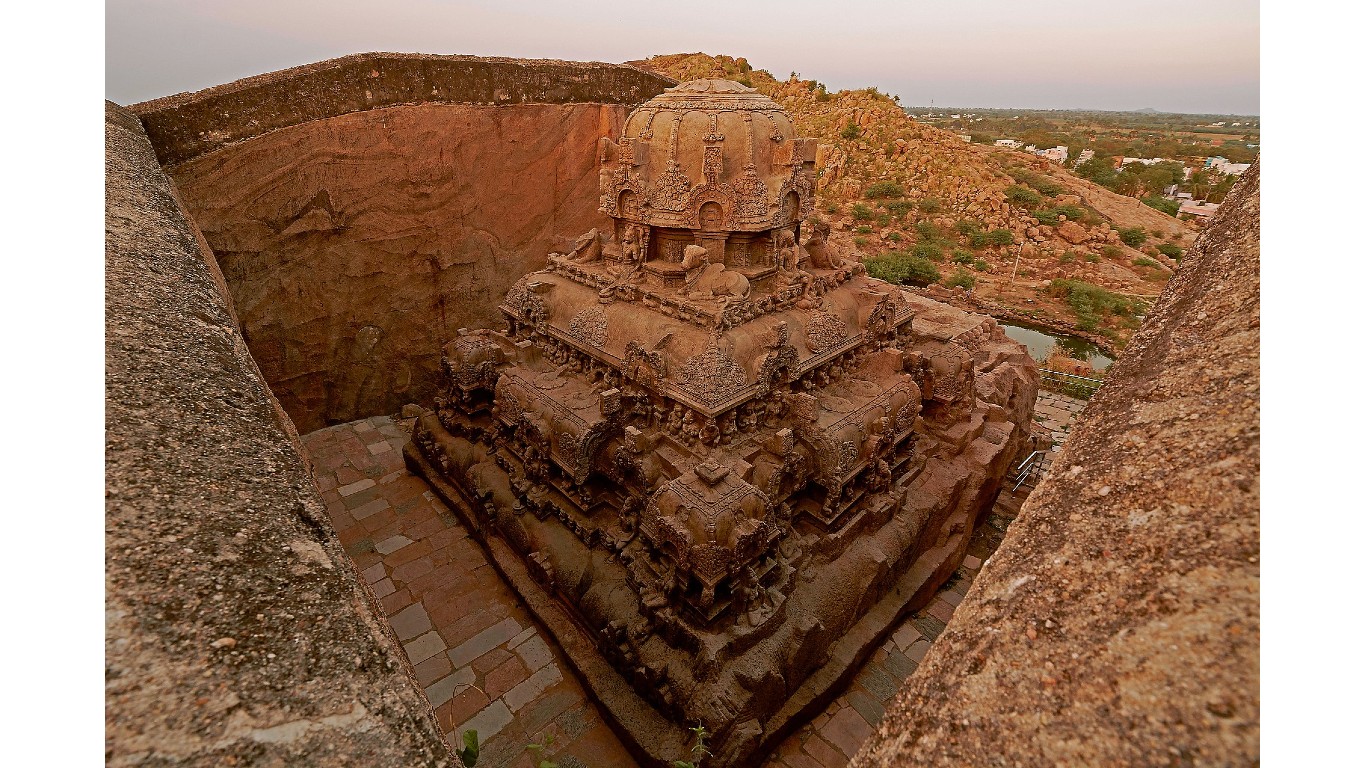
3. Chola Empire
> Dates: 301 B.C.-1279
> Span: 1580 years
The longest-lived of the empires originating in what is now southern India, the Chola dynasty was composed of South Indian Tamil kings. Their empire extended from the Vaigai River in the south to what is now Kanchipuram in the north. The Cholas were able administrators and developed good irrigation systems.

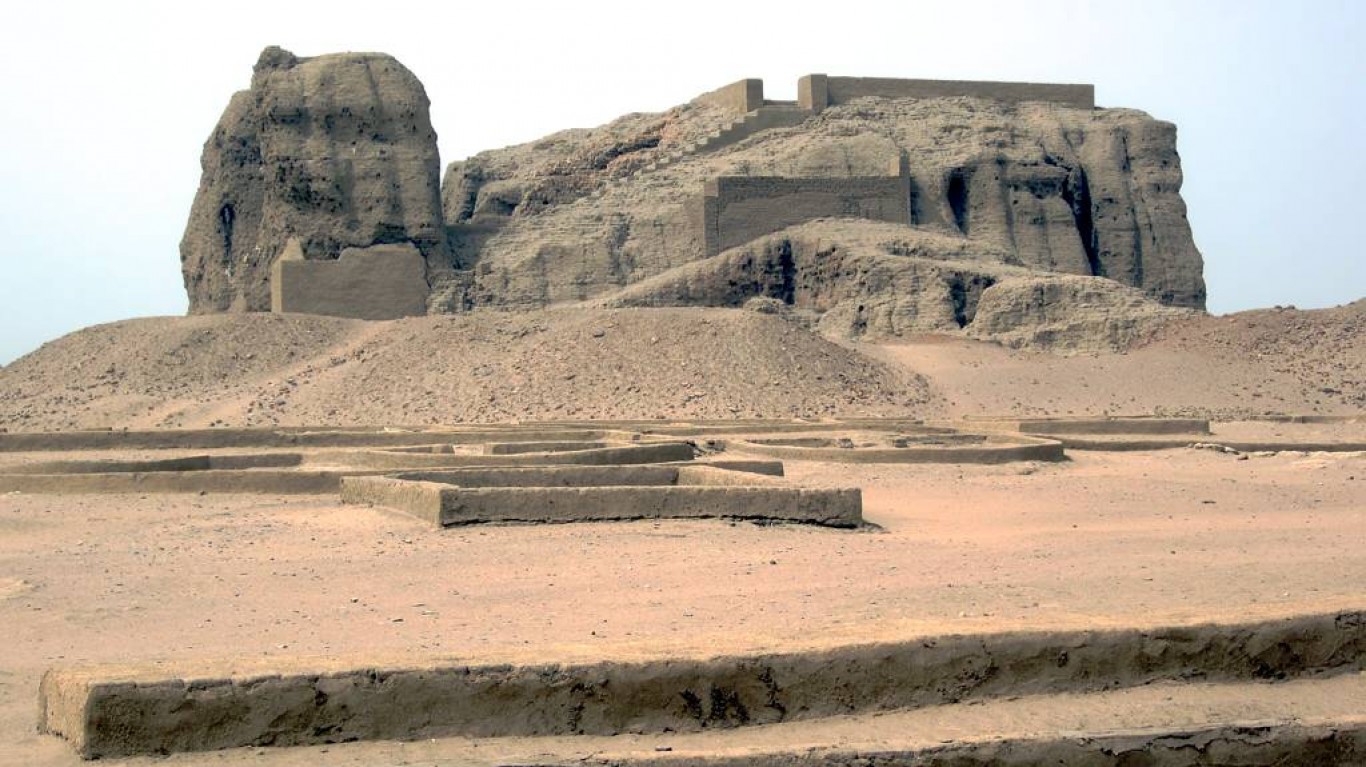
2. Assyria
> Dates: 2500-605 B.C.
> Span: 1895 years
The Assyrian Empire, made up of city-states shielded by high walls, stretched from Egypt in the west to present-day Iran in the east, a reach that included the Fertile Crescent. The empire, whose origin predates that of virtually all other empires, was among the earliest true military powers.
[in-text-ad-2]
1. Pandyan Dynasty
> Dates: 580 B.C.-1345
> Span: 1925 years
This is the world’s longest-lasting empire. Though there were Pandyan kings in earlier centuries, the first Pandyan dynasty is considered to have begun around the early sixth century B.C. Around 960, the Pandyans were driven into exile in Sri Lanka by the Chola (see No. 3), but the empire slowly revived - in the early 1200s, Marco Polo identified the Pandyan dynasty as the world’s richest empire – lasting until a two-decade period of wars and invasions culminated in its dissolution.
It’s Your Money, Your Future—Own It (sponsor)
Are you ahead, or behind on retirement? For families with more than $500,000 saved for retirement, finding a financial advisor who puts your interest first can be the difference, and today it’s easier than ever. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three fiduciary financial advisors who serve your area in minutes. Each advisor has been carefully vetted and must act in your best interests. Start your search now.
If you’ve saved and built a substantial nest egg for you and your family, don’t delay; get started right here and help your retirement dreams become a retirement reality.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.


 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.

 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.

 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.











