Most people love being out in the sun. It provides warmth and a chance to avoid wearing 20 layers of clothes outside. But sunshine offers more than just warmth and mental well-being — it offers a variety of physical health benefits.
There is no doubt that exposure to the sun should not be excessive as the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays are a major risk factor of skin cancer and premature aging. Neglecting protective measures like applying sunscreen is just one of at least 20 “harmless” habits that is aging you faster than you can imagine.
Dermatologists recommend daily use of sunblock lotion, even in the winter.
People don’t have to be out in the sun all day to benefit from it. Most people need about 15 minutes to gain the benefits. And it’s best to avoid it between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., especially in the summer when the UV rays are strongest.
A little sunlight every day has many advantages. So don’t deny yourself of enjoying the sun — as long you protect yourself properly.
Click here to read about the 14 benefits you never knew sunshine offered
To compile a list of 14 possible health benefits of exposure to sunlight, 24/7 Tempo reviewed research and studies examined by the National Institutes of Health and other organizations about the effects of sunlight and vitamin D on both people’s physical and mental health.
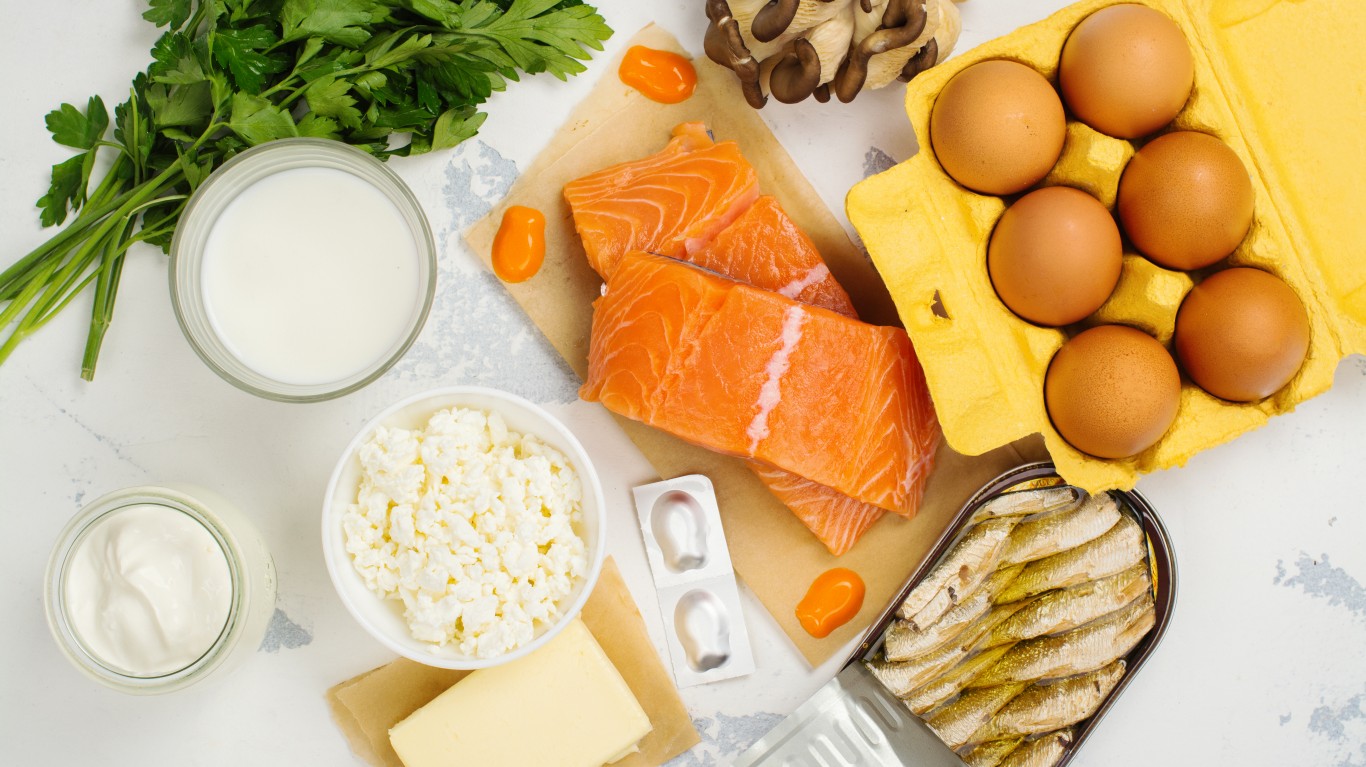

1. It’s a great source of vitamin D
Vitamin D is called the “sunshine” vitamin for a reason — your body produces it naturally when the skin is exposed to sunlight. You can also get it from supplements, and certain fortified foods such as milk and cereal. Vitamin D is vital as it helps the body absorb and retain calcium.
Half of the world’s population lacks enough vitamin D, according to the National Institutes of Health. This is largely due to lifestyle and environmental factors such as reduced exposure to sunlight. People with dark skin are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency because the pigment melanin in the skin doesn’t absorb as much ultraviolet B light, reducing the skin’s ability to make vitamin D. Lack of vitamin D is one of several dangerous conditions experts have linked to heart disease.
[in-text-ad]

2. It may lower the risk of dementia
Because sunlight is needed for the body to make vitamin D, it plays an important role in lowering the risk of brain health decline. A link between vitamin D deficiency and higher risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people was established in a 2014 study by the University of Exeter in England. People with well below the recommended amount of vitamin D — at least 50 nmol/L — were more than twice as likely to develop dementia and Alzheimer’s. Researchers believe regular physical activity, frequent social and cognitive engagement, and a healthy diet — specifically regular consumption of this one common vegetable — can help reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s.

3. It puts you in a better mood
Serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps transmit brain signals, is often referred to as the “happy” hormone. Serotonin is usually produced by the brain during the day after exposure to daylight. Higher serotonin levels have been linked to more positive moods. Seasonal affective disorder, also known as the “winter blues,” has been associated with lower levels of serotonin, possibly the result of the shorter days during the winter and of people not spending much time outdoors. A study of people with depression found that being exposed to less sunlight was linked to worse cognitive function.

4. It acts like an anti-inflammatory
Sunlight is what helps the body produce vitamin D, and some evidence suggests it may help tame inflammation, which has been linked to numerous health problems, including heart disease and depression.
A 2017 study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that exposure to sunshine may help reduce inflammation because nitric oxide, a chemical that helps increase circulation, was released into the bloodstream.
[in-text-ad-2]

5. It may delay onset of diabetes
There is some evidence that persons with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and those at risk of developing diabetes or metabolic syndrome have lower levels of vitamin D. Some research suggests that an adequate intake of vitamin D may prevent or delay the onset of the conditions, and may also reduce complications such as heart disease and poor function of the kidneys. Diabetes affects how the body turns food into energy — these are the 10 warning signs you might have the disease.
6. It keeps the bones healthy
Vitamin D and calcium work hand in hand to keep the bones strong. Almost all of the calcium in the body is found in the bones and teeth, and we lose it through our skin, nails, hair, sweat, and urine. We get it back by eating foods rich in the mineral, but we need vitamin D to absorb it. Lack of vitamin D may result in lack of calcium, which may result in weaker bones that are more likely to break as people get older.
[in-text-ad]
7. It may lower the risk of multiple sclerosis
Half a century ago, epidemiologist Don Acheson from Ireland famously suggested the incidence of multiple sclerosis may be related to the location of the patients and daylight hours there. Since then, the effects of sunshine exposure, and more specifically, the effects of vitamin D production triggered by sunlight, have been studied in many countries. Research has shown that people who get more sunlight, and thus vitamin D, have a lower risk of multiple sclerosis.
8. It may lower the risk of some cancers
Sunlight triggers the production of vitamin D, which has been linked with reduced risk of certain non-skin cancers such as colon, breast, prostate, and ovarian cancers. Several long-term studies have shown a connection between moderate intake of vitamin D and lower risk of cancer. How exactly vitamin D lowers the risk of cancer is not clear. One theory attributes this to the vitamin’s anti-inflammatory properties, which may inhibit cancer cells. There is one form of cancer that is deadlier than many more common types of the disease.

9. It boosts the immune system
One surprising benefit of sunlight — it surprised even researchers — is the effect it has on the immune system. A 2016 study by Georgetown University Medical Center found that sunlight energizes T cells, which play a central role in the body’s immunity. After coming in contact with sunlight, T cells appear to be faster — getting to the site of the infection quicker and starting the repair process sooner. This may reduce the chance of the infection spreading, which is what makes some infections so scary — these are infections even doctors are afraid of.
[in-text-ad-2]

10. It may help with weight loss
People living in colder climates know you tend to gain weight in winter. While lower levels of activity is one likely reason, another could be less sunlight. Research published in the International Journal of Science suggests that white fat, which is where the body stores energy, shrinks and is released under the sun’s blue light. Lack of sunlight therefore may promote fat storage, contributing to weight gain, according to the lead author of the study.

11. It may lower risk of nearsightedness
Nearsightedness, or myopia, in young adults may be affected by the amount of sunlight exposure, more specifically UVB, according to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association. UVB rays affect the skin’s top layer and cause most sunburns. Separate research has found that longer exposure to moderate sunlight intensity, such as in the shade, was equally effective as being directly under the sun for a short period of time.
[in-text-ad]

12. The heart benefits
Some of the sunlight’s benefits are completely separate from vitamin D. Researchers at the University of Edinburgh suggest that when nitric oxide, a molecule naturally produced by the body, is released in the blood vessels after the skin has been exposed to sunlight. Nitric oxide helps reduce blood pressure, which in turn helps lower the risk of heart disease. (A recent study linked this specific juice with lower risk of heart disease, too.) Participants in the study were exposed to UV rays for 20 minutes. In addition, there is evidence that vitamin D can promote the production of nitric oxide, too.

13. You feel more creative
Maybe next time you need a new source of inspiration, go out to the sun. Some research has suggested that spending time in natural settings may boost creativity. High school students who were working in places with direct sunlight and natural surroundings as opposed to a space with artificial light and mainly furnished with manufactured materials such as drywall and plastic created more innovative collages.

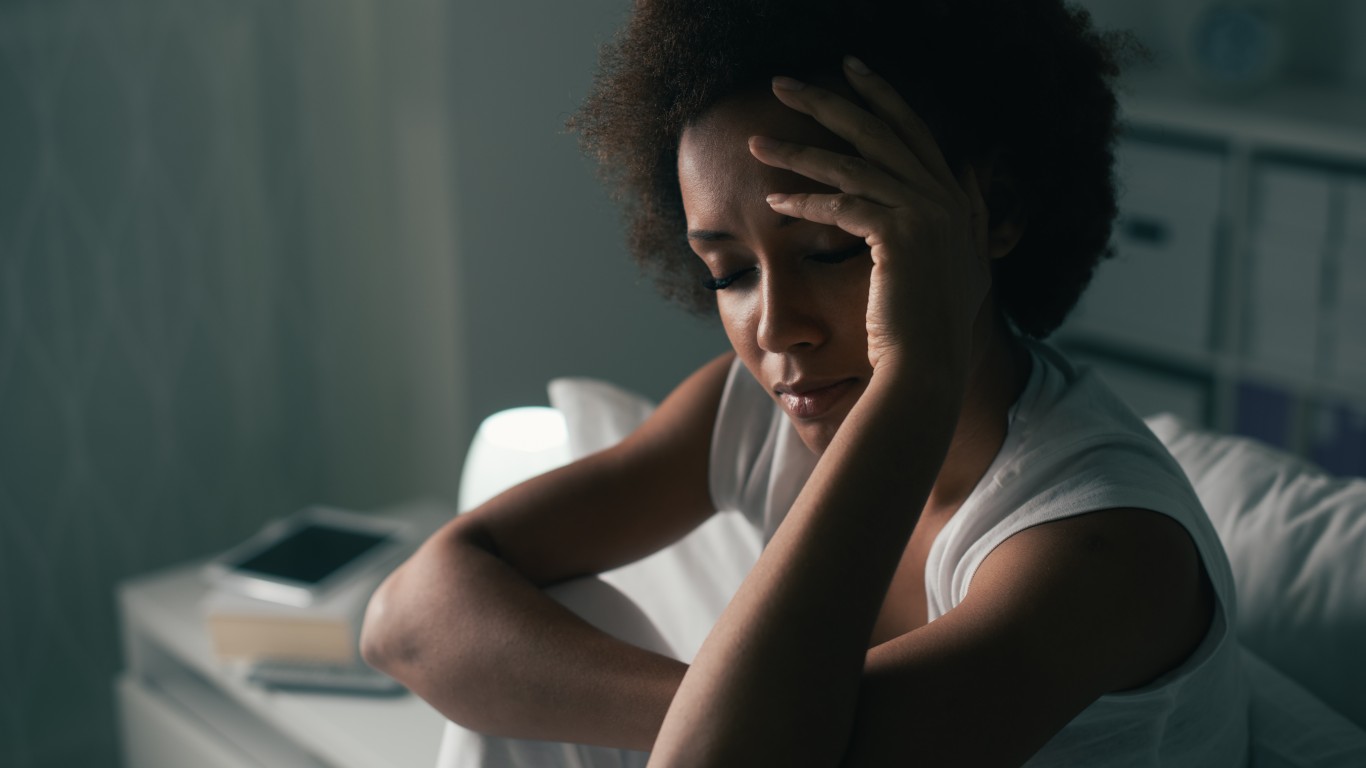
14. You may sleep better
When it gets dark, serotonin, which is produced after exposure to sunlight, is converted to melatonin, which regulates the body’s sleep-wake cycles. In a study from Northwestern Medicine and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, researchers observed 49 people who worked during the day — 27 of them were in windowless workplaces and 22 worked near windows. They found that the latter group of people slept better at night — they received 173% more light and slept an average of 46 minutes more per night. Embracing natural light is just one of 23 things you can do for a better night sleep.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.