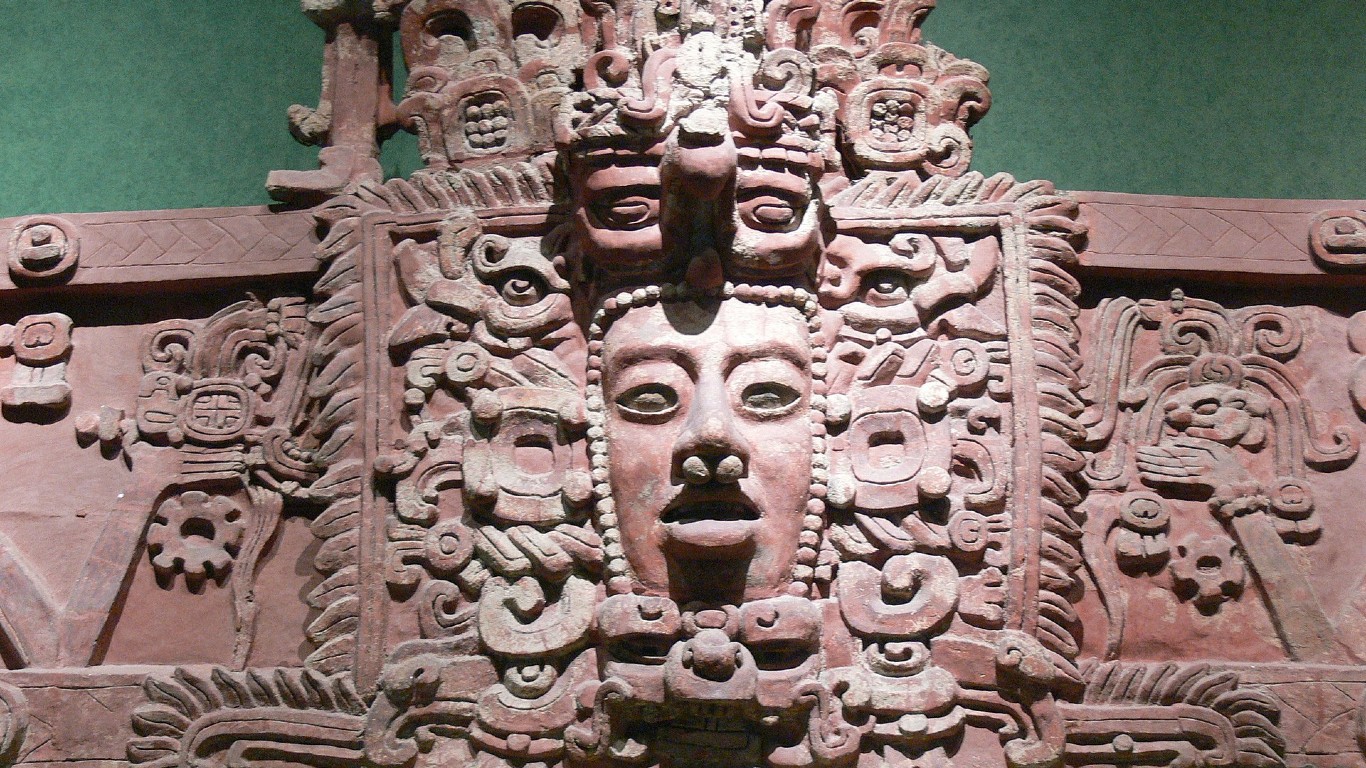
Humans are fascinated by mysteries, whether they’re unsolved crimes, lost treasures, missing persons, vanished civilizations, or strange sounds from outer space. Every year, scientists are able to solve some of these mysteries, yet others only deepen. (These are the most mysterious places on earth.)
24/7 Tempo has compiled a list of some of the most famous unsolved mysteries in the world, drawing information from various encyclopedias and media reports, as well as regional publications. The list is by no means comprehensive. We used editorial discretion to determine which mysteries have captivated the public’s interest the most and/or generated significant media coverage.
Throughout history, whole cultures, including mighty empires, have seemingly vanished into thin air. They’ve often left buildings and artifacts behind, yet without the existence of a recorded history, we may never know what actually caused their decline.
Other disappearances include planes that disappear in mid-air, as it were – since 1948, over 80 planes have been declared missing, according to the Aviation Safety Network – and people who are never seen again. (Here are the 25 most puzzling disappearances in American history.)
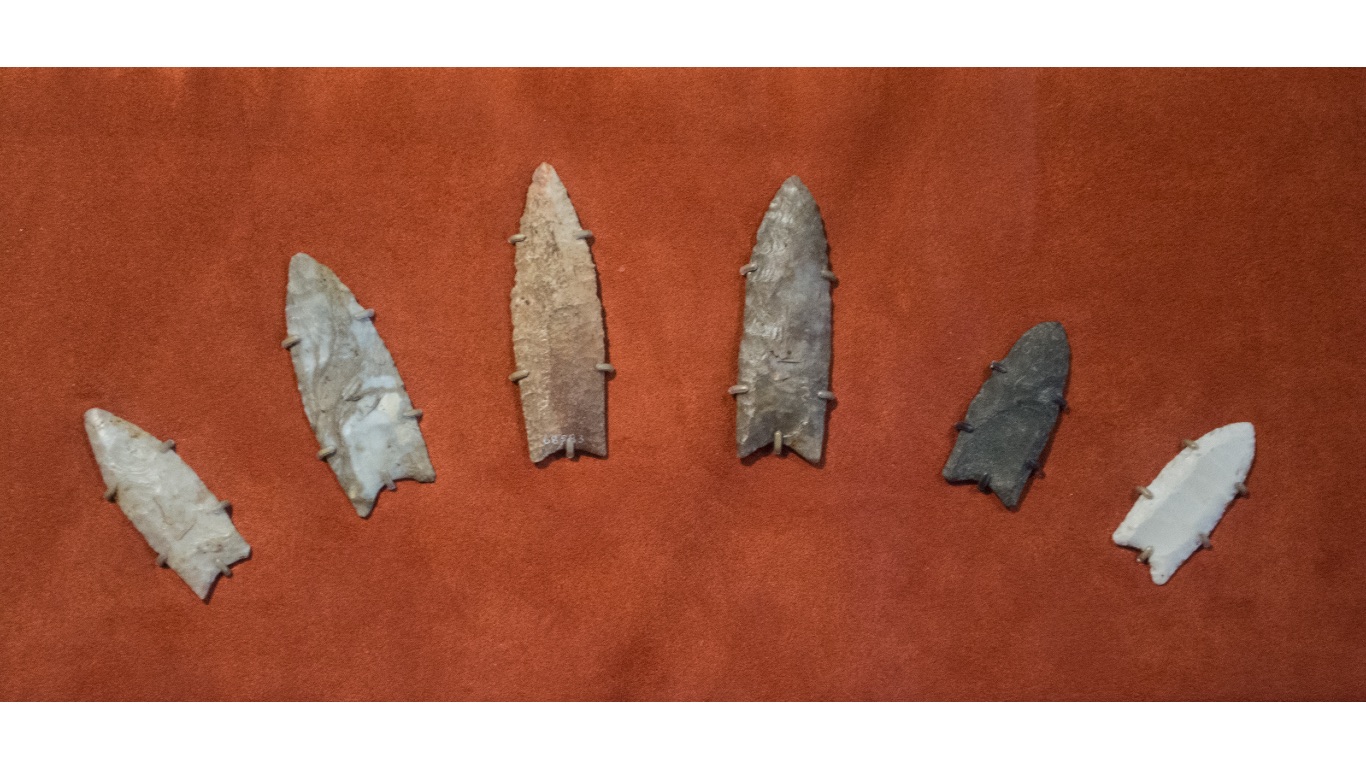
Why did the Clovis people vanish?
> When: 10,800-8800 B.C.
> Where: Present-day Clovis, New Mexico
One of the earliest American civilizations, the Clovis people inhabited expansive lands in North America, probably centered in New Mexico, migrating down to South America before mysteriously vanishing. Remains of their tools and weapons suggest they were highly sophisticated for their time. Some believe that they dispersed into smaller groups, while others insist that their reliance on hunting large mammals led to their demise as big game became scarce.
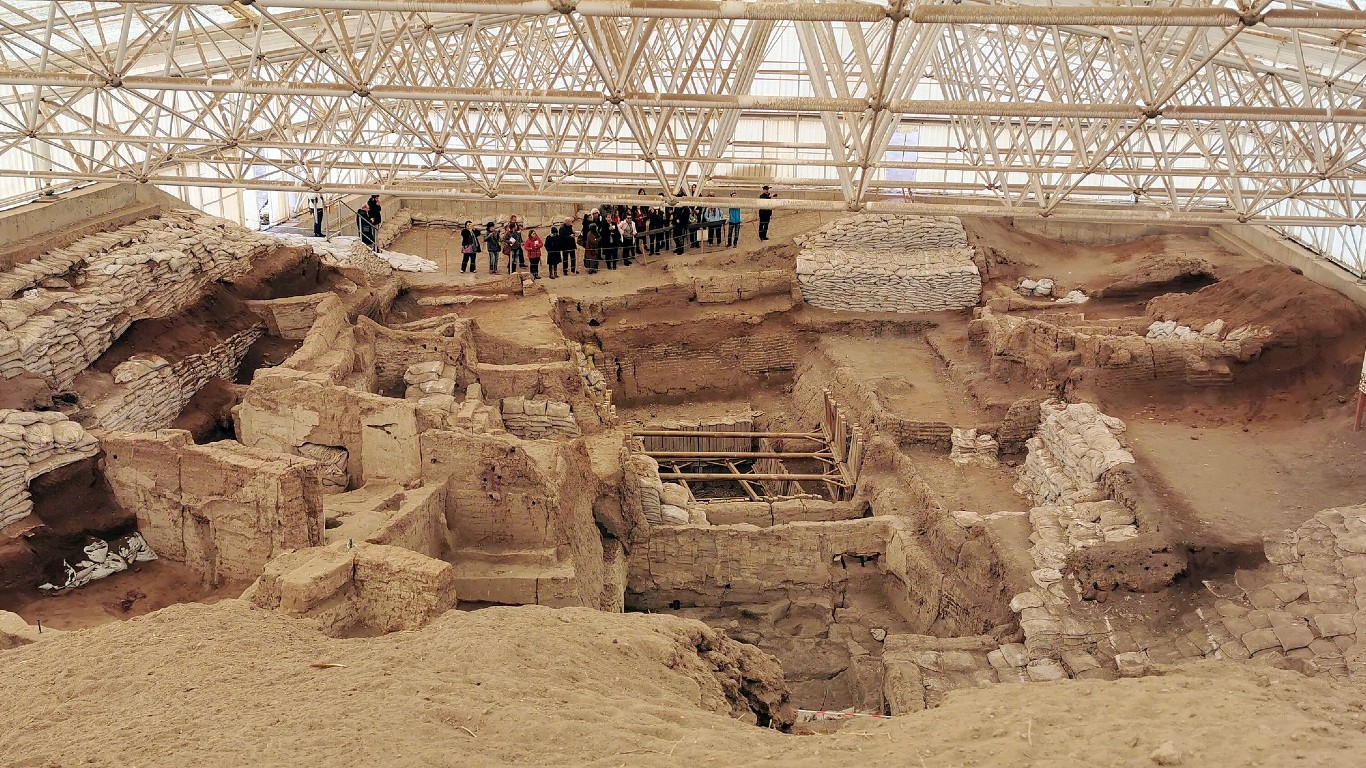
What happened to the people of Çatalhöyük?
> When: 5000 B.C.
> Where: Present-day Turkey
Çatalhöyük, one of the world’s oldest cities, flourished in modern-day south-central Turkey between 9,000 and 7,000 years ago before its inhabitants seemingly abandoned it, though no one knows why. The Neolithic city was unique for its hivelike structure, with houses constructed adjacent to each other and entered through roof holes. A wealth of artifacts detailing the inhabitants’ lives and rituals remain.
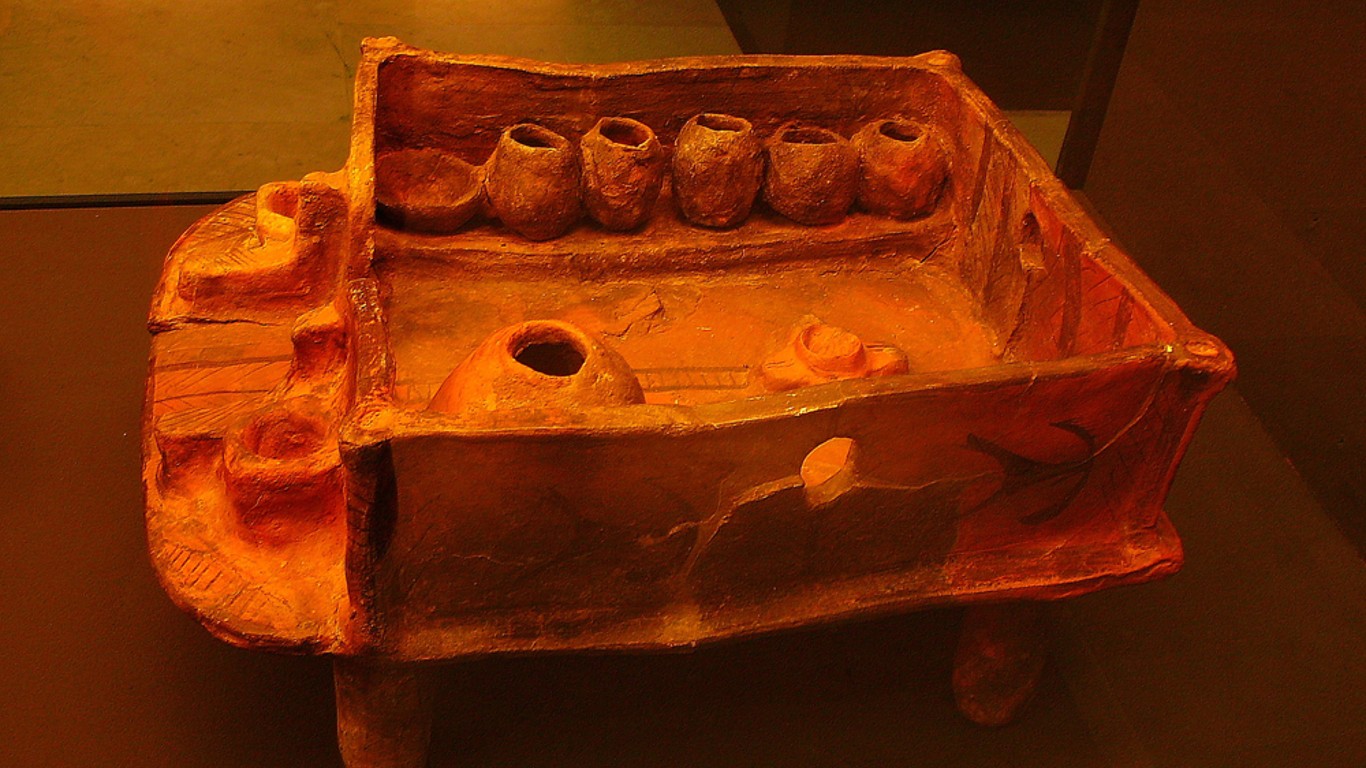

Why did the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture burn down its houses?
> When: 2700 B.C.
> Where: Modern-day Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
The Cucuteni-Trypillian culture existed between 5400 and 2700 B.C. in present-day Eastern Europe. This early civilization relied on agriculture and was known for its artistry in sculpting and pottery. The society practiced a peculiar ritual of burning down their large, densely packed settlements every 60 to 80 years. Some theories suggest that this was a form of honoring their dead through mass cremation.
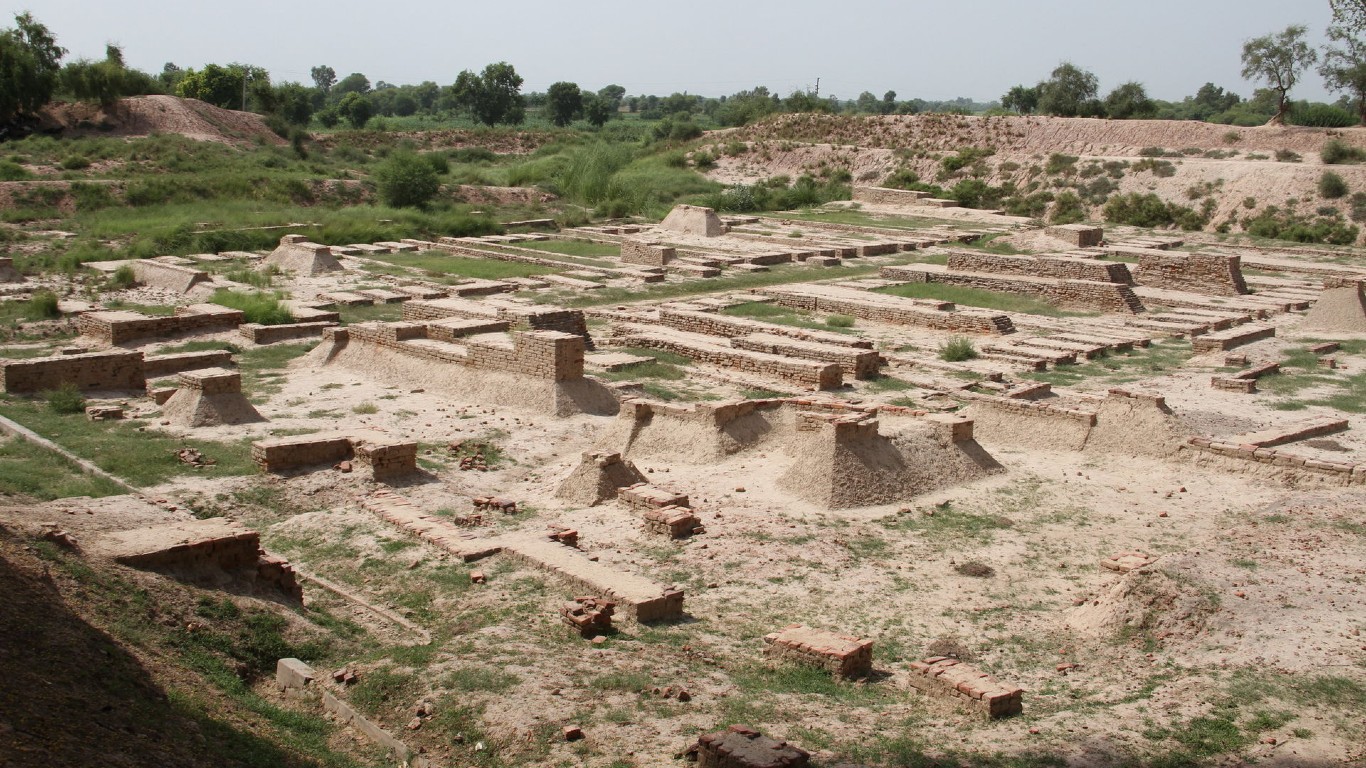
Why did the Indus Valley civilization collapse?
> When: 1900 B.C.
> Where: Present-day India, Pakistan and Afghanistan
Also known as the Harappan civilization, the Indus civilization, flourishing between 3300 and 1900 B.C., was notable for its advanced urban planning and impressive architecture. Huge settlements including Mohenjo-daro housed tens of thousands of people. Several theories have been proposed as reasons for its collapse, including climate change, overpopulation, disease, and invasions. However, due to their as yet undeciphered writing system, the true cause remains elusive.
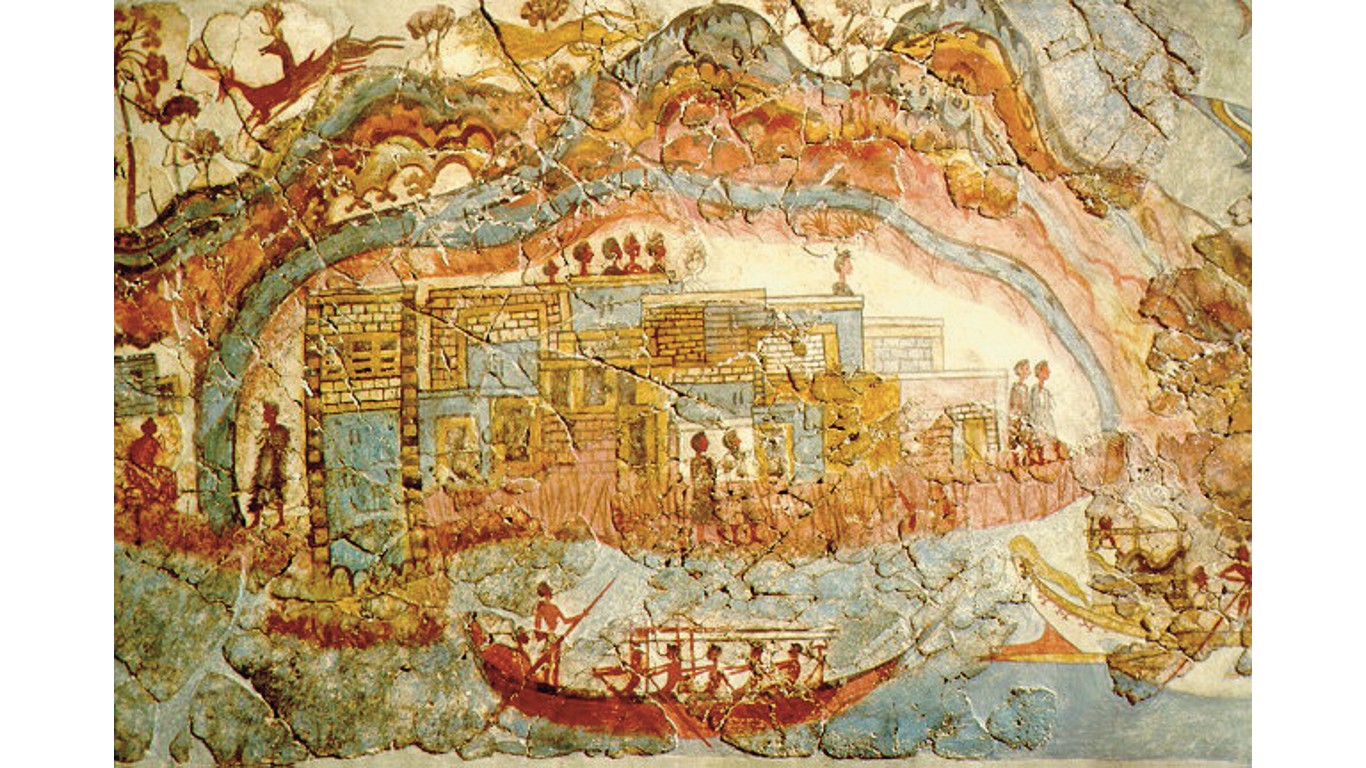

What wiped out the Minoans?
> When: 1000 B.C.
> Where: Present-day Crete
This Bronze Age civilization on the Greek island of Crete existed between appeared as early as 3000 B.C., predating the Golden Age of Athens and Alexander the Great. The Minoans were known for their advanced technologies, impressive arts, and vibrant pagan culture. Some historians suggest they might have been wiped out by a volcanic eruption in the nearby Santorini islands, while the Greek historian Heroditus claimed they were decimated by plagues.
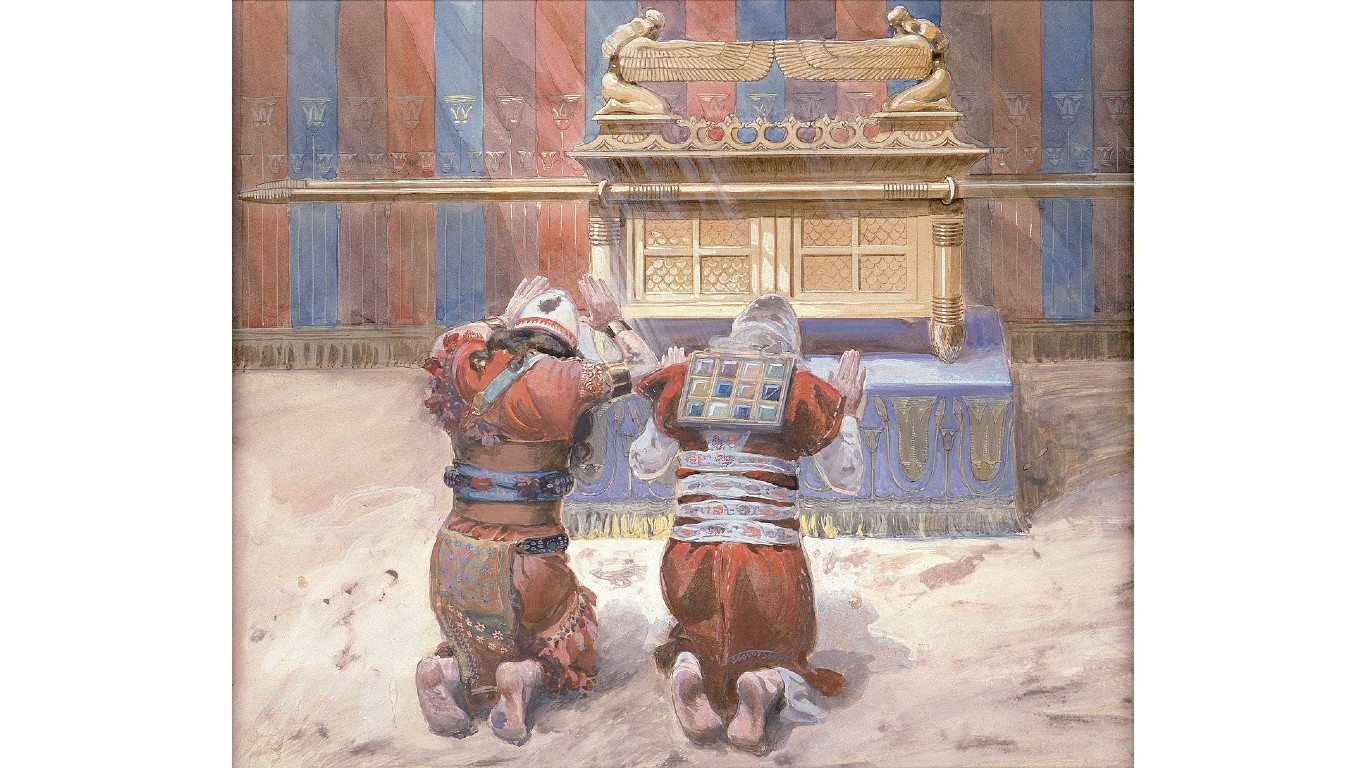

Where is the Ark of the Covenant?
> When: 587 B.C.
> Where: Jerusalem
The Ark of the Covenant, the Israelite relic containing the stone tablets recording the 10 Commandments, disappeared in 586 or 587 B.C. when the Babylonians conquered Jerusalem and destroyed its repository, the First Temple. Multiple theories abound as to the Ark’s fate. Some suggest it was carried back to Babylon, while others claim it was hidden prior to the city’s capture, destroyed during the sacking of the city, or taken to Ethiopia, where it remains guarded to this day.
What happened to the society of Tartessos?
> When: 5th century B.C.
> Where: Modern-day southwestern Spain
The Tartessos civilization, believed to have thrived in the Iberian Peninsula between the 9th and 5th centuries B.C., comprised a mixture of indigenous people and Greek and Phoenician colonizers. The civilization was known for its wealth in metals, expansive trade, and advanced construction techniques. Theories about their disappearance include a potential earthquake and tsunami and societal tensions due to a slow-down in trade.
Where did the Olmec people go?
> When: 400 B.C.
> Where: Central America
The Olmecs, the earliest major Mesoamerican civilization, existed from 1200 to 400 B.C. They built pyramid-like temples and carved colossal stone heads. Besides these structures and artifacts, no trace of the Olmec people remains, not even bones, and the cause of their disappearance is unknown. Some suspect that the humid climate in the area caused their skeletons to rapidly decompose.
Why was the city of Niya abandoned?
> When: 400 B.C.
> Where: Xinjiang province in China
The Niya ruins in China mark the site of what was once a thriving city along the Silk Road – the trade route connecting China with Central Asia, Africa, and Europe. It was once a vibrant town full of culture, riches, and temples, but over time, the importance of the Silk Road waned, especially after the collapse of the Mongol Empire, possibly leading to the city’s abandonment.
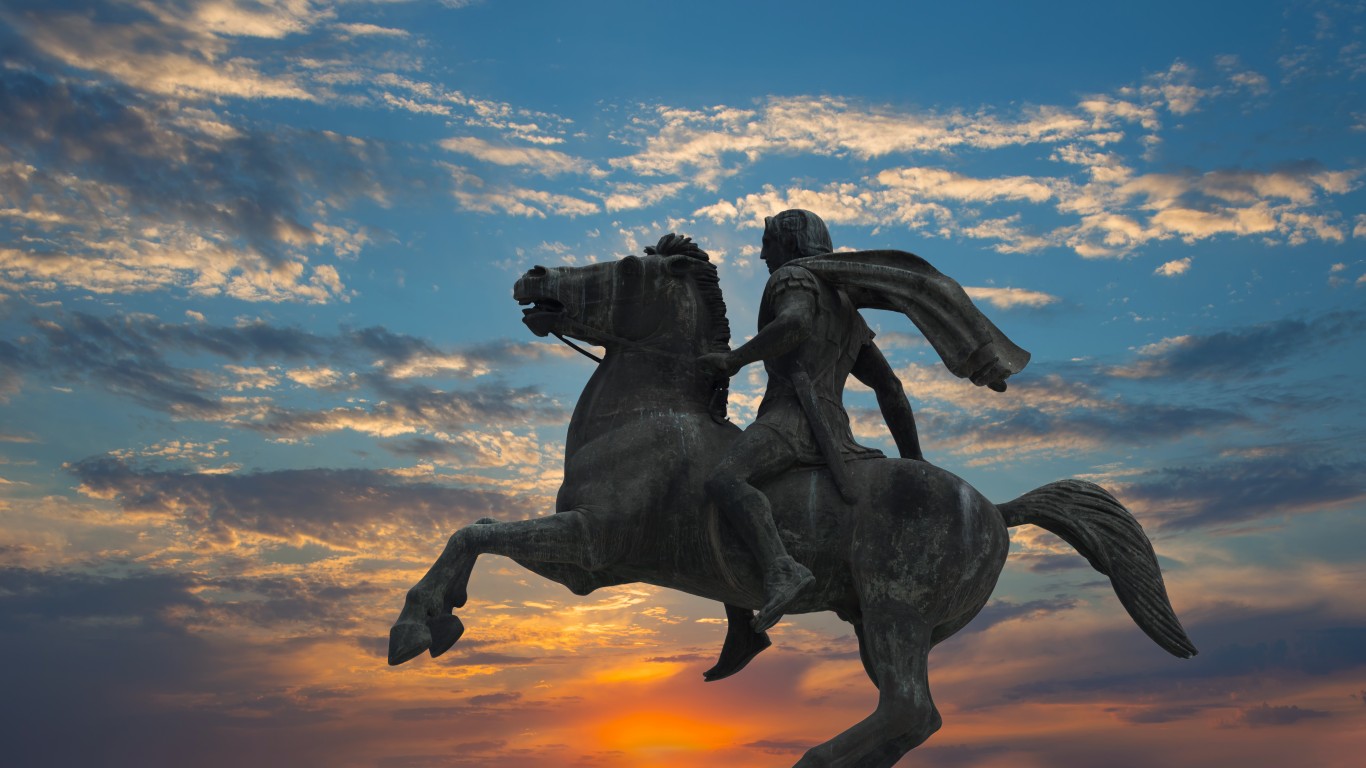

Where is the tomb of Alexander the Great?
> When: 323 B.C.
> Where: Possibly Egypt
After conquering numerous lands, Alexander the Great fell ill and died in Babylon. His body, in a golden sarcophagus, was taken to Egypt and held in Memphis while a tomb was built in Alexandria. However, the exact location of the tomb has been lost to time. Some theories suggest it may have sunk beneath the sea, as it was built in a now-submerged district.
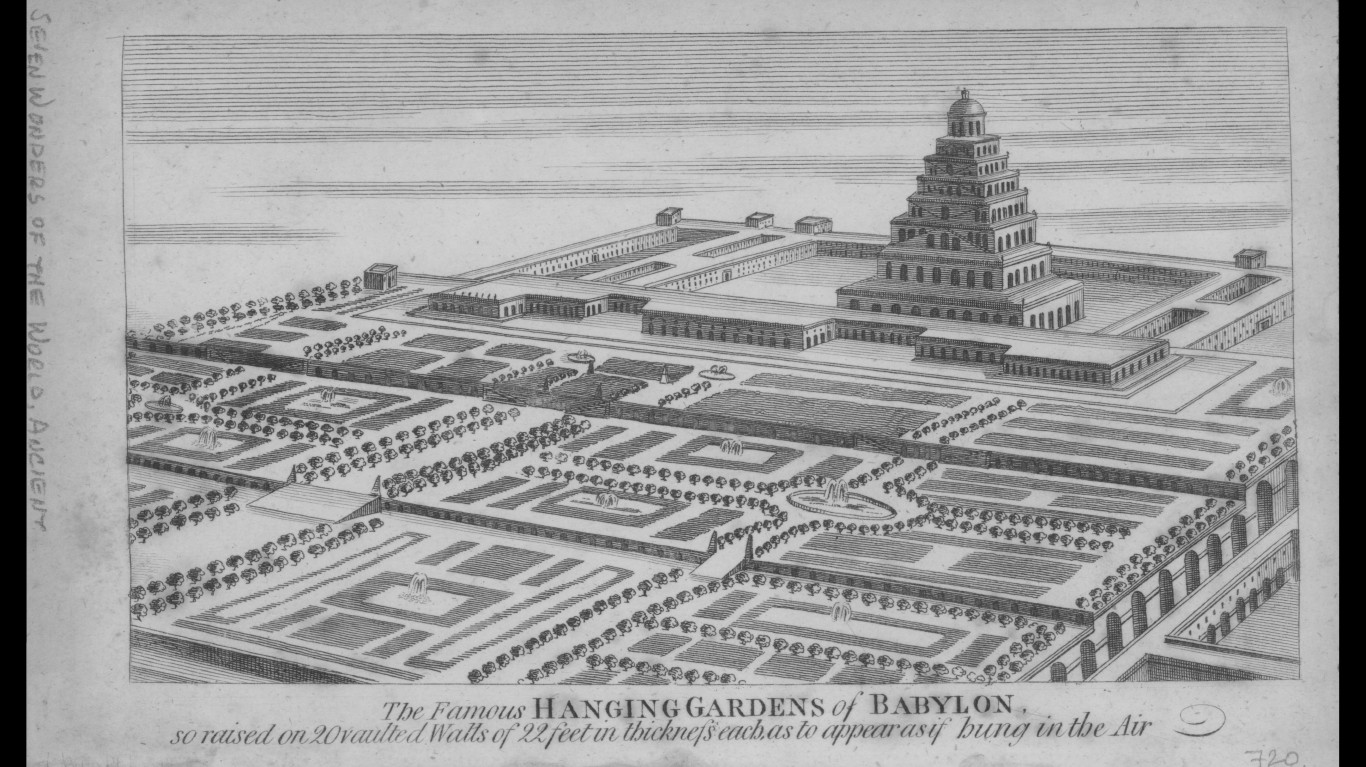
Where were the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
> When: 1st century B.C.
> Where: Modern-day Iraq
Ancient writers describe these gardens as one of the wonders of the world, with hanging plants cultivated on four floors of terraces. However, archaeologists haven’t found any physical evidence that these gardens existed. While some records report that they were destroyed by earthquakes in the 1st century B.C, another theory is that the gardens may have actually been located in the Assyrian city of Nineveh.
Where is Cleopatra’s tomb?
> When: 30 B.C.
> Where: Present-day Egypt
Cleopatra VII and her lover, Mark Antony, are said to have been buried together in a tomb near a temple of Isis after their deaths in 30 B.C. The tomb, however, has never been identified. Excavations at a site near Alexandria called Taposiris Magna, which contains tombs from Cleopatra’s era, did not uncover her burial place. Most archaeologists assume that it lies underwater in a now-submerged section of Alexandria.
Why did the Maya abandon their cities?
> When: 900
> Where: Yucatán Peninsula
Spanning what is now Central America and Mexico, the Mayan empire was once an advanced civilization boasting such technological accomplishments as a calendar system, the use of mathematics, sophisticated agricultural practices, and urban planning. The civilization experienced a dramatic decline around 900. Some factors that may have contributed to their departure include ongoing war or climate change, decimating of their natural resources.
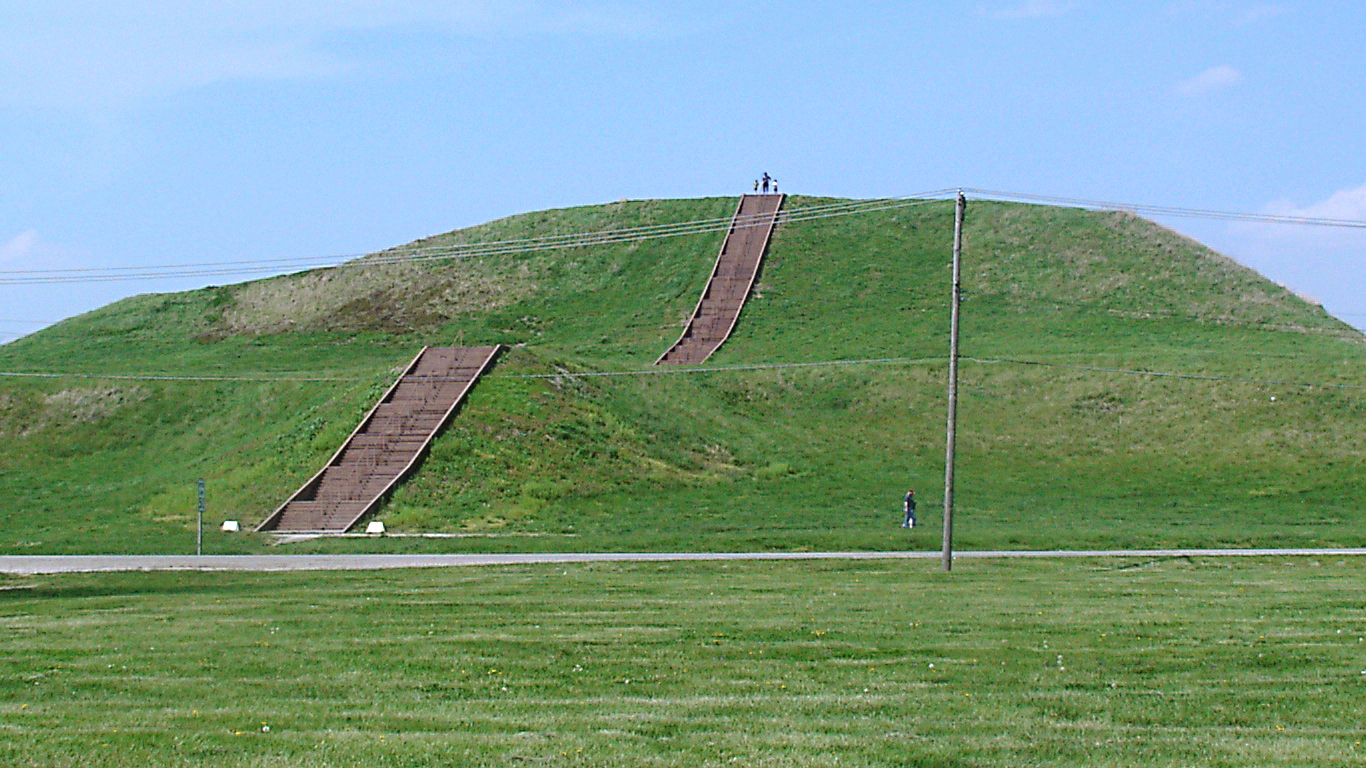
Why was the city of Cahokia abandoned?
> When: 1200
> Where: Present-day Illinois
The Mississippian culture, known for its massive burial mounds, thrived in what is now the American Midwest starting around 700. The largest Mississippian city was Cahokia, home to as many as 20,000 residents. However, the city started declining around 1200, likely due to a disastrous flood, and everyone left. Other factors like overexploitation of resources, political unrest, diseases, and the Little Ice Age may have also contributed to its collapse.
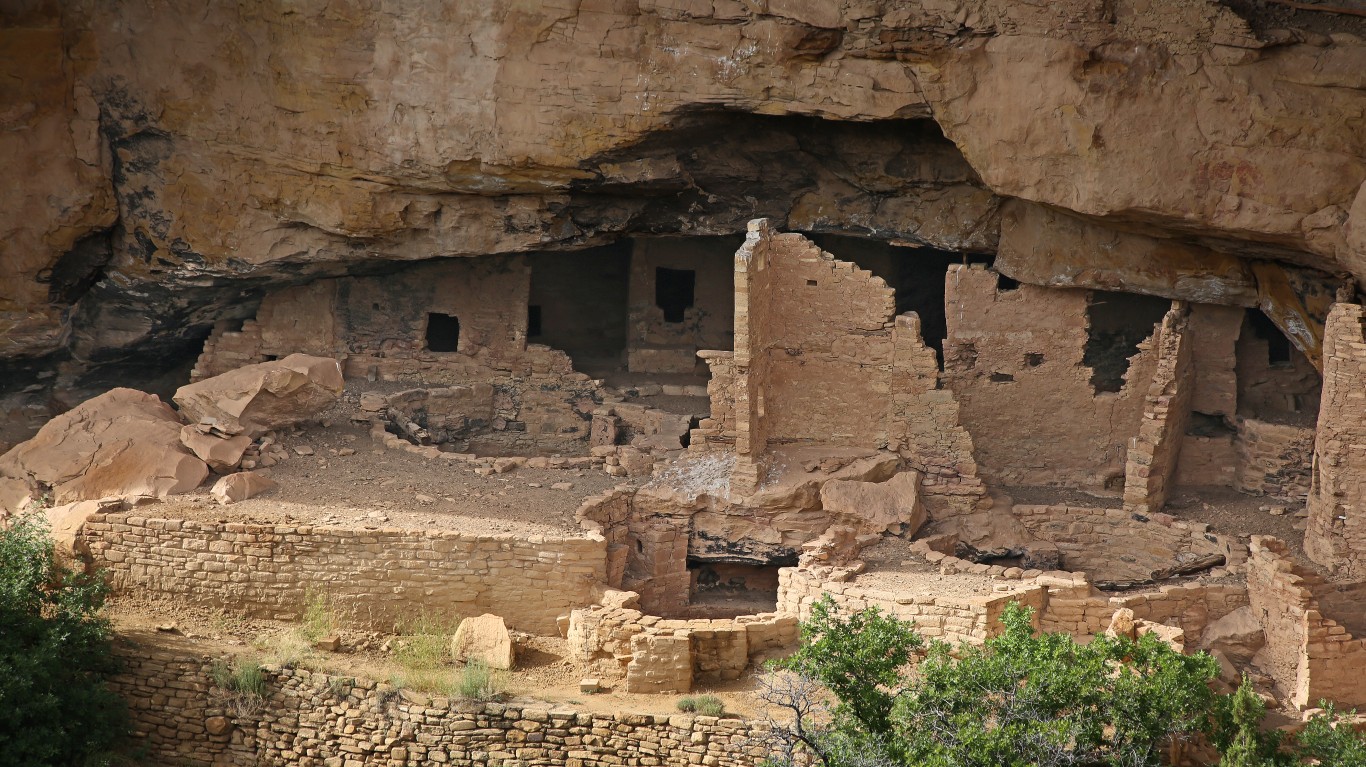
Why did the Ancestral Puebloans migrate?
> When: 1300
> Where: Southwestern United States
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, built remarkable cliff dwellings in the arid Four Corners region of the U.S. during the 12th and 13th centuries. By 1300, however, they had abandoned the region. Researchers suggest deforestation, water management issues, and a long-term drought may have led to violence and chaos, which, along with religious and political upheaval, forced them to migrate south.
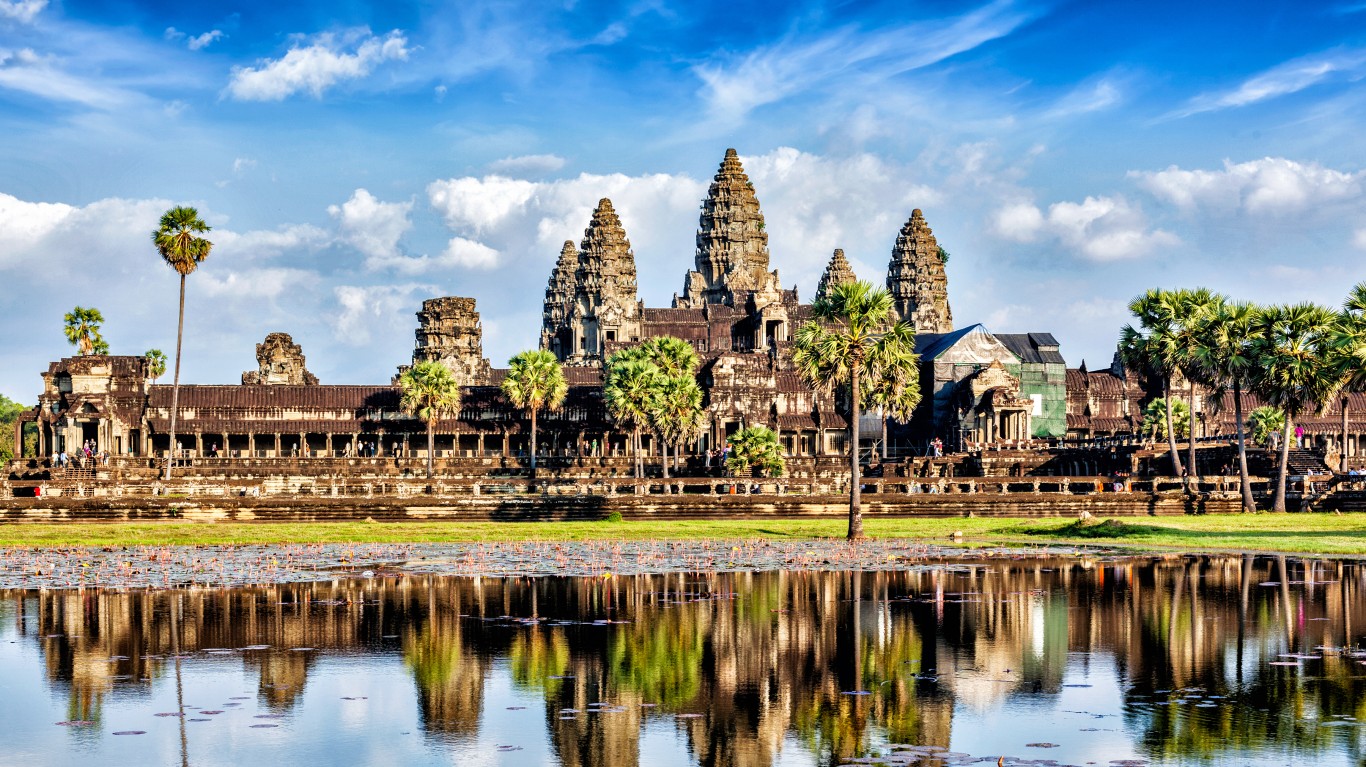

Why did the Khmer empire dissolve?
> When: 1431
> Where: Present-day Cambodia
The Khmer empire, at its height between 1000 and 1200, was a dominant civilization in modern-day Cambodia. Angkor was its capital and one of its largest cities, with a population that may have reached a million, and astonishing temples, roads, and canals. Its demise has long been linked to the sacking of Angkor by the Ayutthaya Kingdom from neighboring Siam (Thailand), but modern historians are uncertain as to what finally ended its prominence, with environmental catastrophe, political instability, and economic decline proposed as alternate theories.
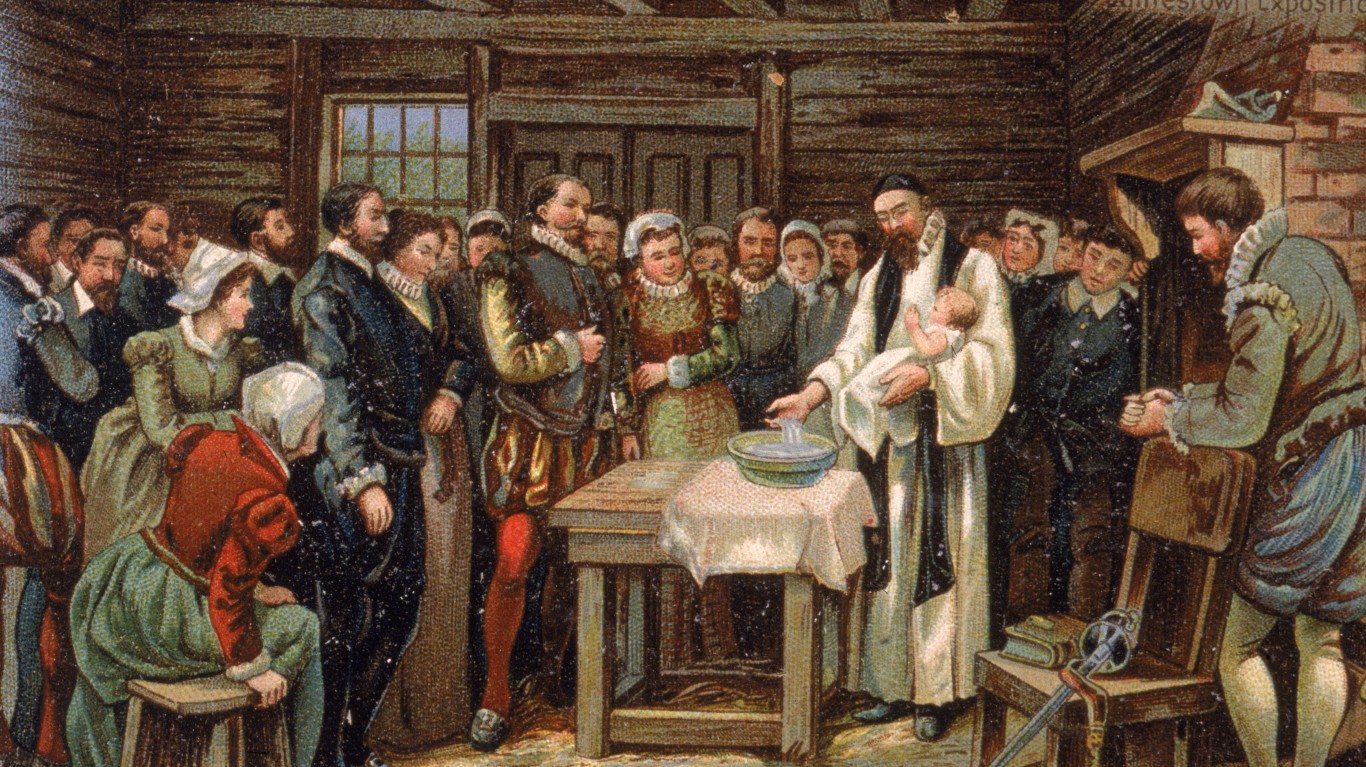

Why did the Roanoke Colony disappear?
> When: 1590
> Where: Modern-day North Carolina
A group of 115 English settlers attempted to start a colony on an island off the coast of what is now North Carolina in 1587. When a ship of supplies arrived from England three years later, the settlers were nowhere to be found. The only clue as to their fate was the word “Croatoan” – the name of a nearby island – carved into a post. Theories suggest the settlers were killed or abducted by Native Americans, lost at sea, killed by Spaniards, or absorbed into a friendly tribe.
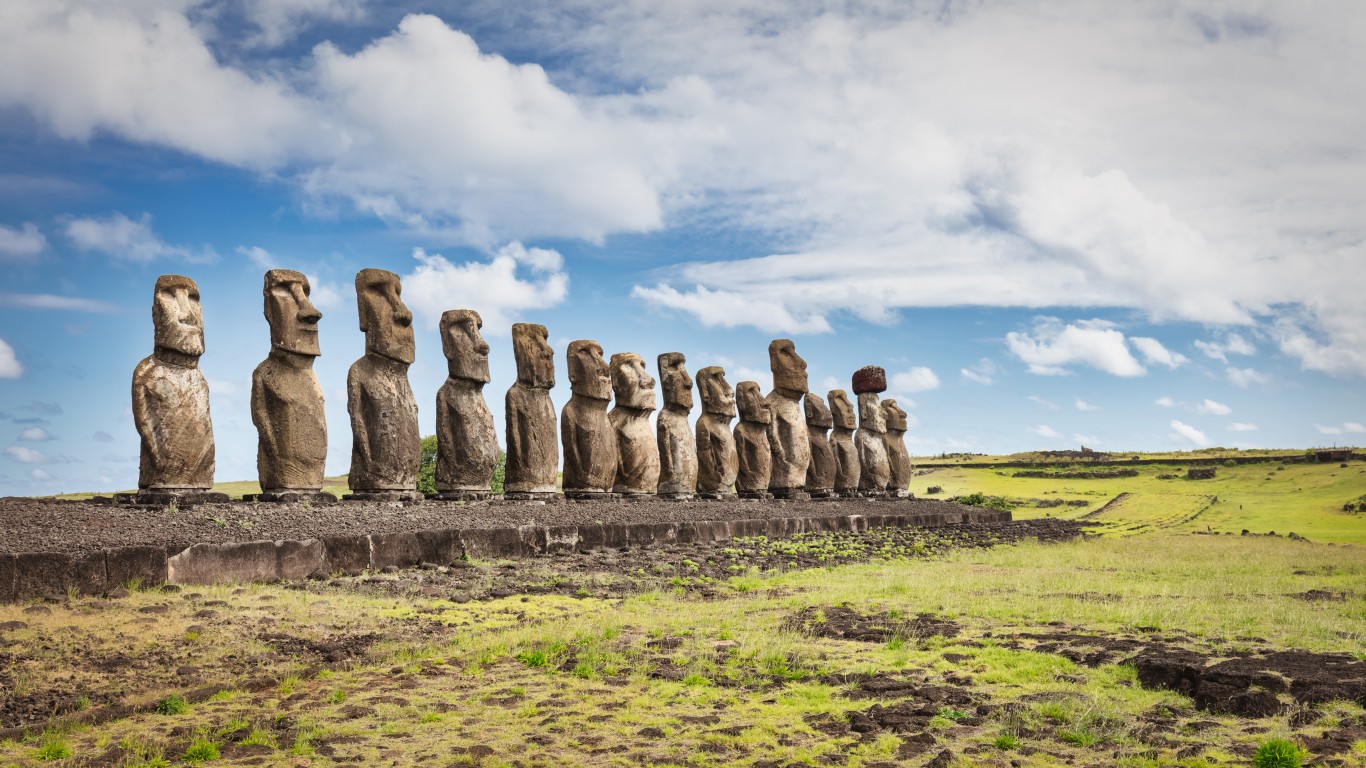

Why did the Rapa Nui civilization collapse?
> When: 18th century
> Where: Easter Island
The original inhabitants of Easter Island, one of the most remote places on earth, are a Polynesian society called the Rapa Nui, known for their construction of massive stone heads. Historians believe that excessive resource consumption and a rat infestation may have led to the society’s decline before the arrival of Europeans, which brought further destruction in the form of smallpox and slave trading. Some Rapa Nui migrated to other islands and mainland South America, and their numbers reached just 111 people by the late 19th century.

Where is the lost Beale Ciphers treasure?
> When: 1822
> Where: Bedford County, Virginia
The Beale Ciphers, a series of coded messages, are the only clues to the whereabouts of a $60 million treasure allegedly buried in Bedford County, Virginia. The ciphers were given to a hotel proprietor by Thomas J. Beale in 1822. Who Beale was or how he accumulated his treasure are not known, and only one of the three ciphers has been decoded, revealing the treasure’s contents but not its location. Treasure hunters have spent countless hours searching for the gold, silver, and jewels, but the stash has yet to be found.
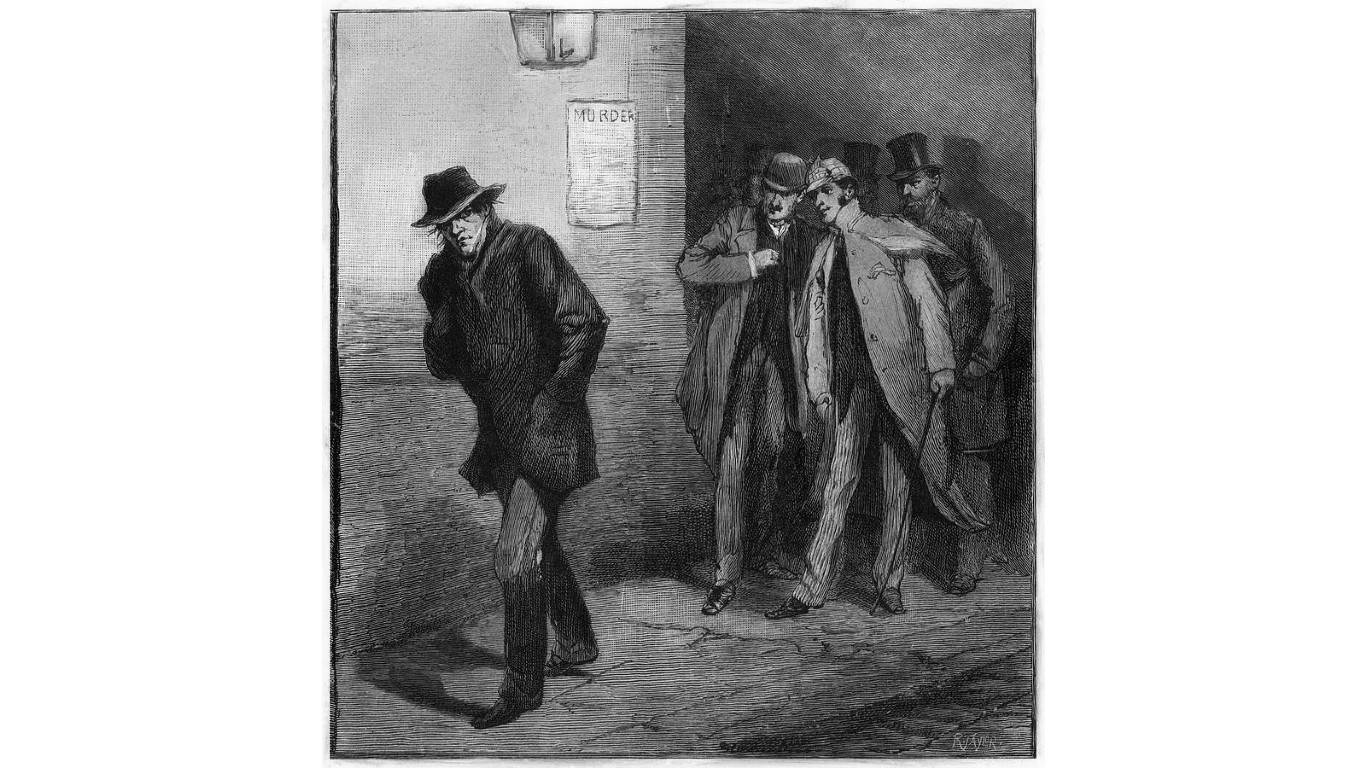

Who was Jack the Ripper?
> When: 1888
> Where: London
“Jack the Ripper” is the name given to an unidentified serial killer who operated in London’s Whitechapel district in 1888. He murdered and mutilated five prostitutes, leading police to suspect he was a surgeon or butcher. The police received several letters detailing the crimes and taunting them for their failure to find him. Although many suspects have been proposed through the years – including artist Walter Sickert, author Lewis Carroll (of “Alice in Wonderland” fame), and even Prince Albert Victor, son of the future King Edward VII of England – the killer’s identity remains unknown.
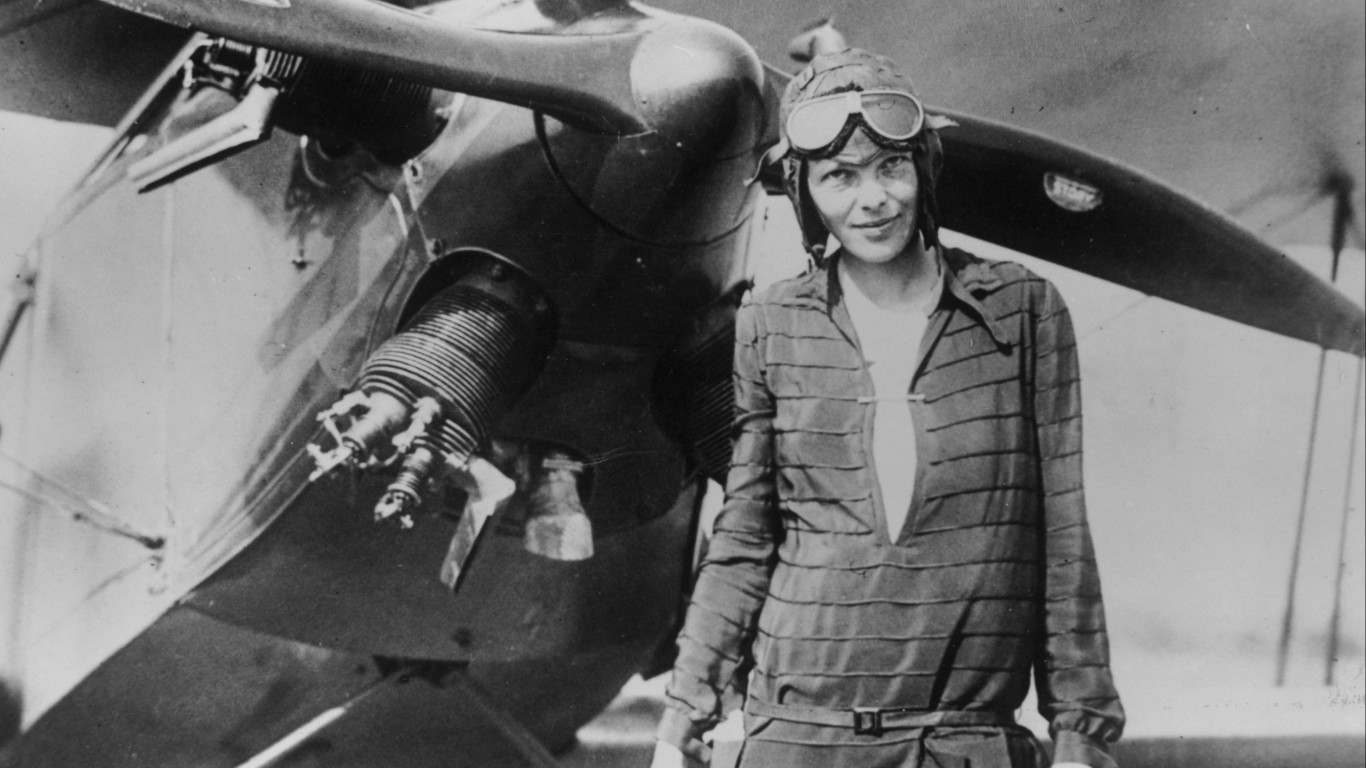

What happened to Amelia Earhart?
> When: 1937
> Where: South Pacific
Amelia Earhart, the first woman to fly solo across the Atlantic, vanished in 1937 during a global flight attempt. With her disappearance remaining unsolved, theories include her crashing and drowning in the Pacific Ocean, landing on a remote island and perishing as a castaway, being captured by Japanese authorities, operating as a spy for the U.S. government, and even surviving capture and assuming a new identity in New Jersey.
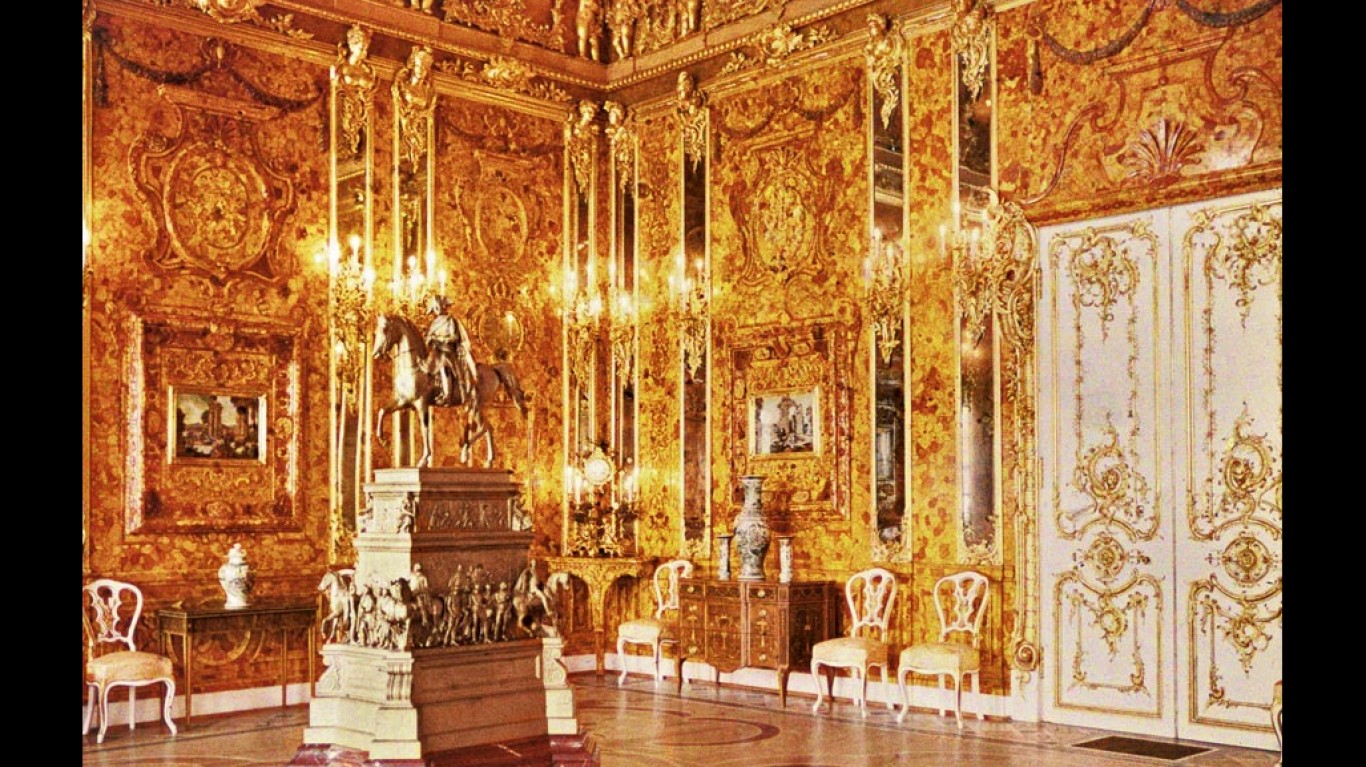

Where is the Amber Room?
> When: 1941
> Where: Germany
The Amber Room, a chamber decorated in amber panels backed with gold leaf and mirrors, was gifted to Peter the Great in 1716 to celebrate peace between Russia and Prussia. It was installed in a palace near Saint Petersburg and was considered an “eighth wonder of the world” until it was stolen by Nazi Germany during World War II. Although the room is known to have been on display in Königsberg during the war, its whereabouts are now a mystery.

Where are missing Sodder children?
> When: 1945
> Where: Fayetteville, West Virginia
During a suspicious Christmas Eve house fire at an Italian family’s home in Fayetteville, West Virginia, four children escaped, while five were presumed dead. However, several irregularities, including a lack of remains, led their parents to believe they had actually been abducted, possibly due to their father’s outspoken criticism of Mussolini. Over the years, various tips and potential sightings of the children were reported, but none were confirmed.
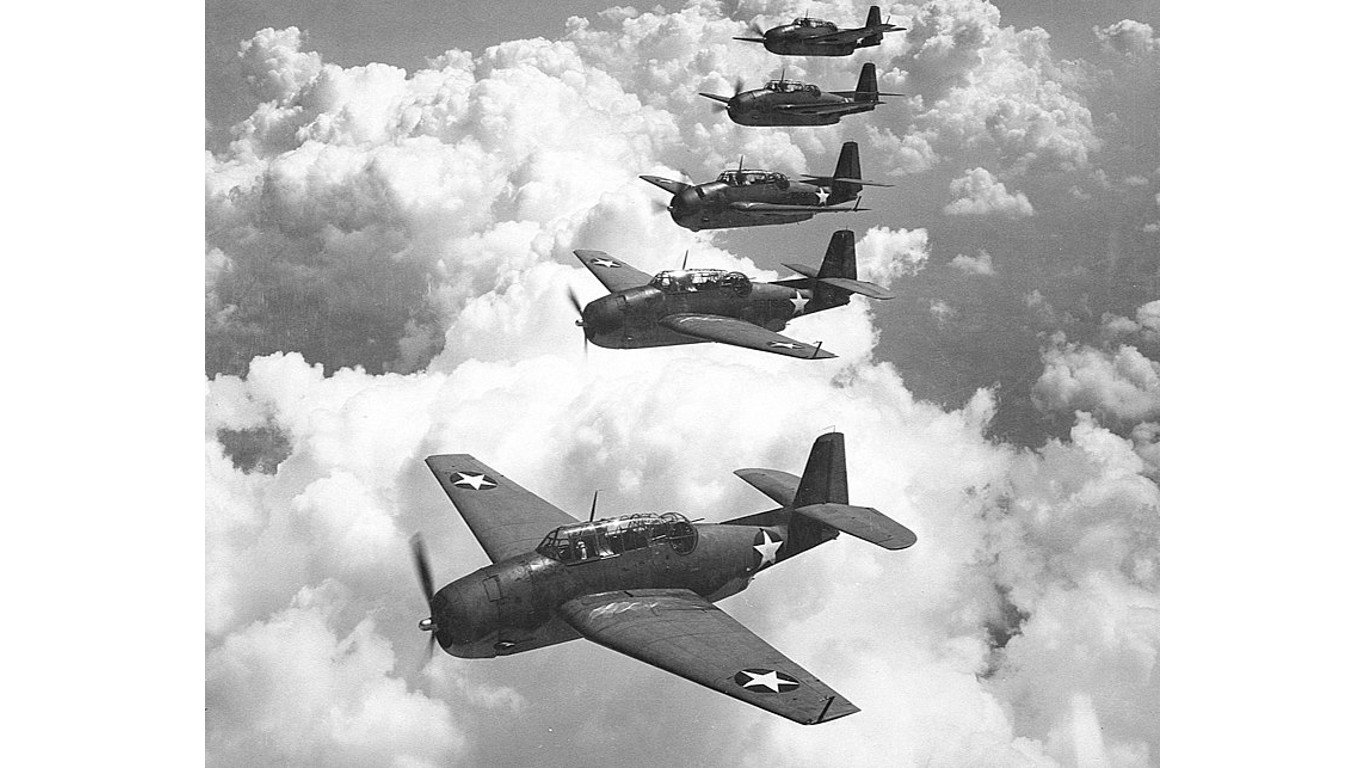

Where did Flight 19 go?
> When: 1945
> Where: Coast of Florida
Flight 19 refers to five U.S. Navy warplanes that vanished during a daytime training flight off Florida’s coast in December 1945. All 14 airmen on the warplanes and 13 crewmembers on a Navy flying boat sent to search for them were lost. No wreckage or bodies have ever been found. The incident is often linked to supernatural or UFO stories, and has contributed to the legend of the Bermuda Triangle.
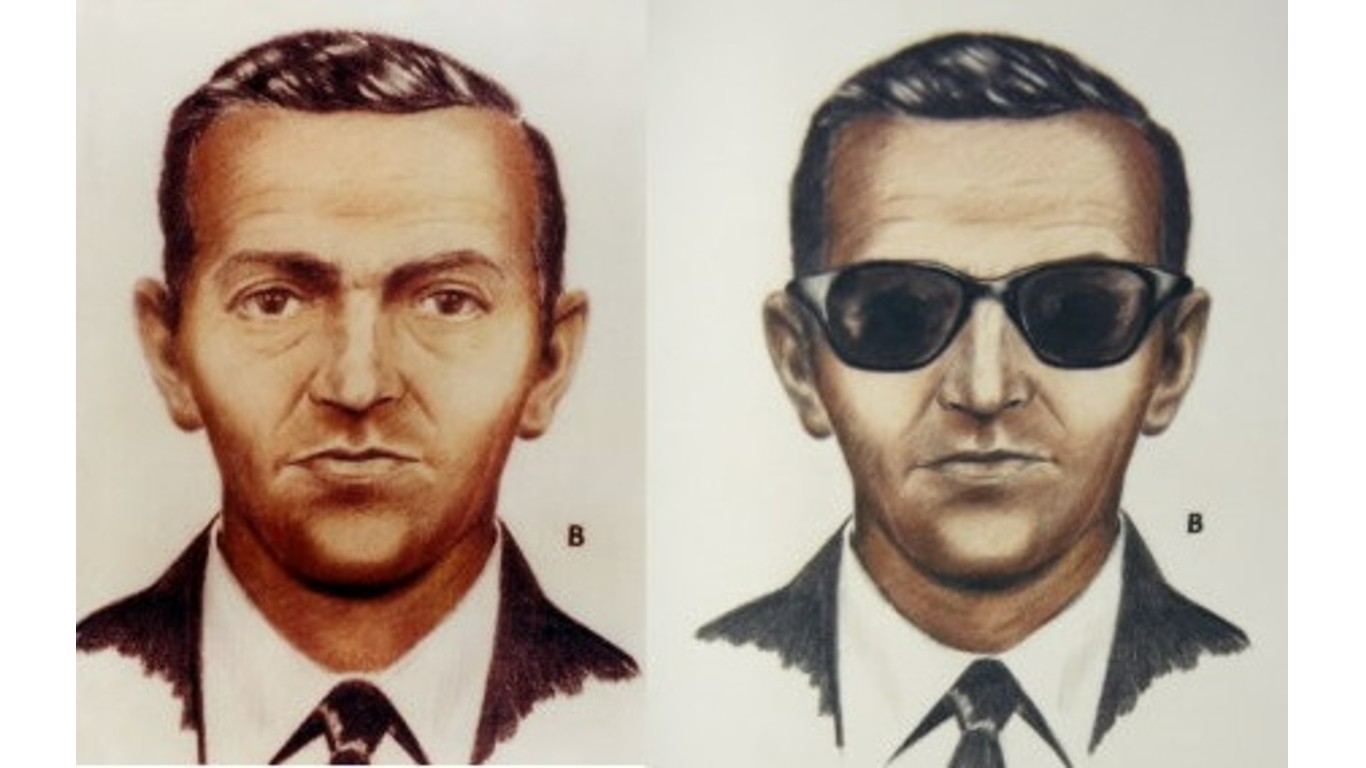

Did D.B. Cooper get away with the money?
> When: 1971
> Where: Pacific Northwest
After a man calling himself Dan Cooper boarded a flight from Portland, Oregon, to Seattle, he hijacked the plane, demanding a payment of $200,000 (about $1.4 million today) and four parachutes to be delivered when the plane landed. After a stop at Sea-Tac, where passengers deplaned and Cooper collected his ransom, the plane took off again towards Mexico. Somewhere along the route, Cooper parachuted out into the night with the cash. His body was never found, but $5,800 of the money was discovered in the Columbia River in 1980.
Where did the Wow! signal come from?
> When: 1977
> Where: Ohio
Received in 1977, the Wow! Signal was an extremely loud radio signal close to 1420 MHz, a frequency associated with hydrogen, the universe’s most common element. The signal came from the direction of the Sagittarius constellation but its source remains unknown. Theories suggest it could be from a moving extraterrestrial intelligence, but it has never repeated, leaving its origin a mystery.

What happened to Malaysian Airlines Flight 370?
> When: 2014
> Where: Southern Indian Ocean
Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 disappeared on March 8, 2014 with more than 200 passengers on board. After a routine takeoff from Kuala Lumpur, the plane turned off course and veered toward the southern Indian Ocean. Despite an extensive international search, the aircraft remains missing, though debris believed to be from the plane was recovered from the water in 2017. The cause of the disappearance is still unclear, with some theories pointing to hijacking. However, no one has claimed responsibility for the incident.
Are You Ahead, or Behind on Retirement? (sponsor)
If you’re one of the over 4 Million Americans set to retire this year, you may want to pay attention.
Finding a financial advisor who puts your interest first can be the difference between a rich retirement and barely getting by, and today it’s easier than ever. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three fiduciary financial advisors that serve your area in minutes. Each advisor has been carefully vetted, and must act in your best interests. Start your search now.
Don’t waste another minute; get started right here and help your retirement dreams become a retirement reality.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.









