
According to Global Firepower’s 2024 rankings, the United States has retained its title as the strongest and most advanced military on the planet. For the past 18 years, the U.S. has remained in the top spot, besting global rivals China and Russia. However, when it comes to world naval fleets, although the American military still comes out on top in terms of power, it doesn’t take the top position in numbers. China and Russia have more watercraft in their navies than the U.S.
Russia ranks second as the strongest military and is currently using its navy against Ukraine in the ongoing Russo-Ukranian conflict. Ukraine struck at Russia’s Black Sea Fleet Headquarters in Sevastopol, Crimea to devastating effect in late September 2023. Casualties were reported in the dozens. However, there was not any clear indication as to any actual damage to the fleet. (See how Russia’s and NATO’s military capabilities compare.)
24/7 Wall St. reviewed the military data site World Directory of Modern Military Warships’ directory of all active ships in Russia to get a better picture of all warships and submarines in the Russian navy. Ship and submarine classes are ranked in order of the number of vessels currently in active use by the Russian navy, according to WDMMW. Any ships on order were excluded.
The aircraft carrier Admiral Kuznetsov is the largest ship in the Russian fleet, and the only one in its class, measuring roughly 305 meters (1,000 feet) in length, making it one of the largest aircraft carriers in the world. (The Nimitz class aircraft carriers from the United States are 1,092 feet in length.) Equipped with an angled flight deck and a ski-jump ramp, Admiral Kuznetsov can operate a mixture of fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters and carry up to 41 aircraft, including an array of fighter jets and helicopters. The carrier is powered by a combination of traditional oil-fired boilers and gas turbines, providing it with a maximum speed of around 30 knots.
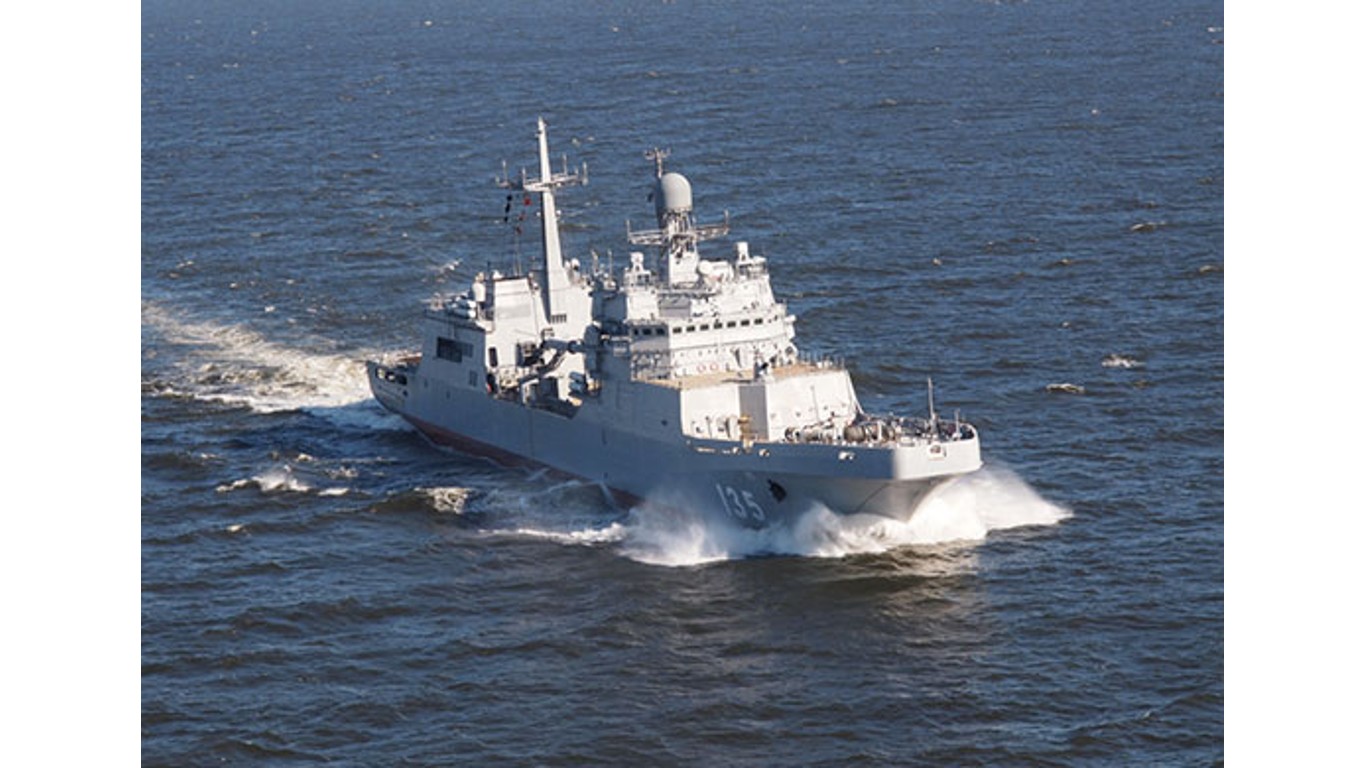
Another notable class is the Admiral Gorshkov guided missile frigates. These frigates are designed for multi-purpose operations and are equipped with modern missile systems, anti-ship and anti-submarine capabilities, and advanced radar systems, according to Military Factory. Although these are not the fastest ships in the fleet, with a maximum speed of roughly 20 knots, or 23 mph, they are very well armed with turreted deck guns, anti-aircraft missiles, and even torpedoes. This class is also one of the newest and most advanced to join the Russian fleet.
Russia has 65 submarines in its fleet, just one more than the U.S., including the Borei class, which is the newest generation of ballistic missile attack submarines. These nuclear-powered vessels possess immense destructive power due to their arsenal of Bulava missiles. These missiles are loaded with multiple nuclear warheads and have a range of 5,000 miles. Although there are only a handful of these submarines in service at the moment, more are on order. (Here are the 20 biggest bombs in Russia’s military arsenal.)
Compared to other major world powers, the majority of Russia’s warships and submarines have been in service for at least a few decades. The median hull age of the fleet is around 30 years, according to WDMMW. For comparison, the median hull age of the U.S. fleet is just over 23 years. The newer classes of submarines, frigates, and corvettes in Russia’s fleet have only been introduced in the past decade or so and therefore do not account for a large portion of the fleet.
Here are all warship and submarine classes in the Russian fleet.
44. Delta III
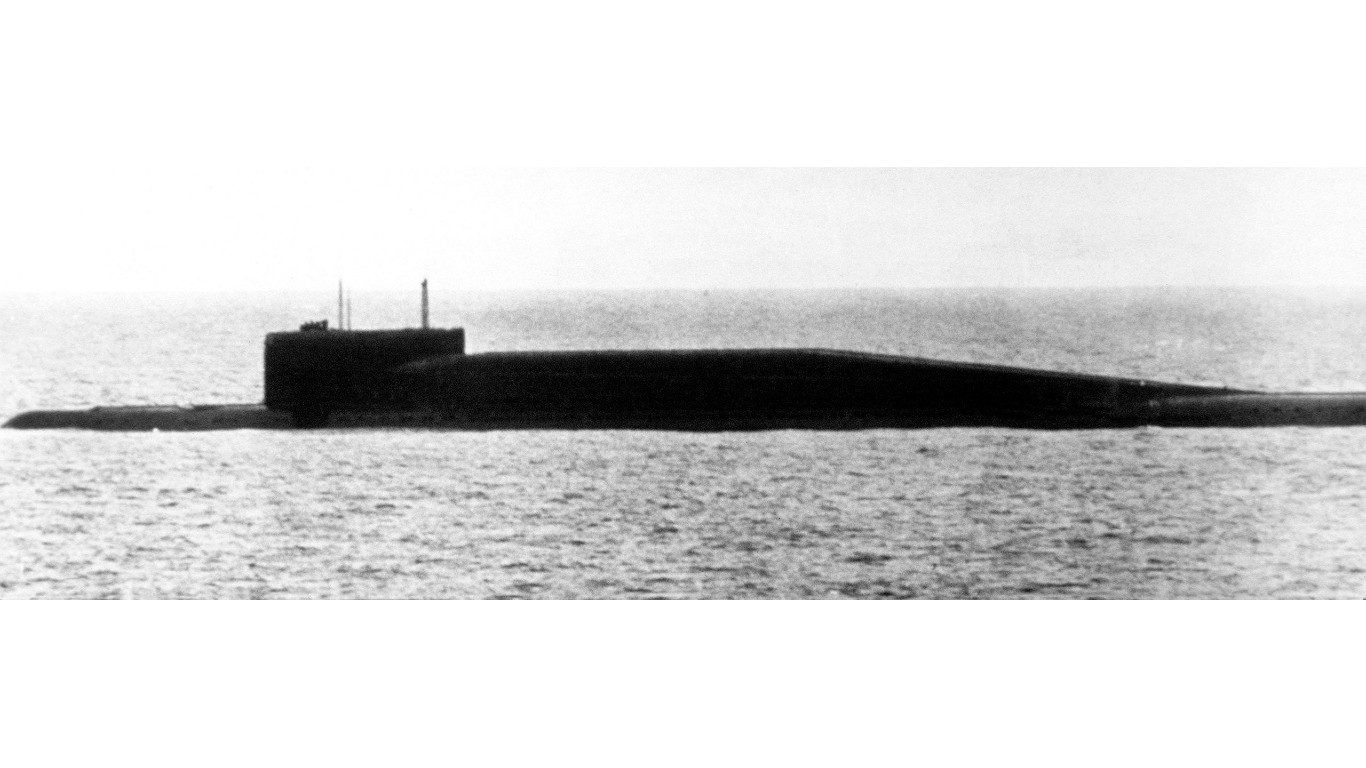

- Number in class: 1
- Type: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1976
43. Gremyashchiy

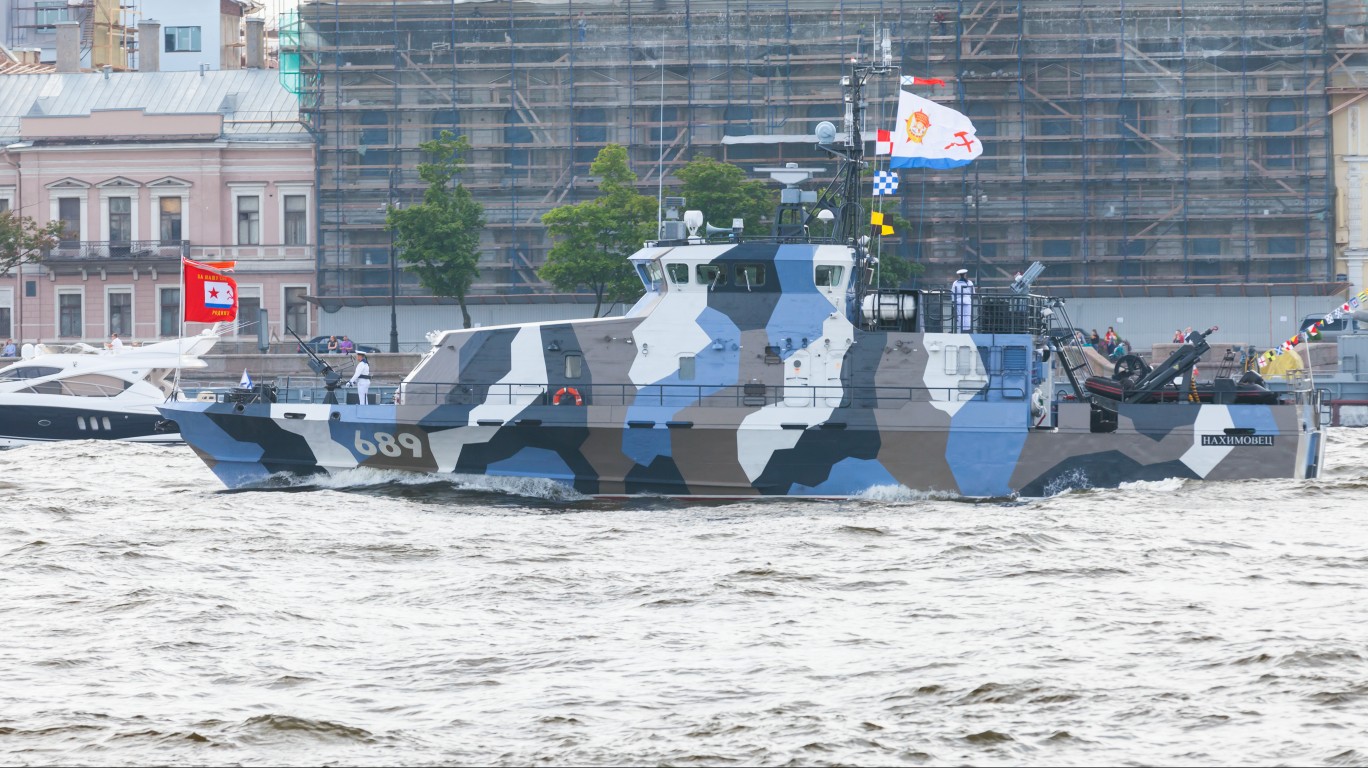
- Number in class: 1
- Type: Guided-missile stealth corvette warship
- Year introduced: 2018
42. Kuznetsov
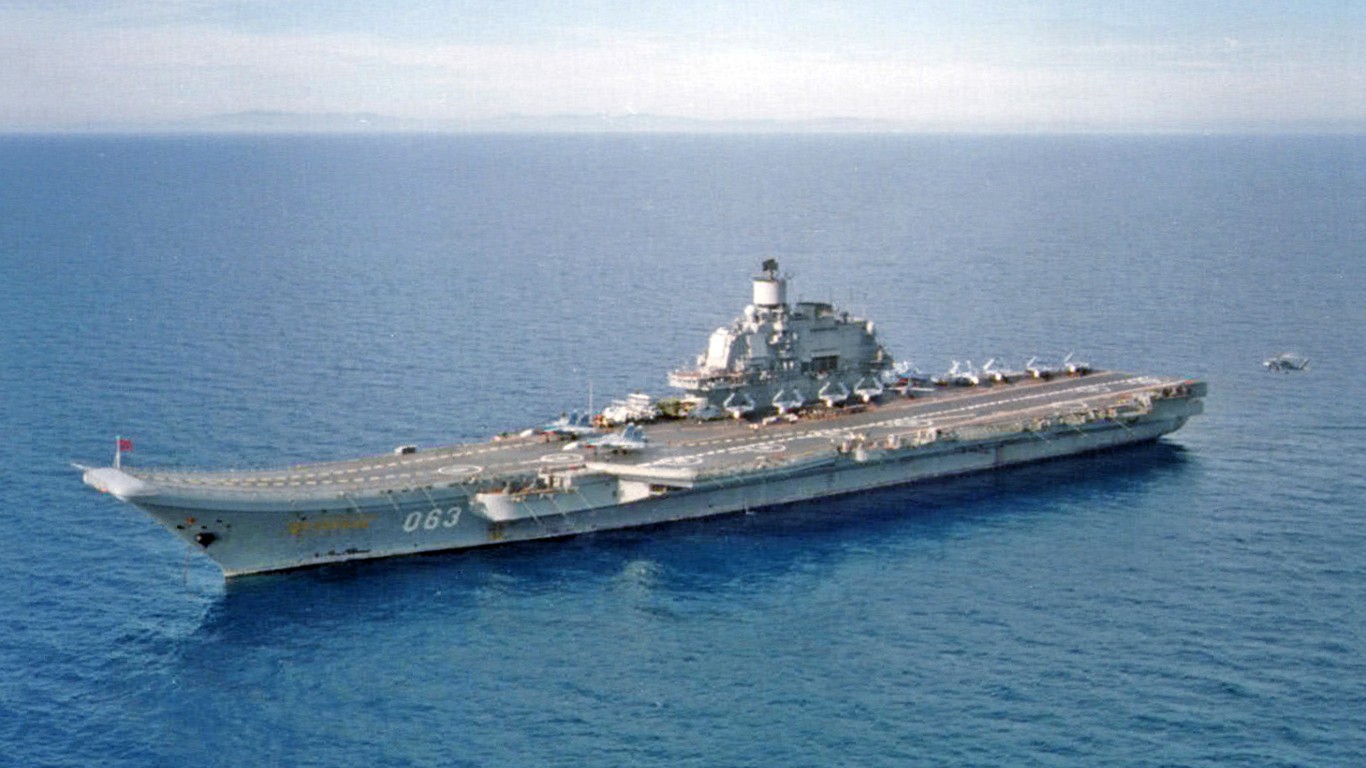

- Number in class: 1
- Type: Conventionally-powered aircraft carrier
- Year introduced: 1991
41. Lada
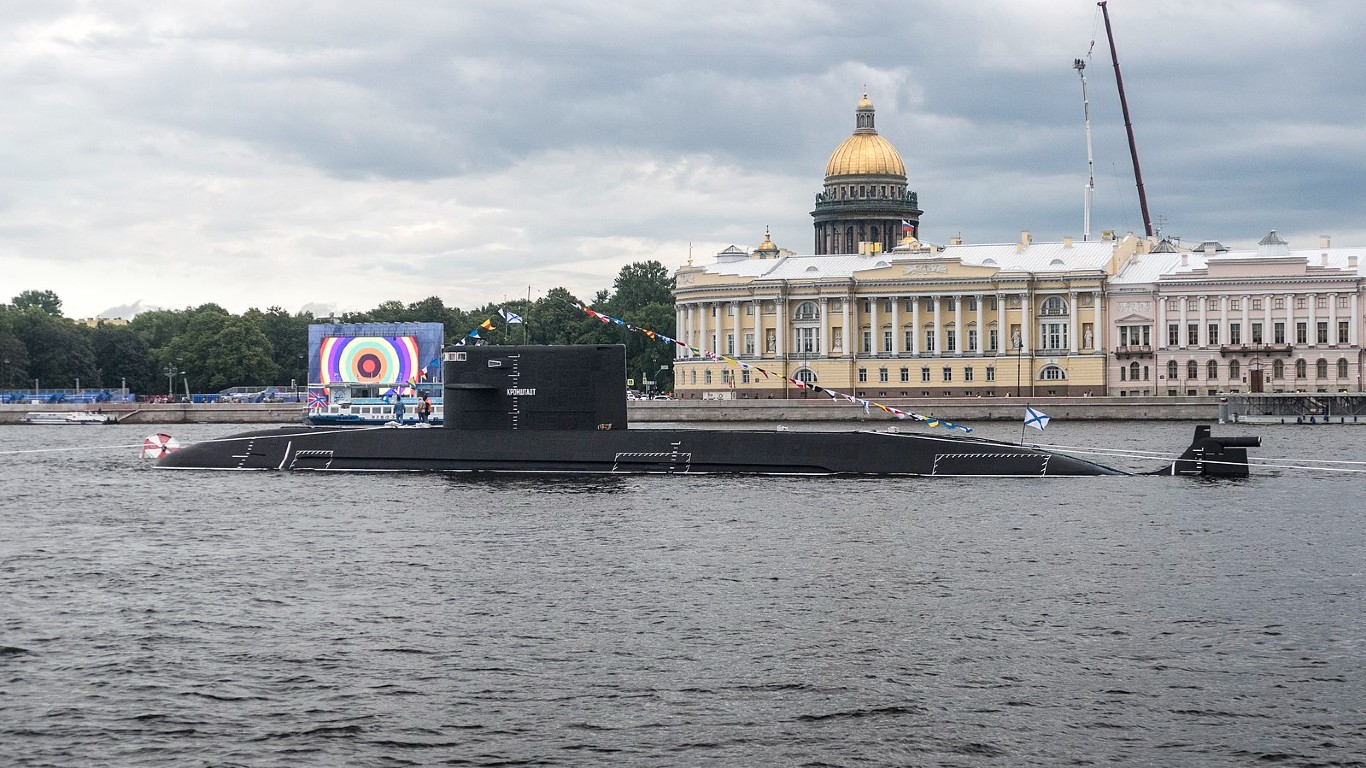

- Number in class: 1
- Type: Diesel-electric attack submarine
- Year introduced: 2010
40. Typhoon
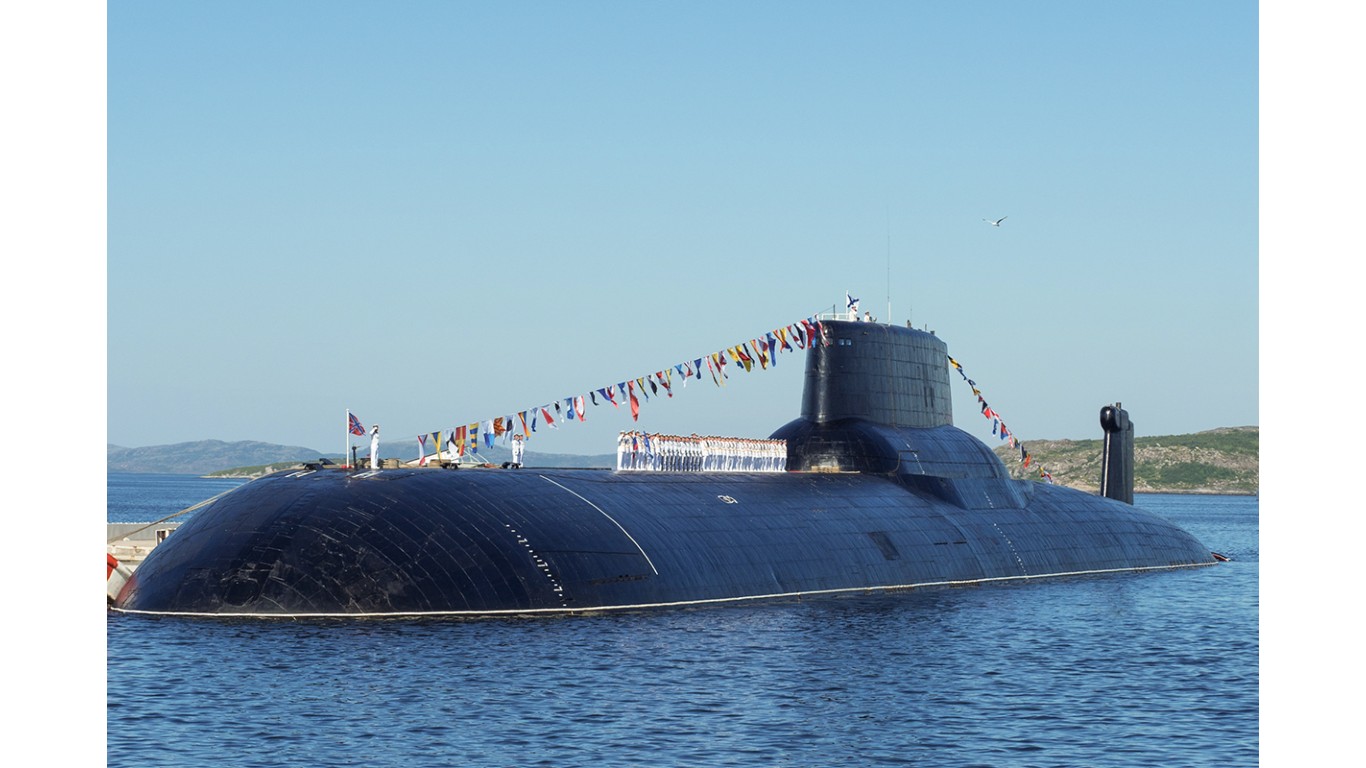

- Number in class: 1
- Type: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine
- Year introduced: 1981
39. Bora
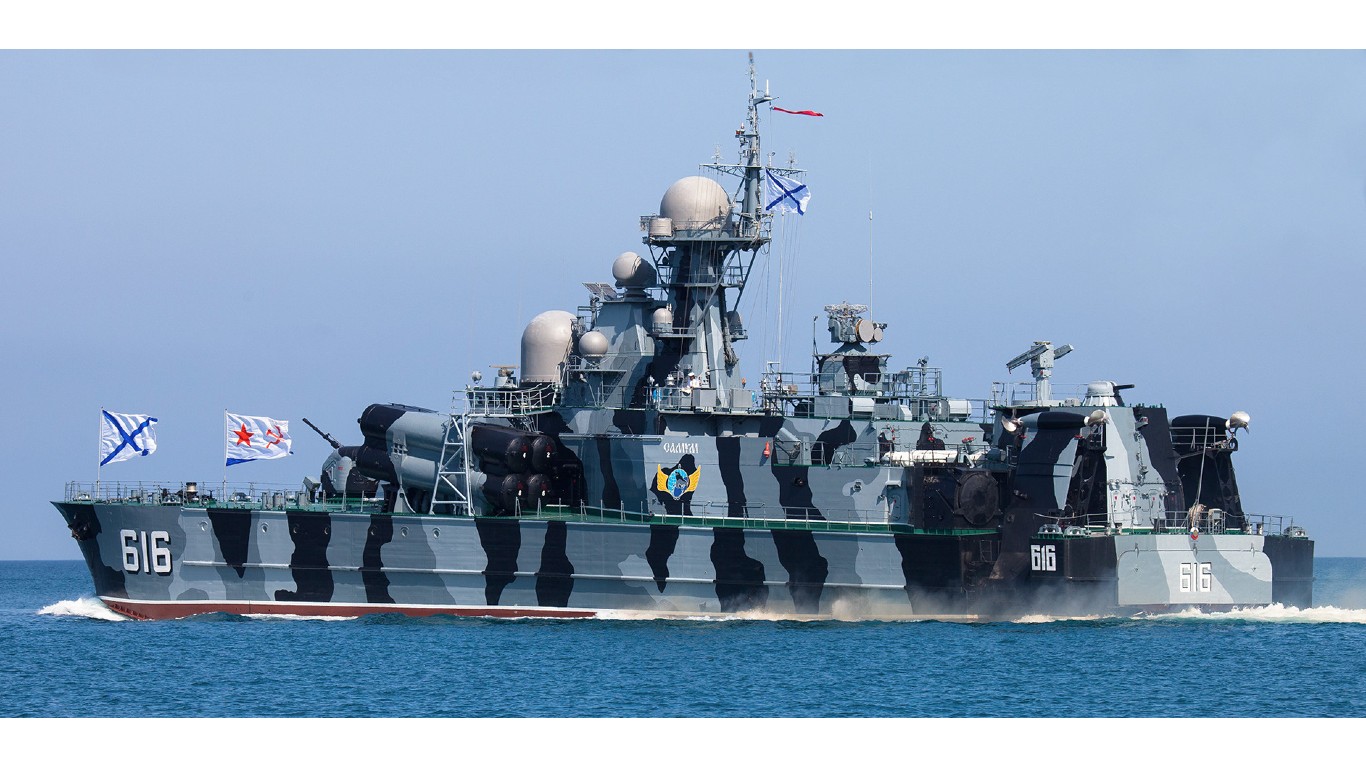

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 1989
38. Gepard
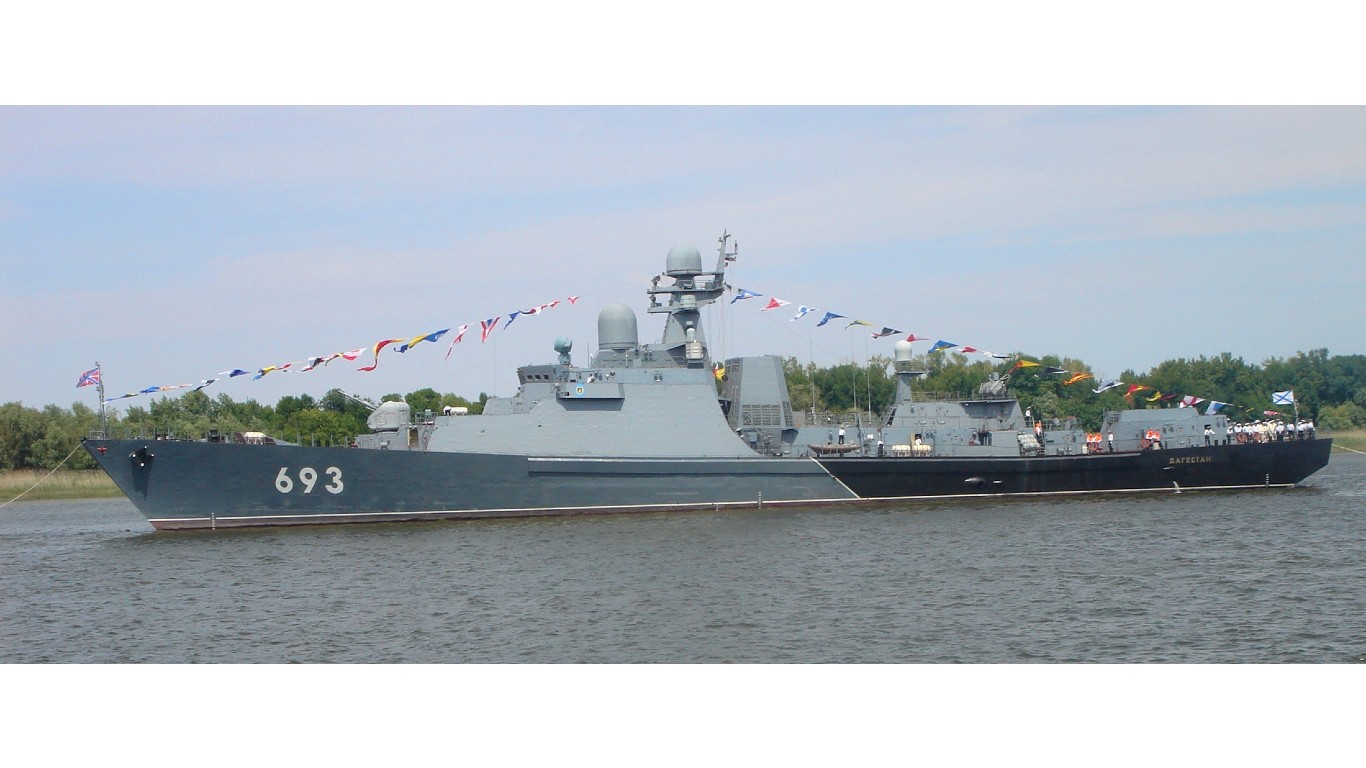

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Guided-missile frigate
- Year introduced: 2003
37. Gorshkov
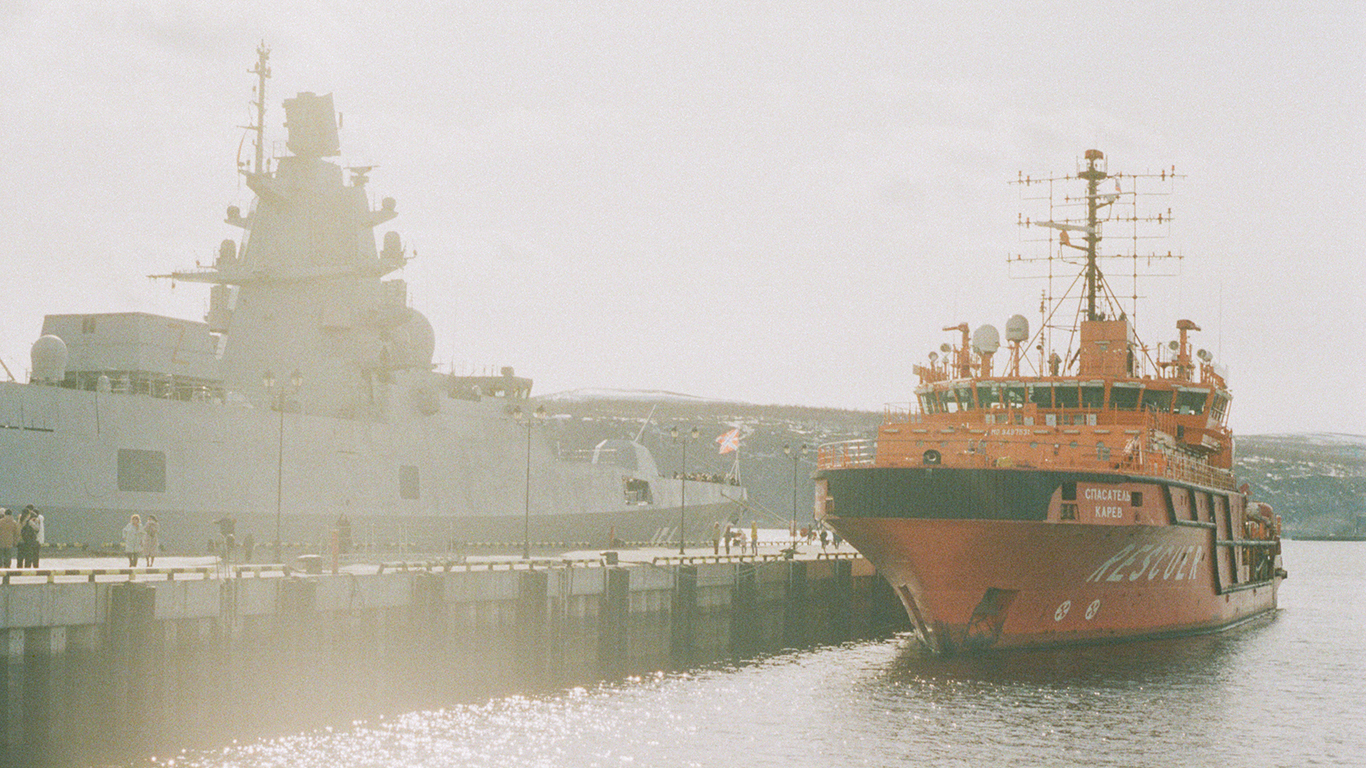

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Guided-missile frigate
- Year introduced: 2018
36. Gorya

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 1988
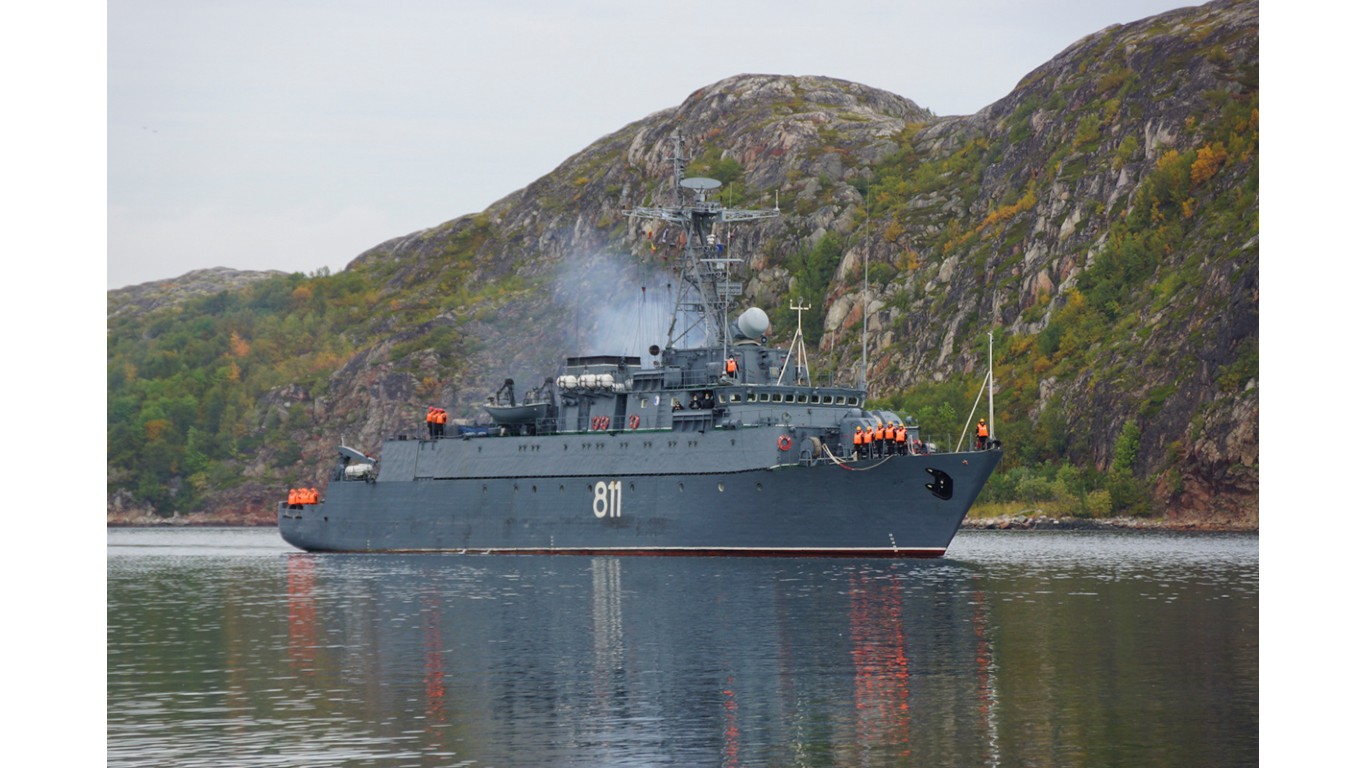
35. Ivan Gren

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Amphibious assault
- Year introduced: 2018
34. Kirov
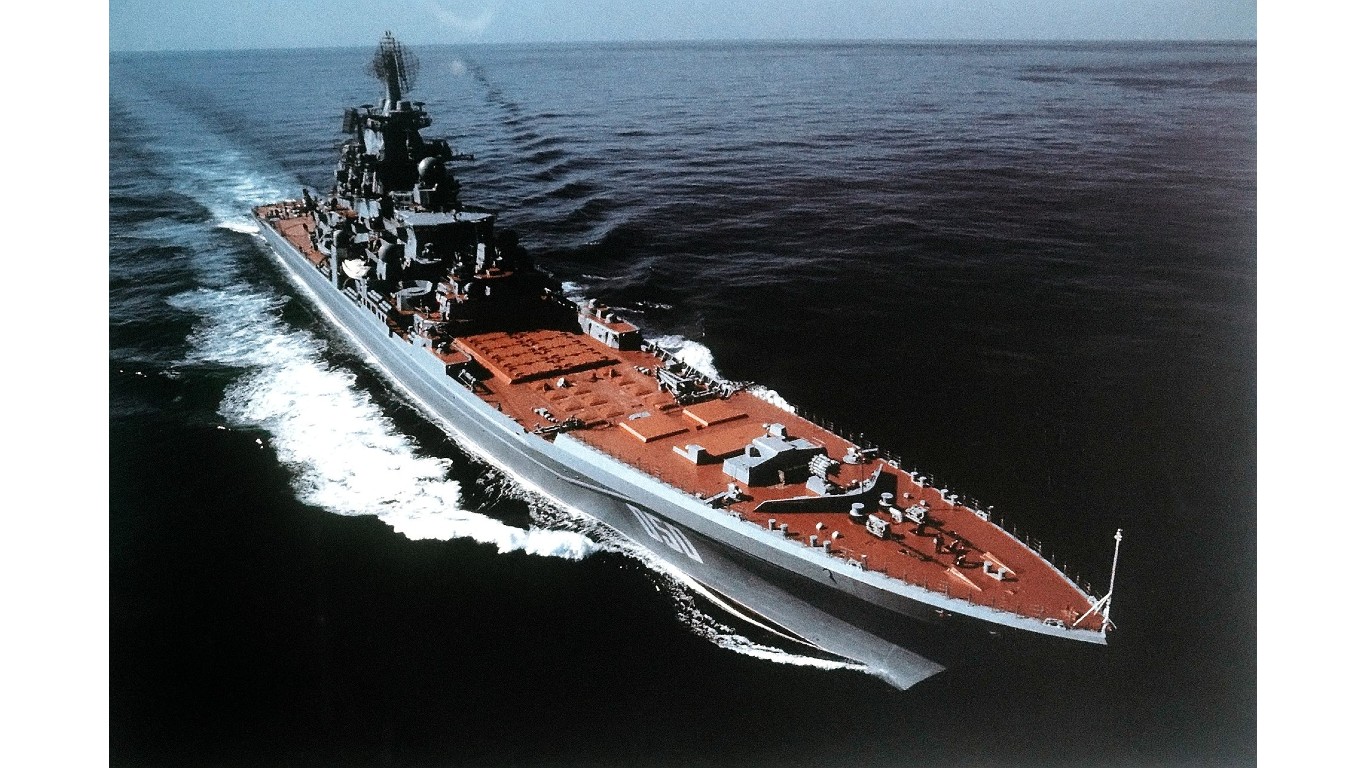

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Nuclear-powered guided-missile battlecruiser
- Year introduced: 1980
33. Krivak
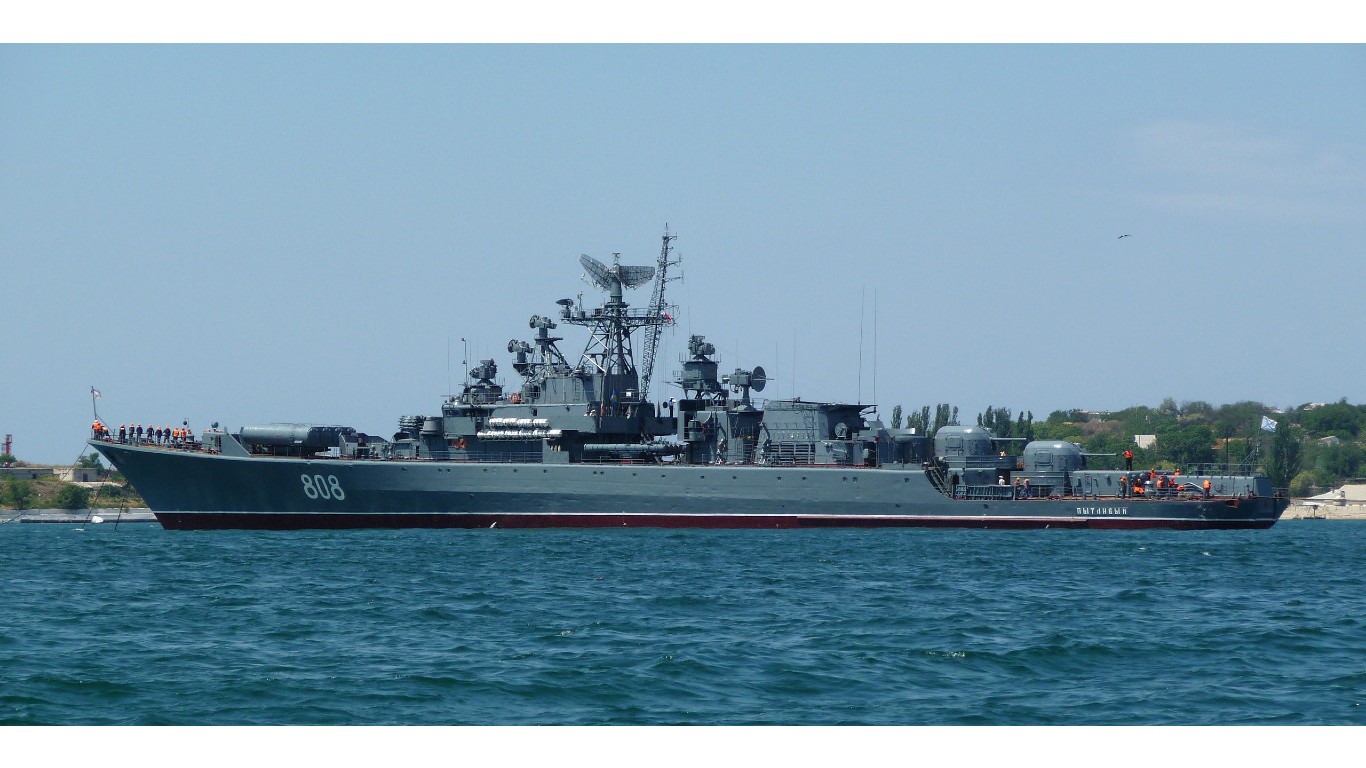

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Guided-missile frigate
- Year introduced: 1970
32. Neustrashimyy
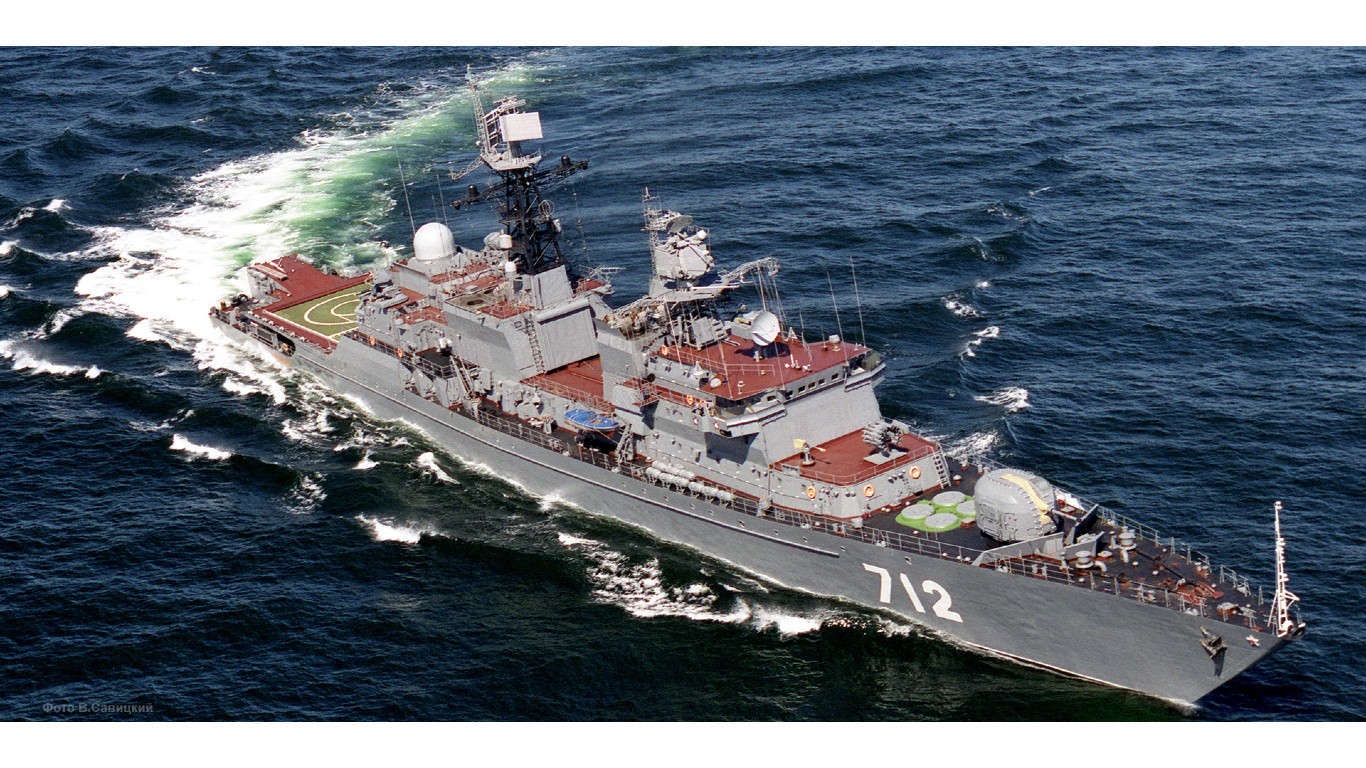

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Multirole frigate
- Year introduced: 1986
31. Sierra II
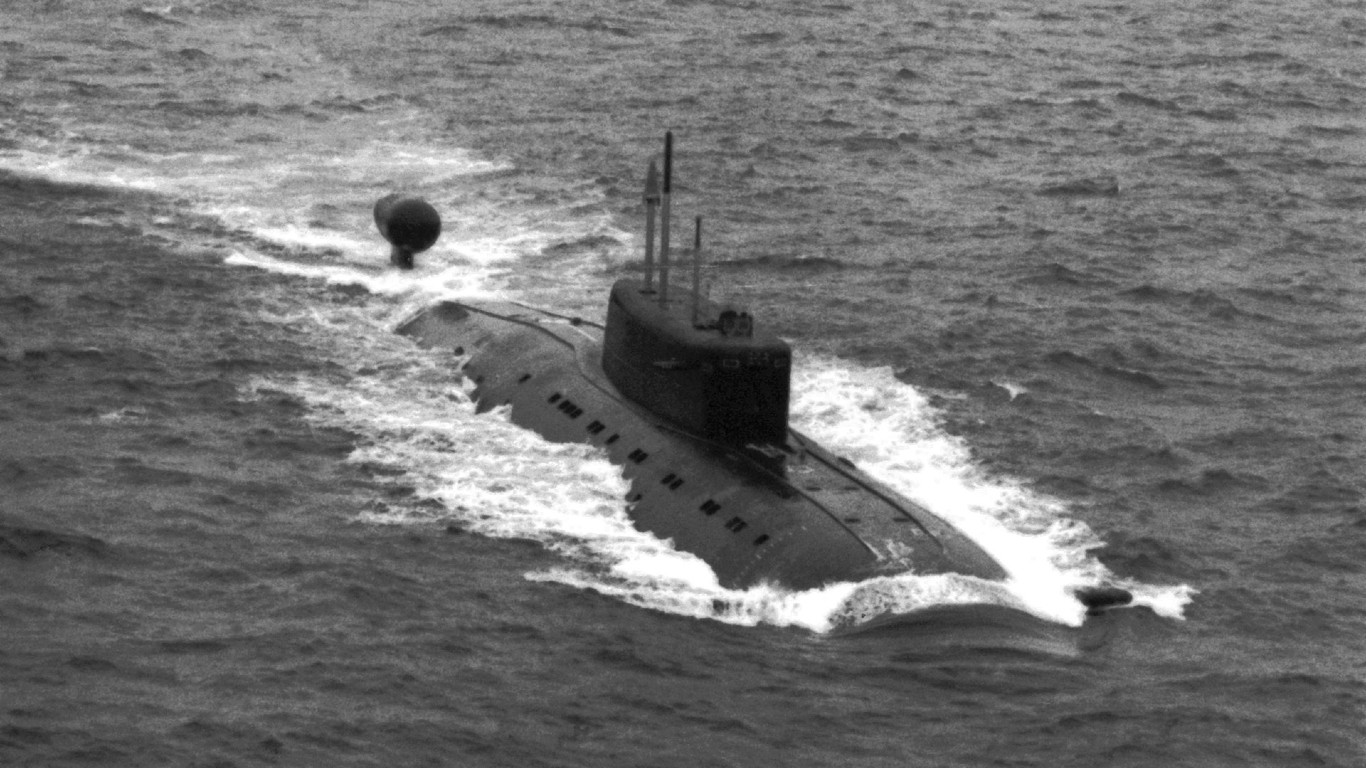

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Nuclear-powered attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1984
30. Slava
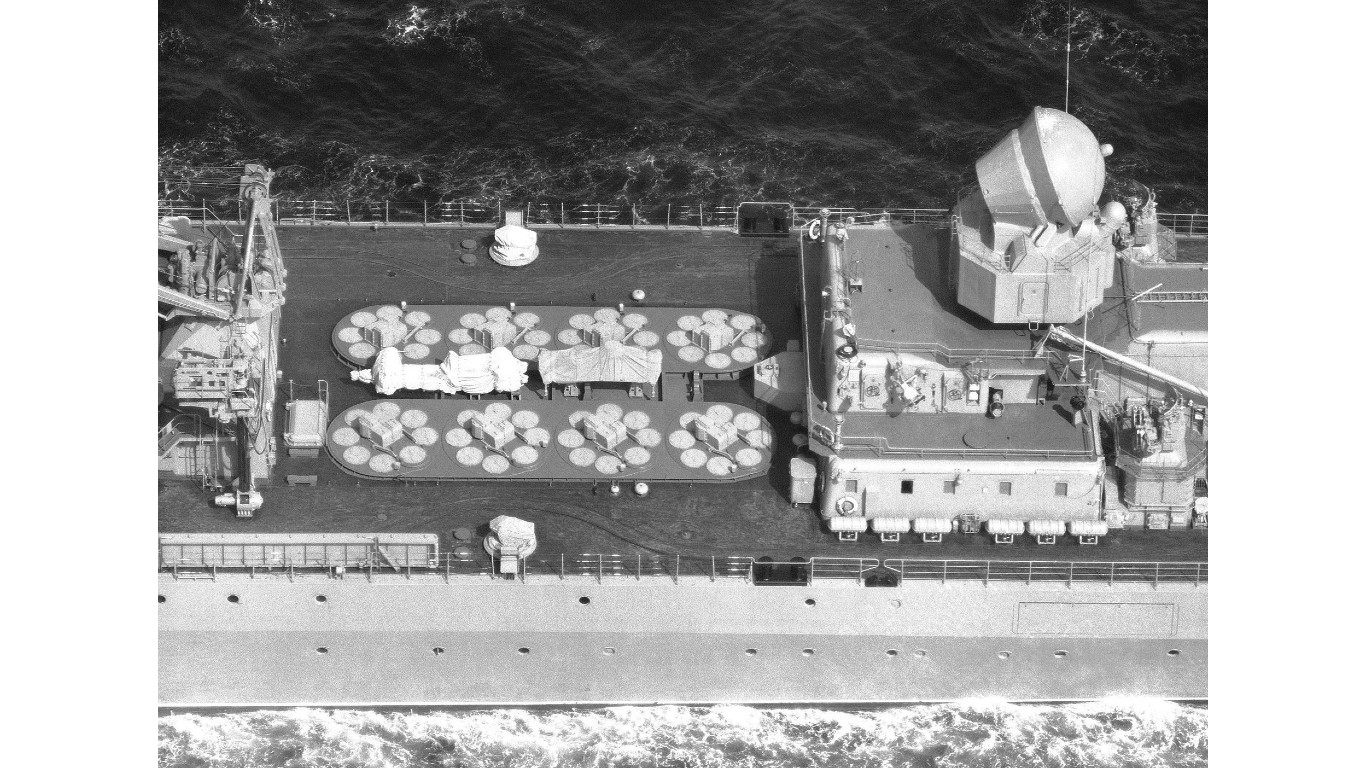

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Guided missile cruiser
- Year introduced: 1982
29. Victor
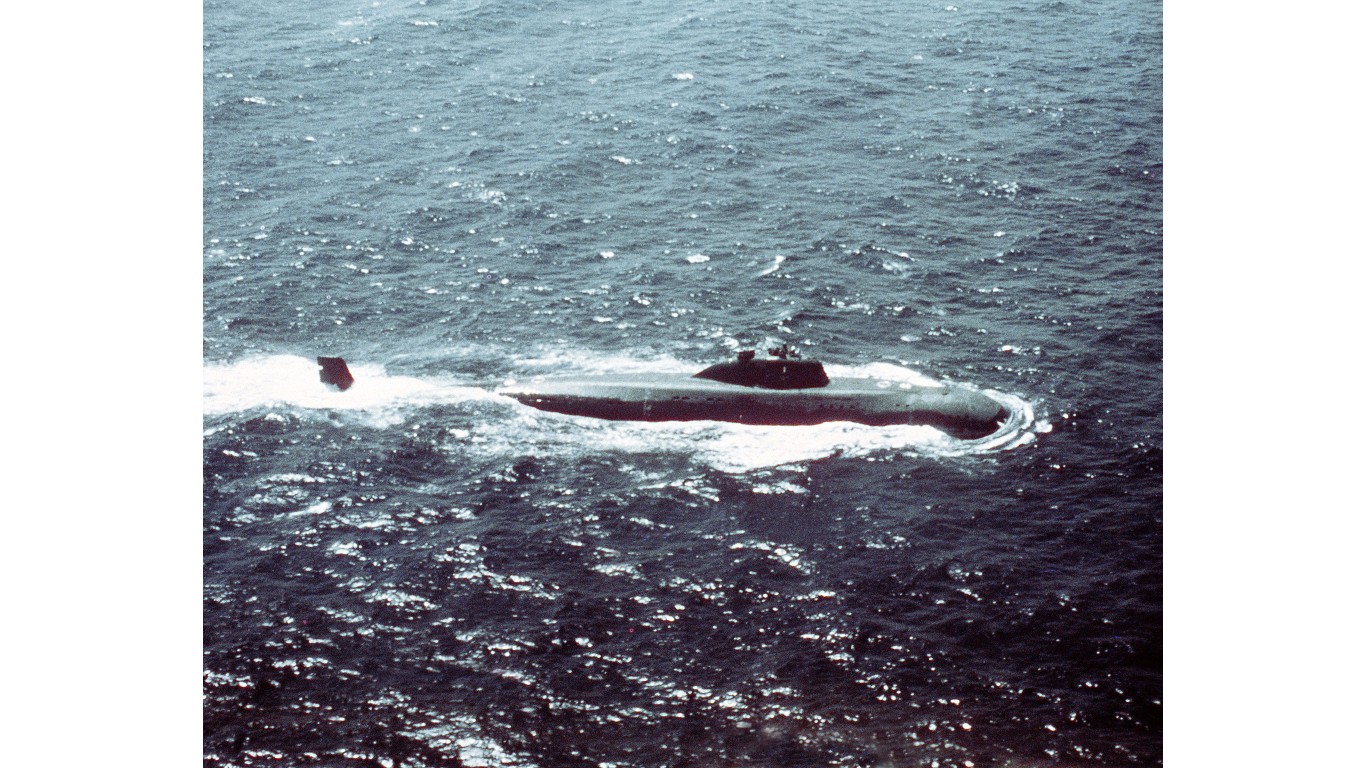
- Number in class: 2
- Type: Nuclear-powered attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1967
28. Yasen
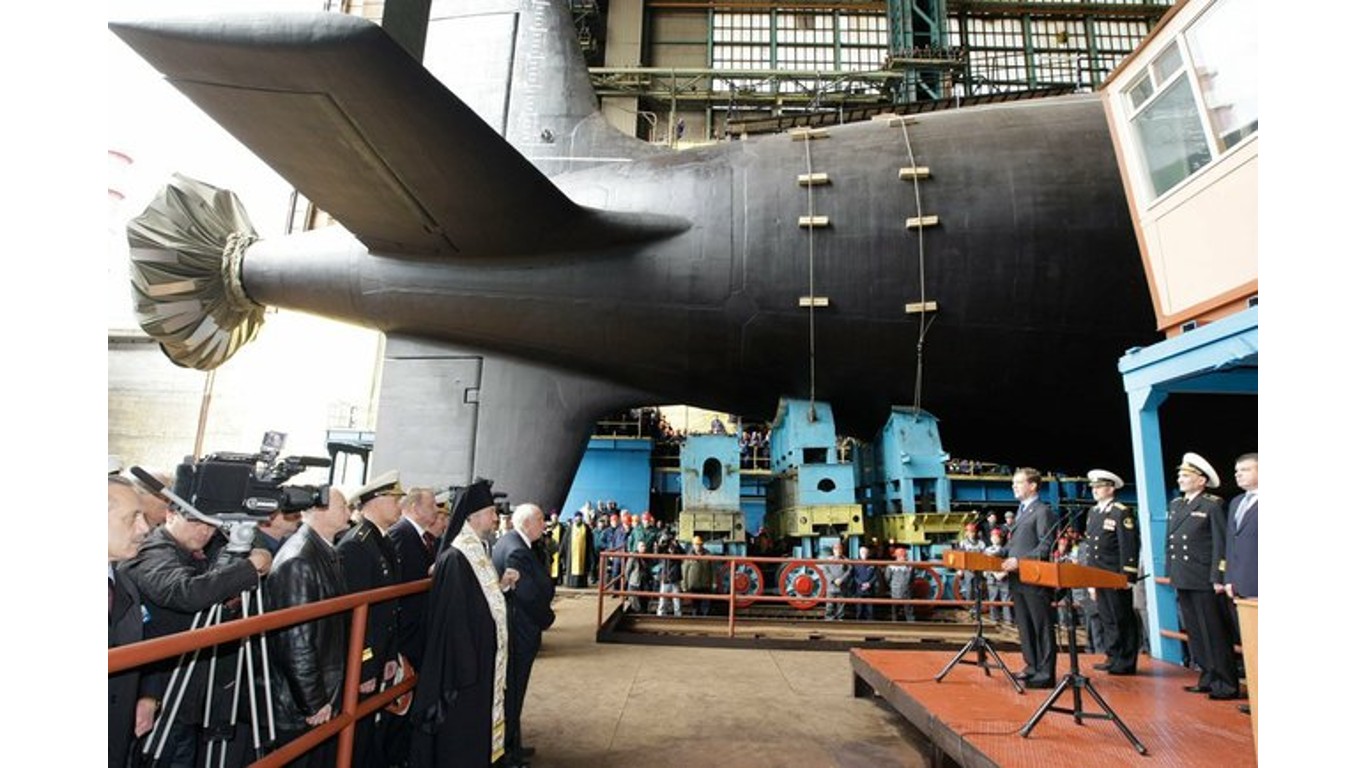

- Number in class: 2
- Type: Nuclear-powered cruise missile submarines
- Year introduced: 2013
27. Buyan
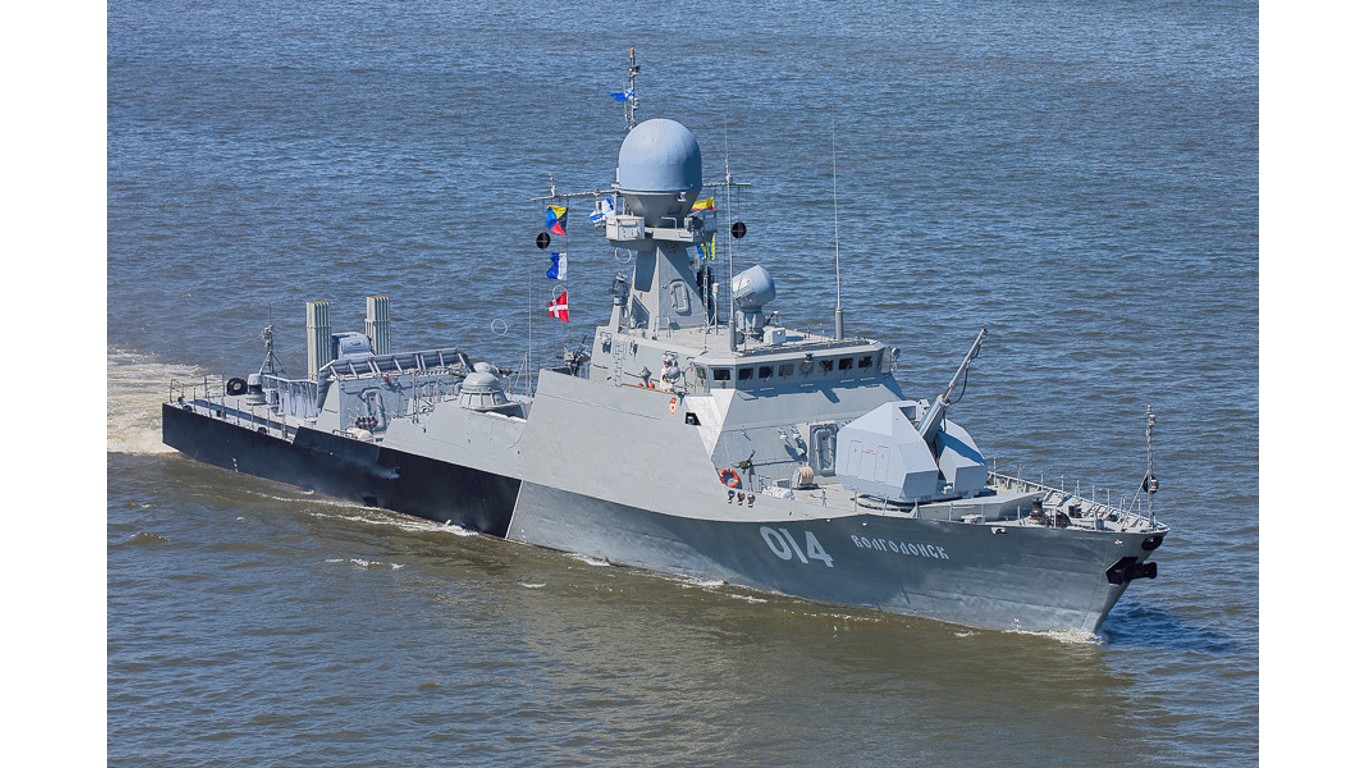

- Number in class: 3
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 2006
26. Grigorovich
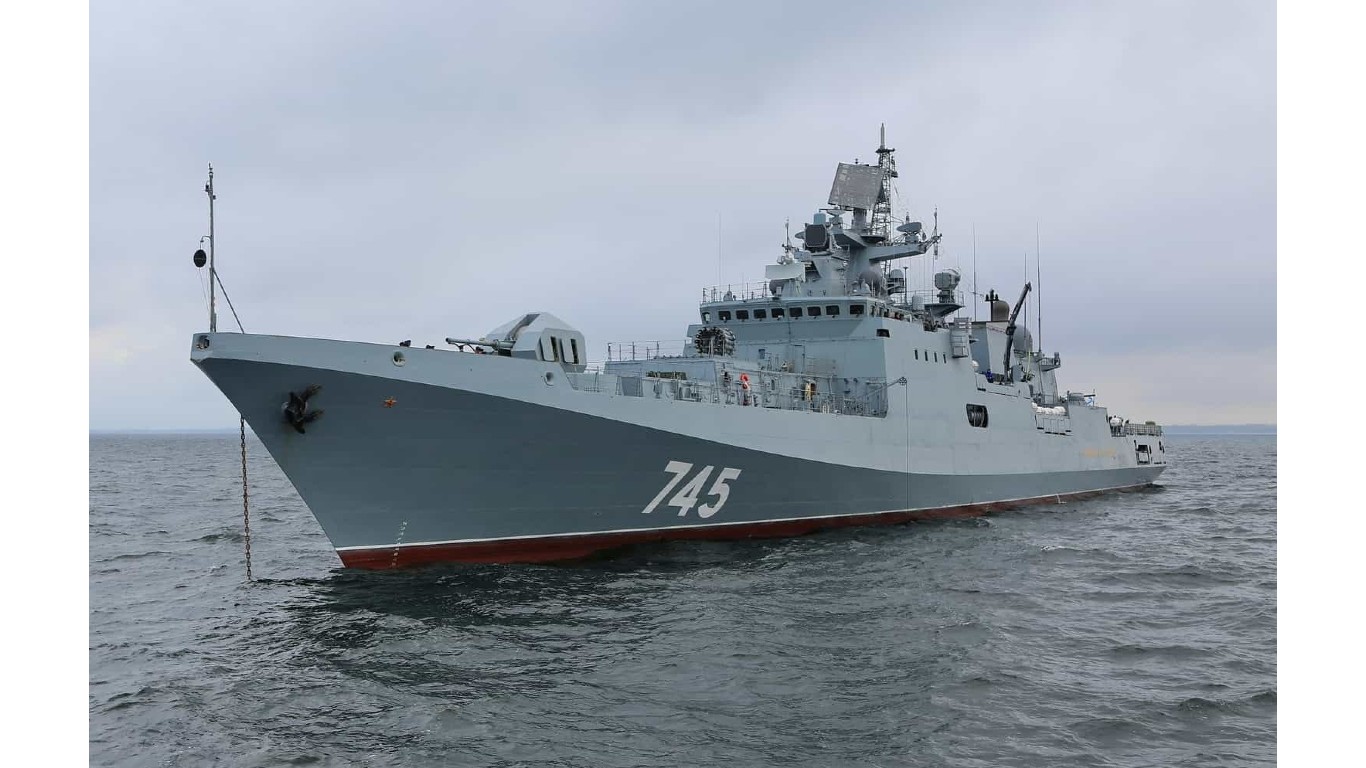

- Number in class: 3
- Type: Guided-missile frigate
- Year introduced: 2016
25. Karakurt
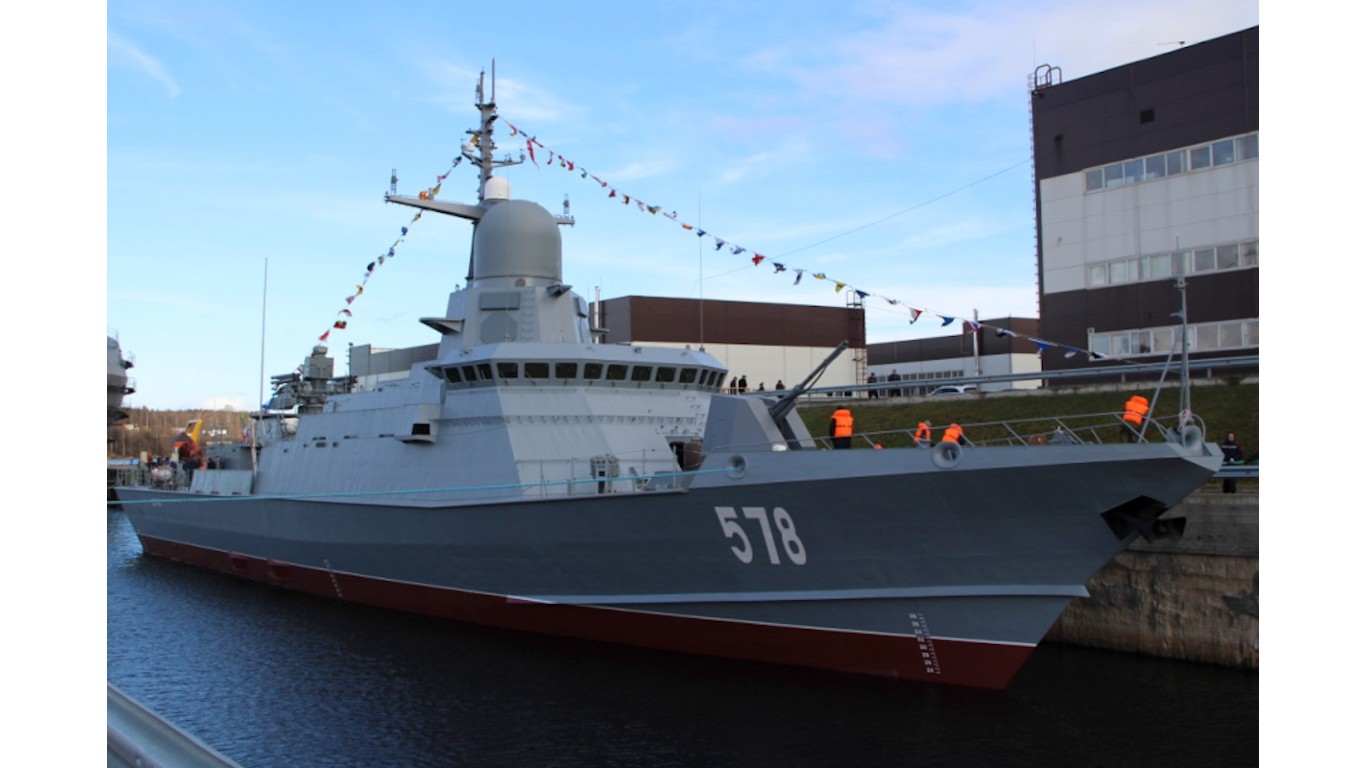

- Number in class: 3
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 2018
24. Project 22160
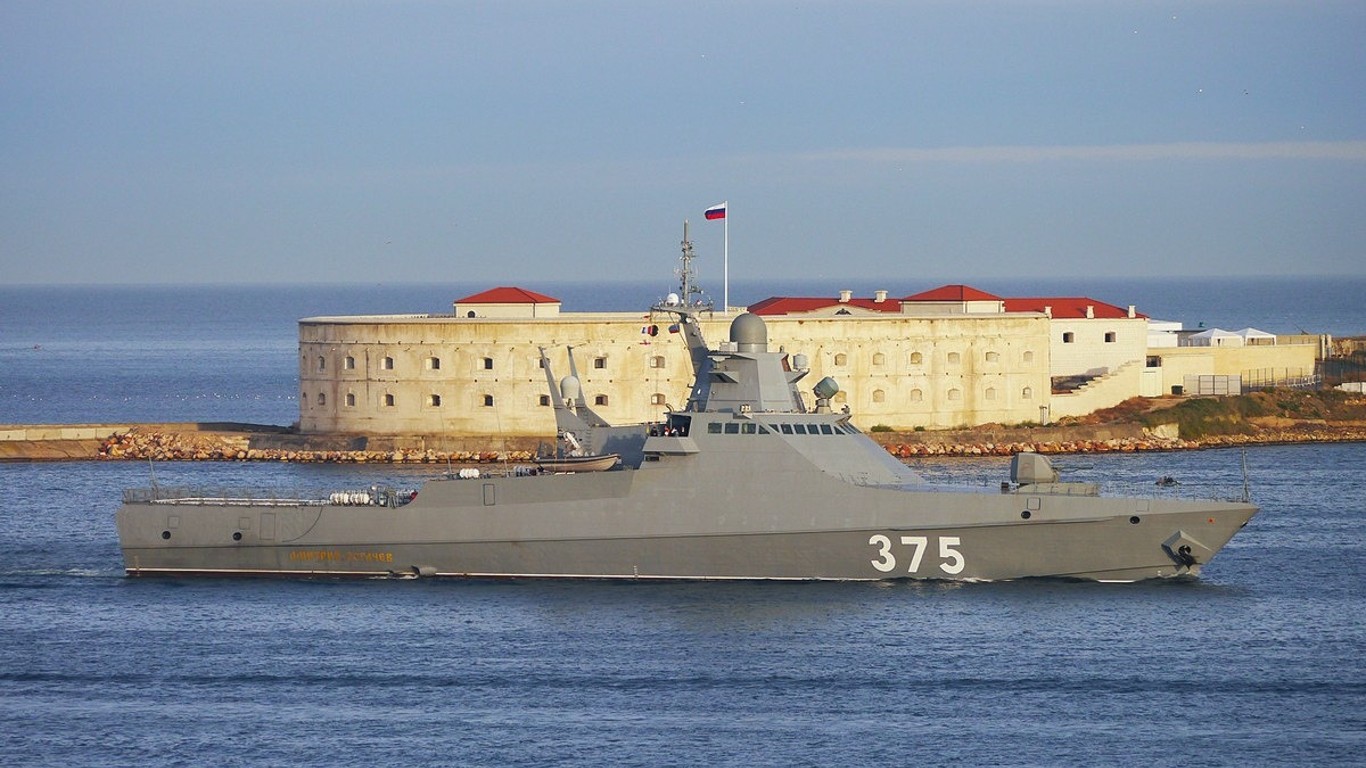

- Number in class: 3
- Type: Offshore patrol vessel
- Year introduced: 2018
23. Alligator
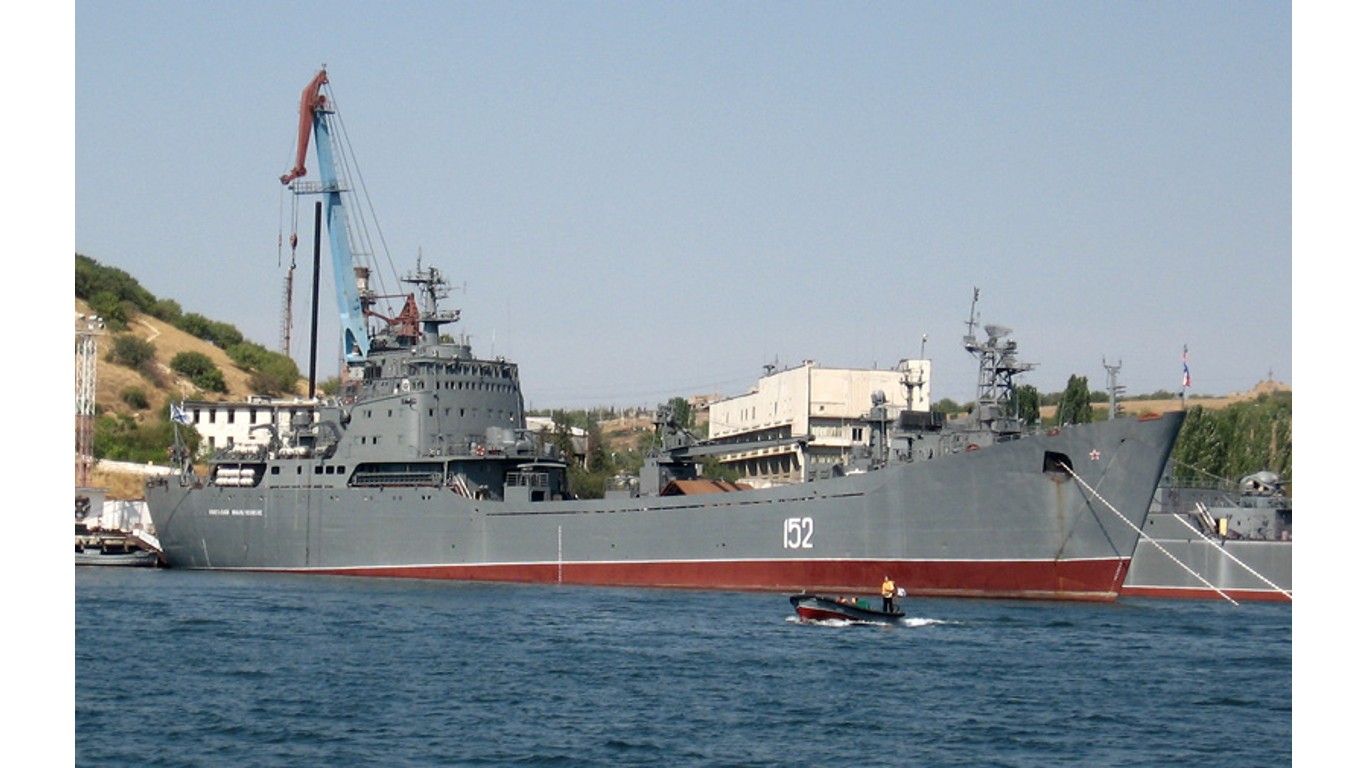

- Number in class: 4
- Type: Amphibious assault
- Year introduced: 1965
22. Borei
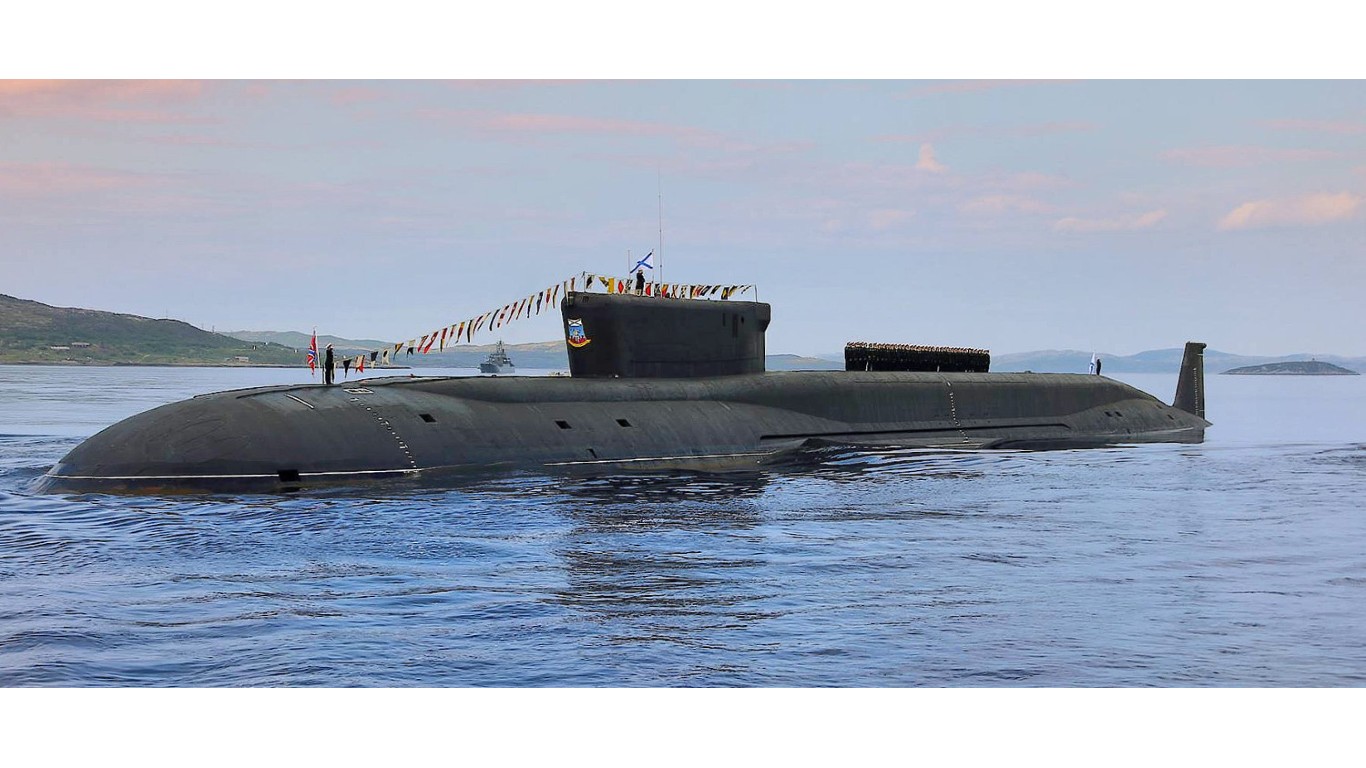

- Number in class: 4
- Type: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine
- Year introduced: 2013
21. Korund
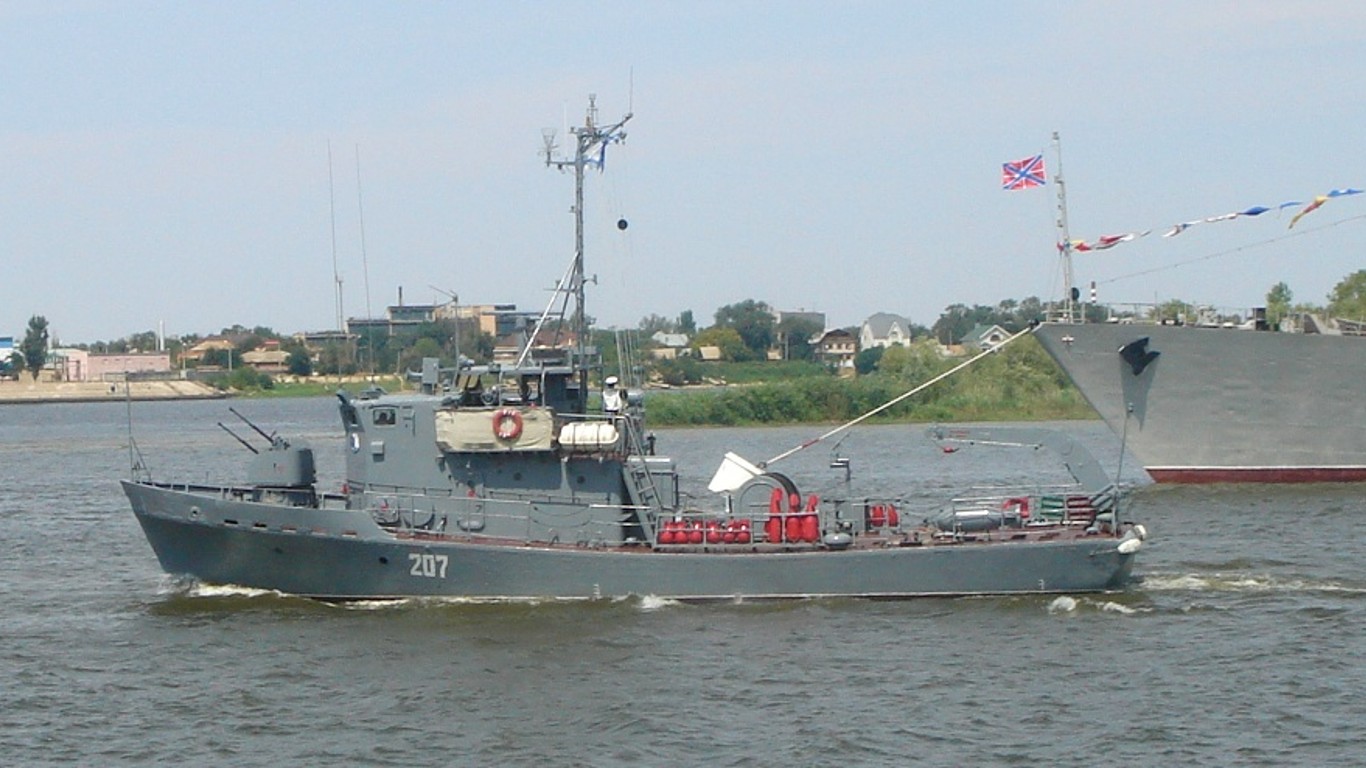

- Number in class: 4
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 1967
20. Shmel

- Number in class: 4
- Type: Armored artillery gunboat
- Year introduced: 1967
19. Sovremenny
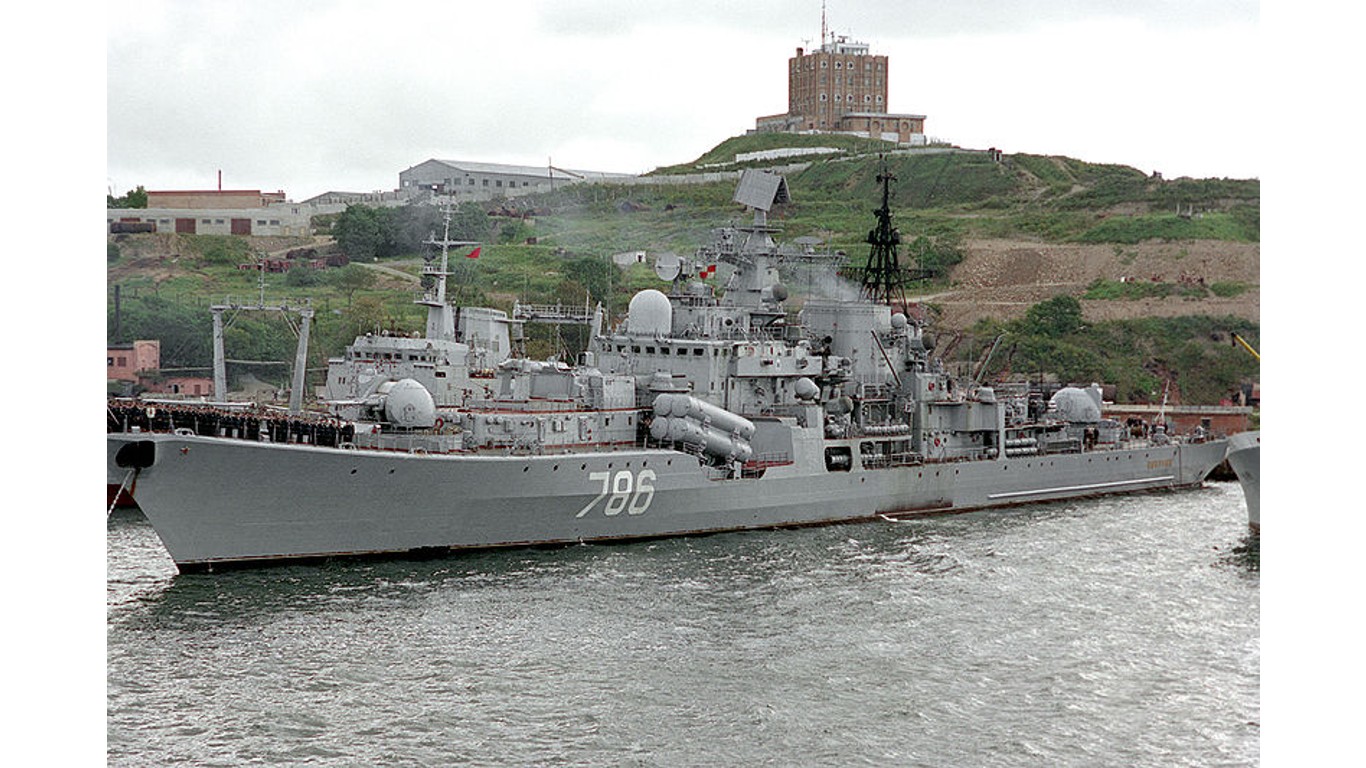

- Number in class: 4
- Type: Anti-aircraft guided-missile destroyer
- Year introduced: 1980
18. Alexandrit
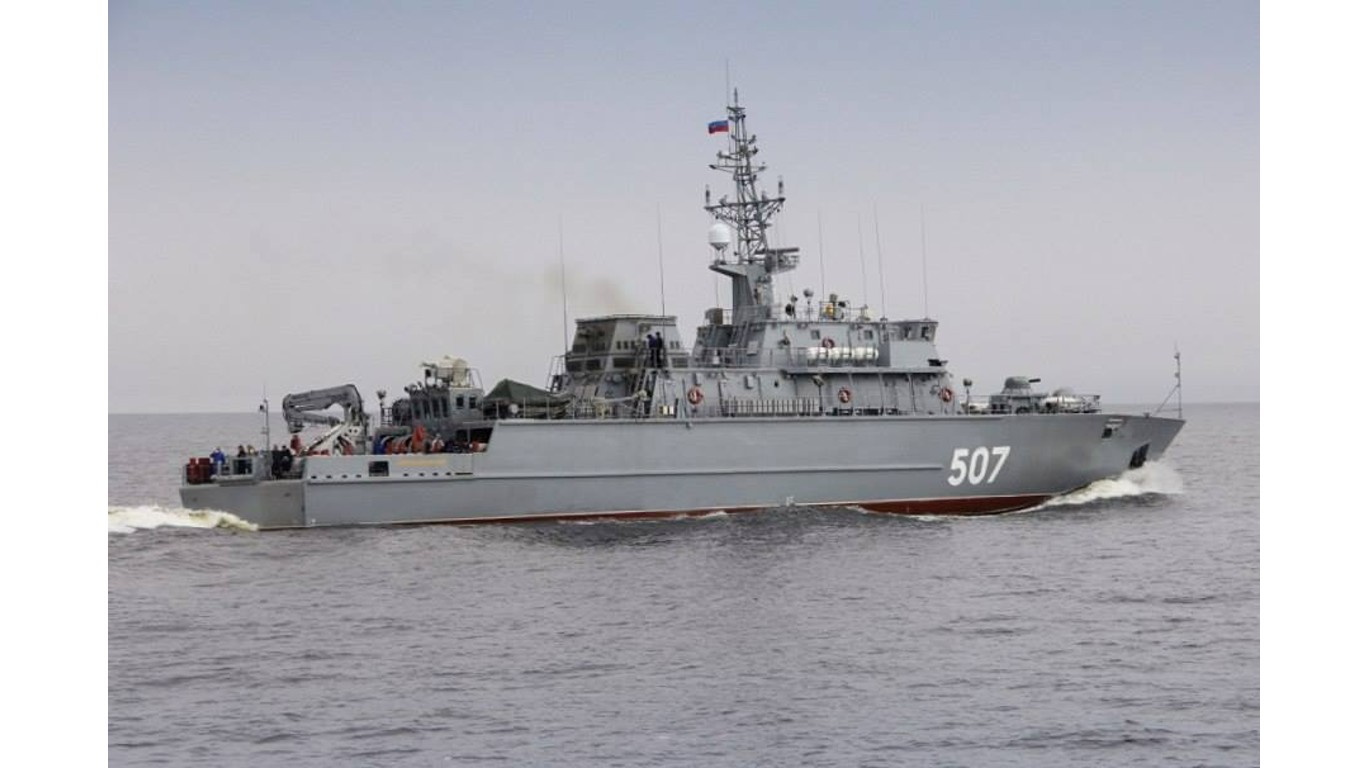

- Number in class: 5
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 2016
17. Delta IV
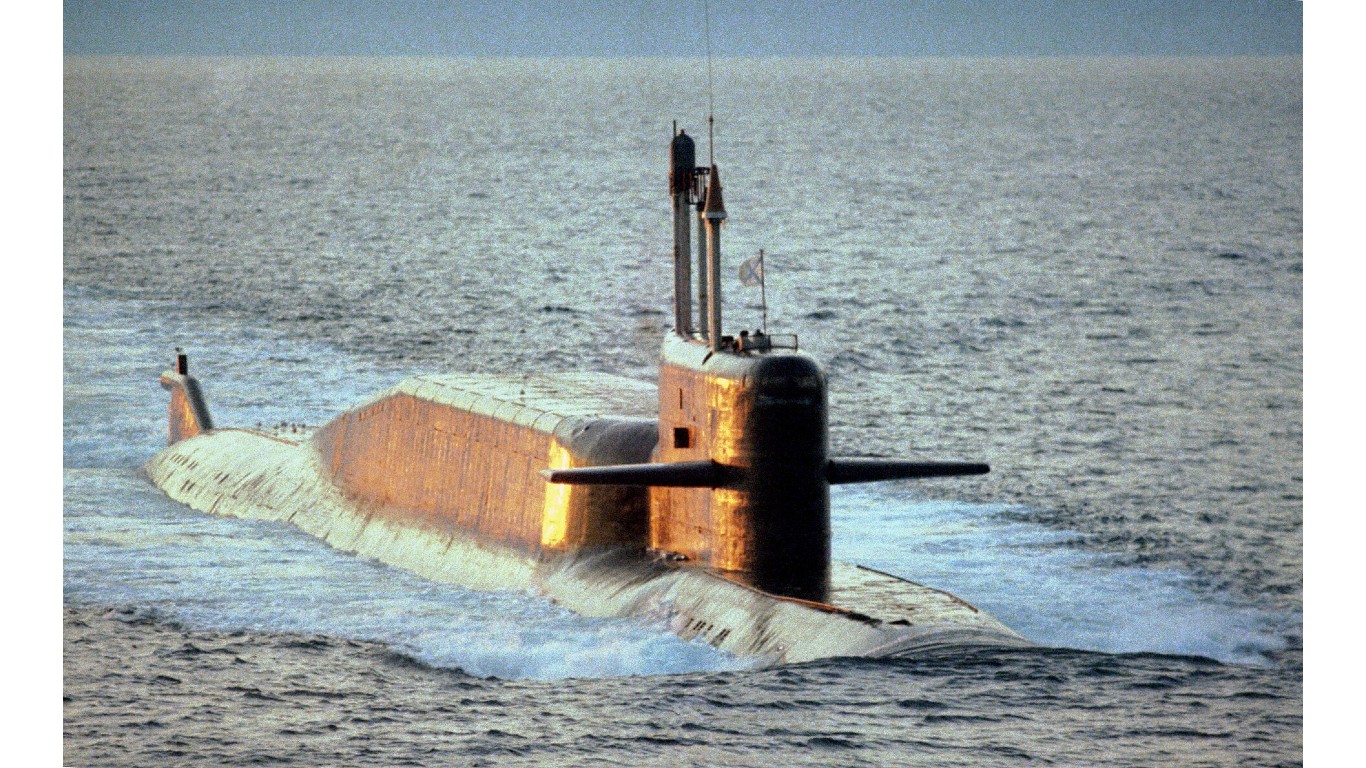

- Number in class: 6
- Type: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1984
16. Parchim
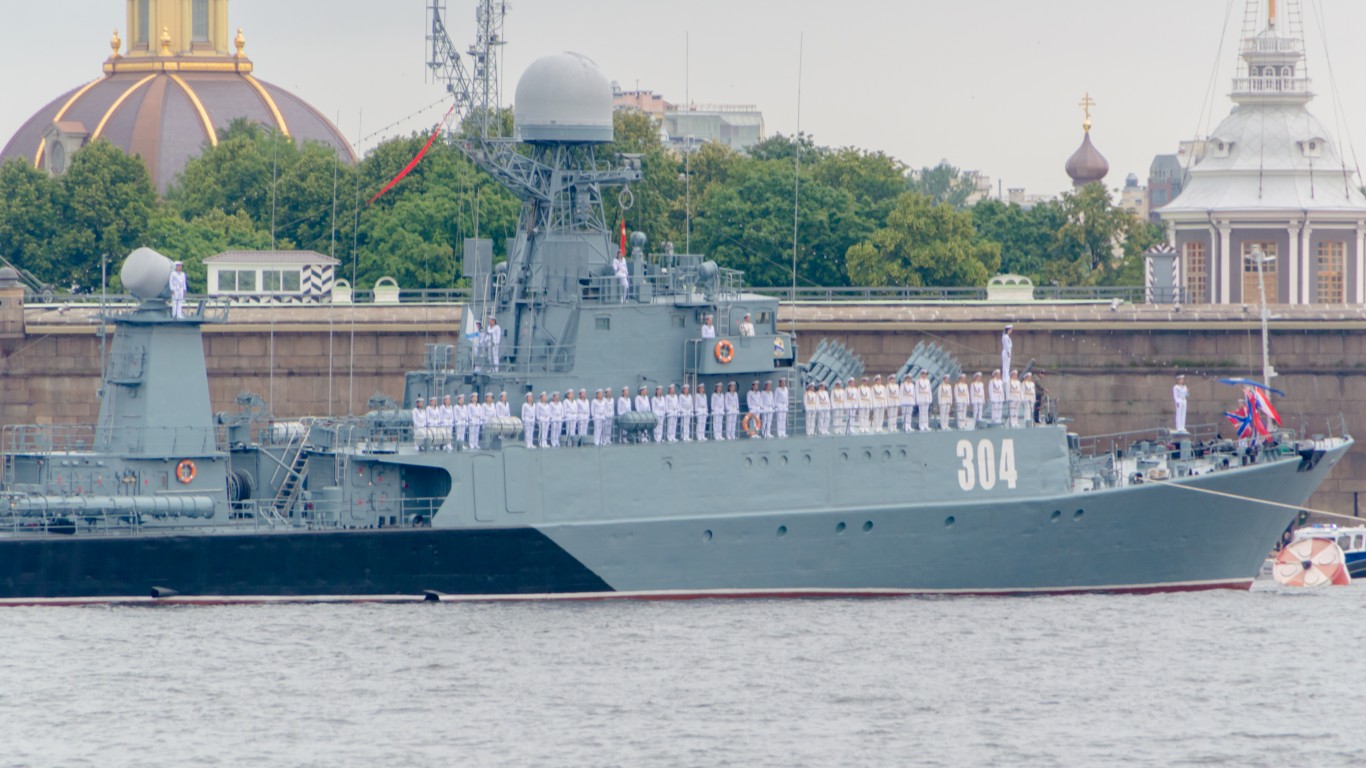

- Number in class: 6
- Type: Anti-submarine corvette
- Year introduced: 1993
15. Lida
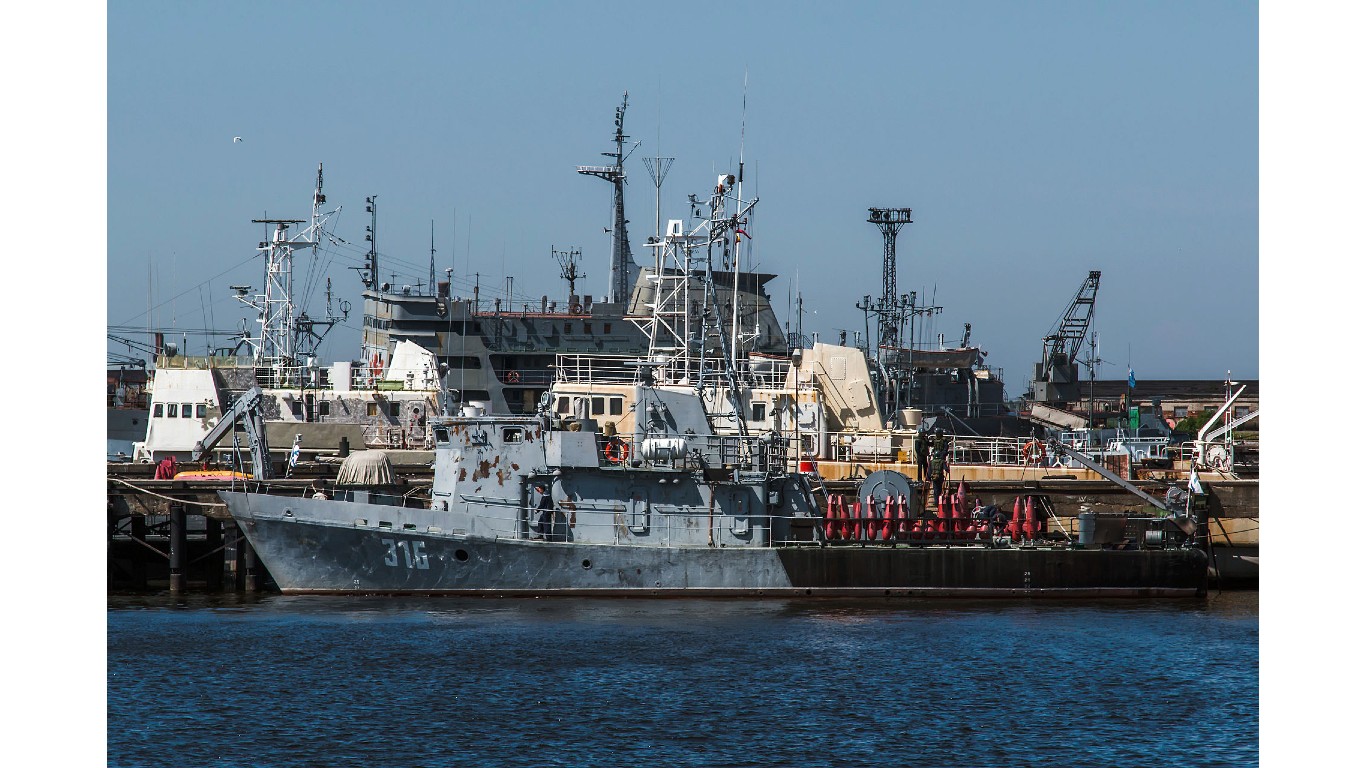

- Number in class: 7
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 1989
14. Steregushchiy
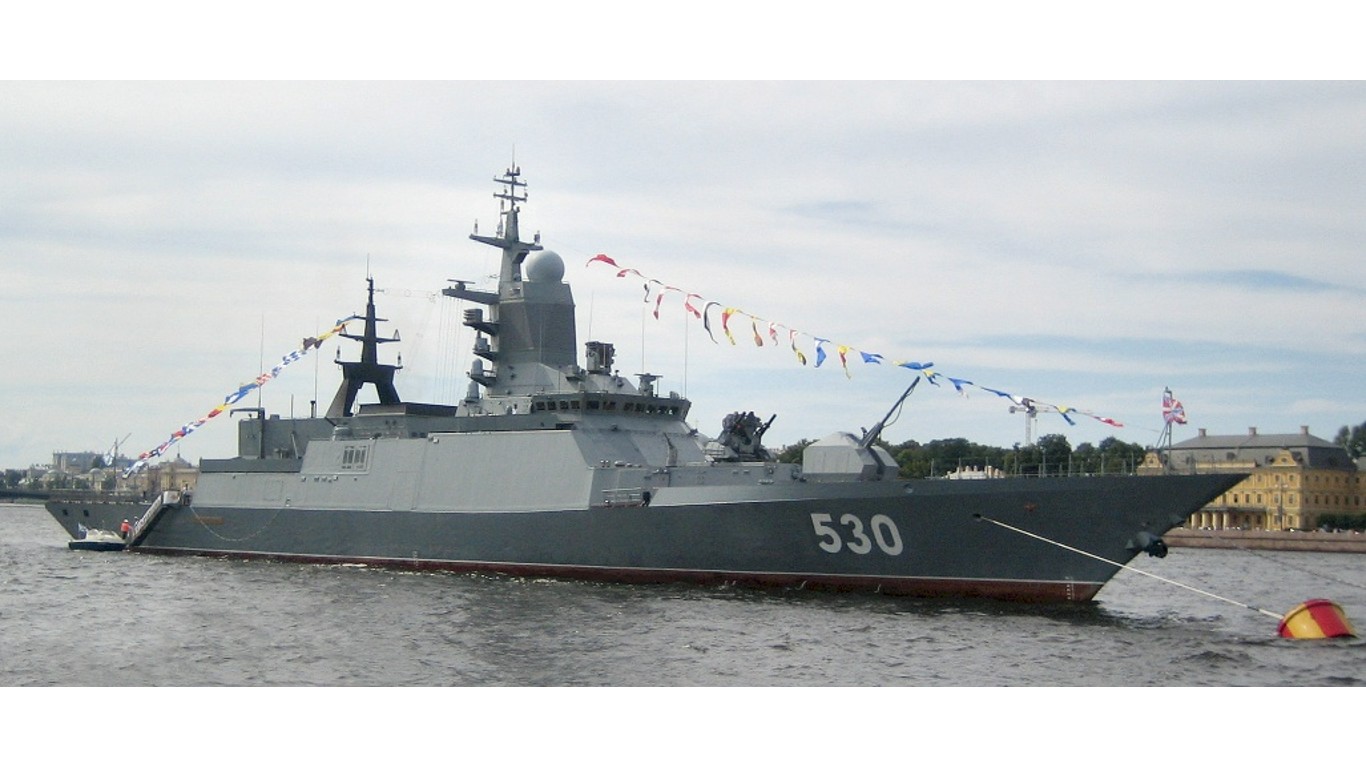

- Number in class: 7
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 2008
13. Natya
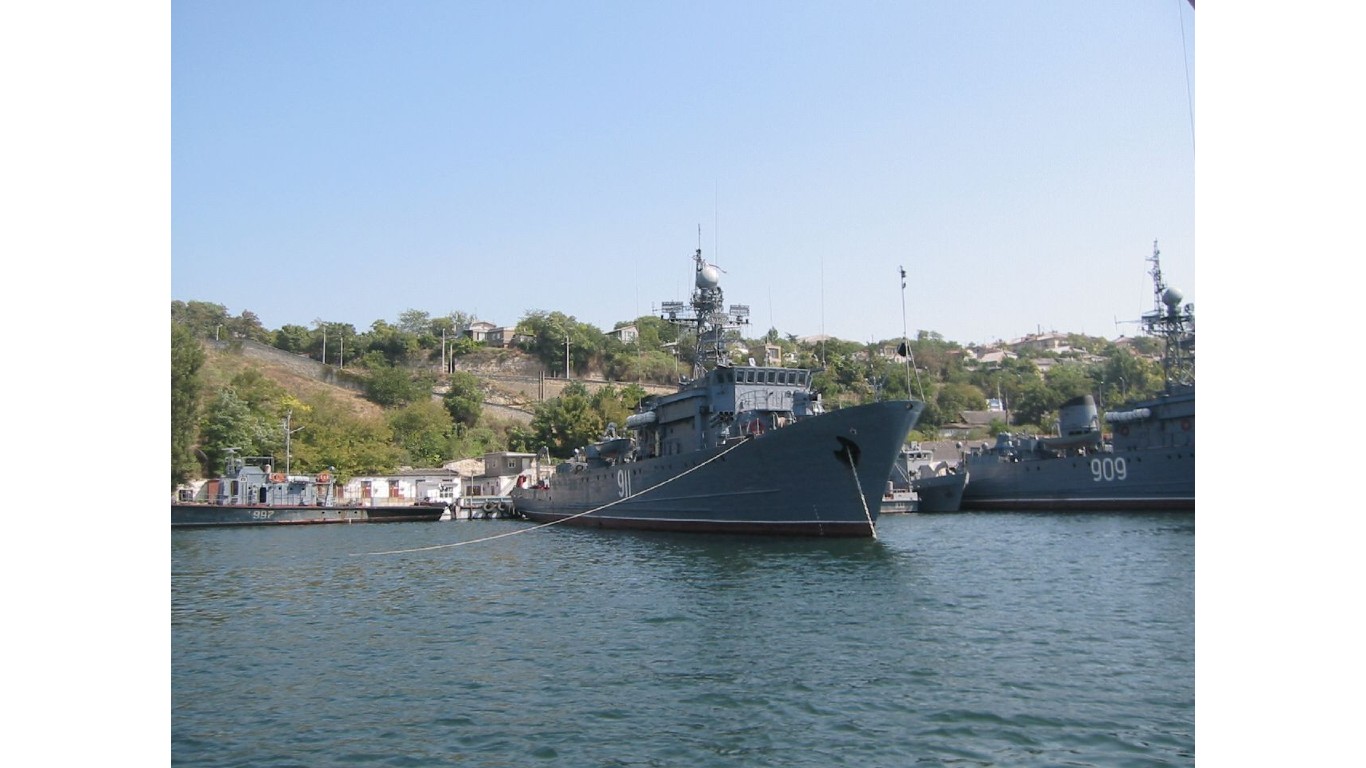

- Number in class: 8
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 1970
12. Oscar II
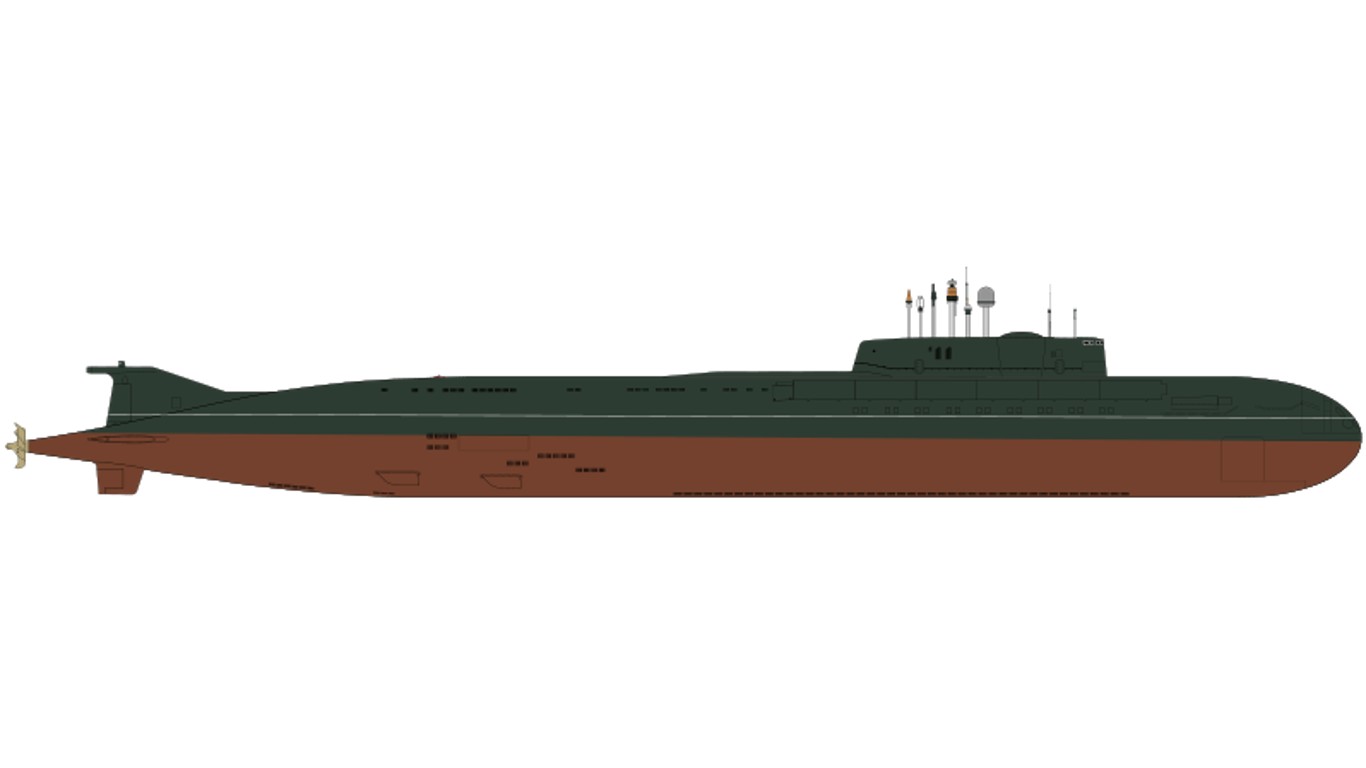
- Number in class: 8
- Type: Nuclear-powered cruise missile submarines
- Year introduced: 1980
11. Udaloy
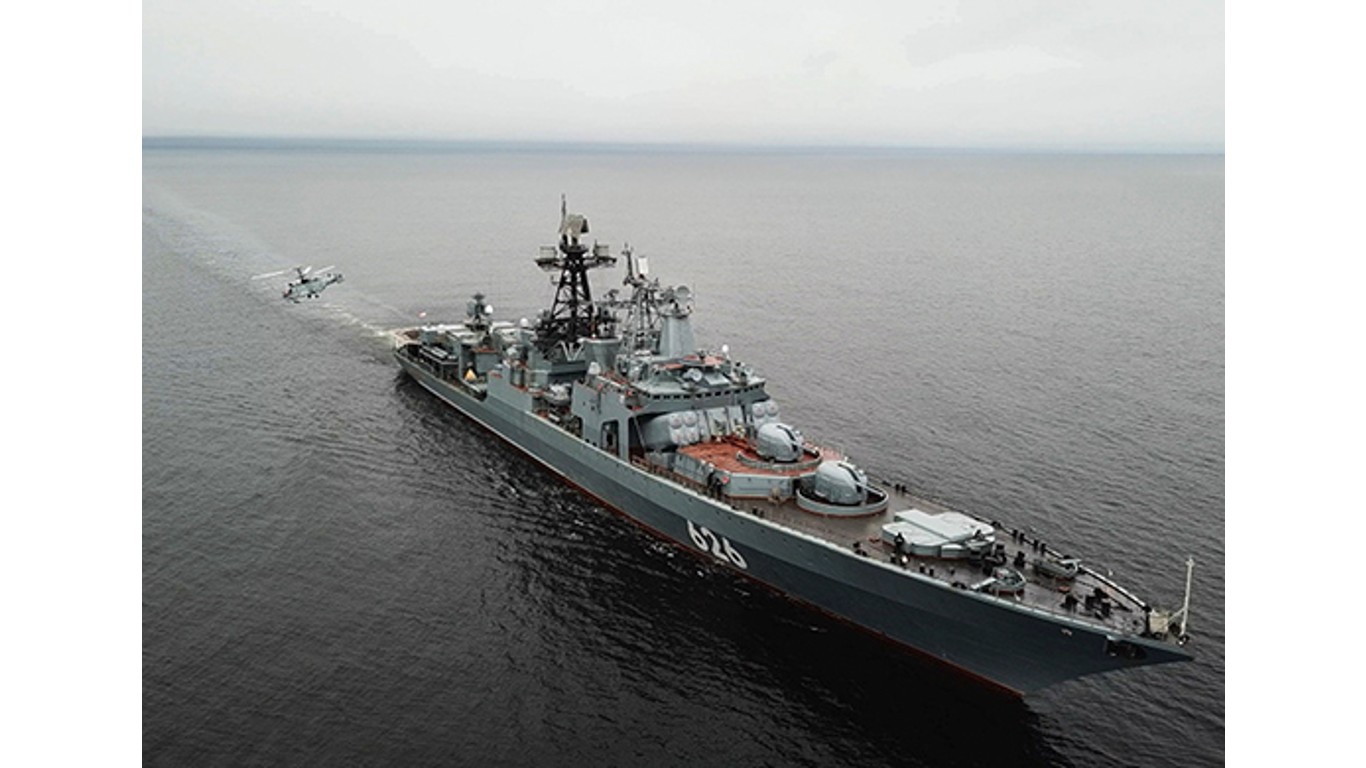

- Number in class: 8
- Type: Anti-submarine guided-missile destroyer
- Year introduced: 1980
10. Akula
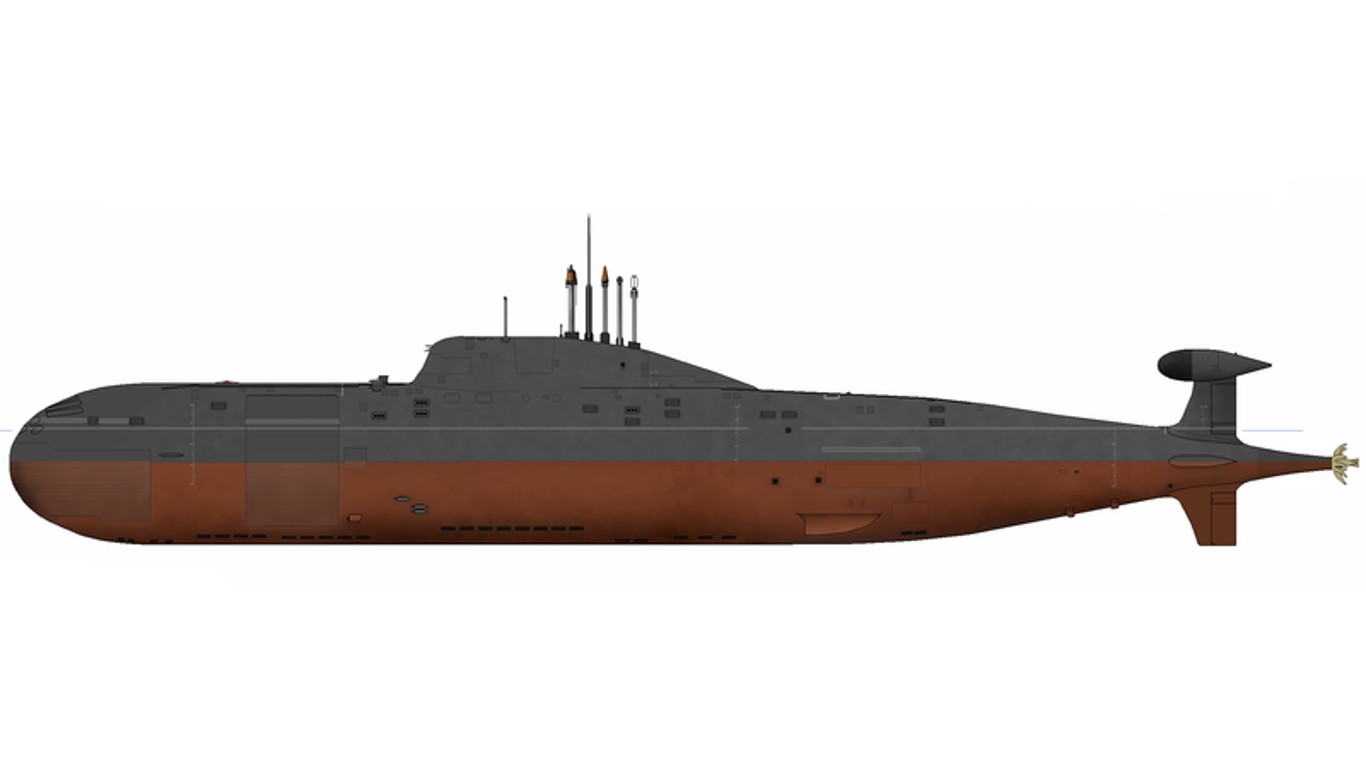

- Number in class: 10
- Type: Nuclear-powered attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1984
9. Buyan M
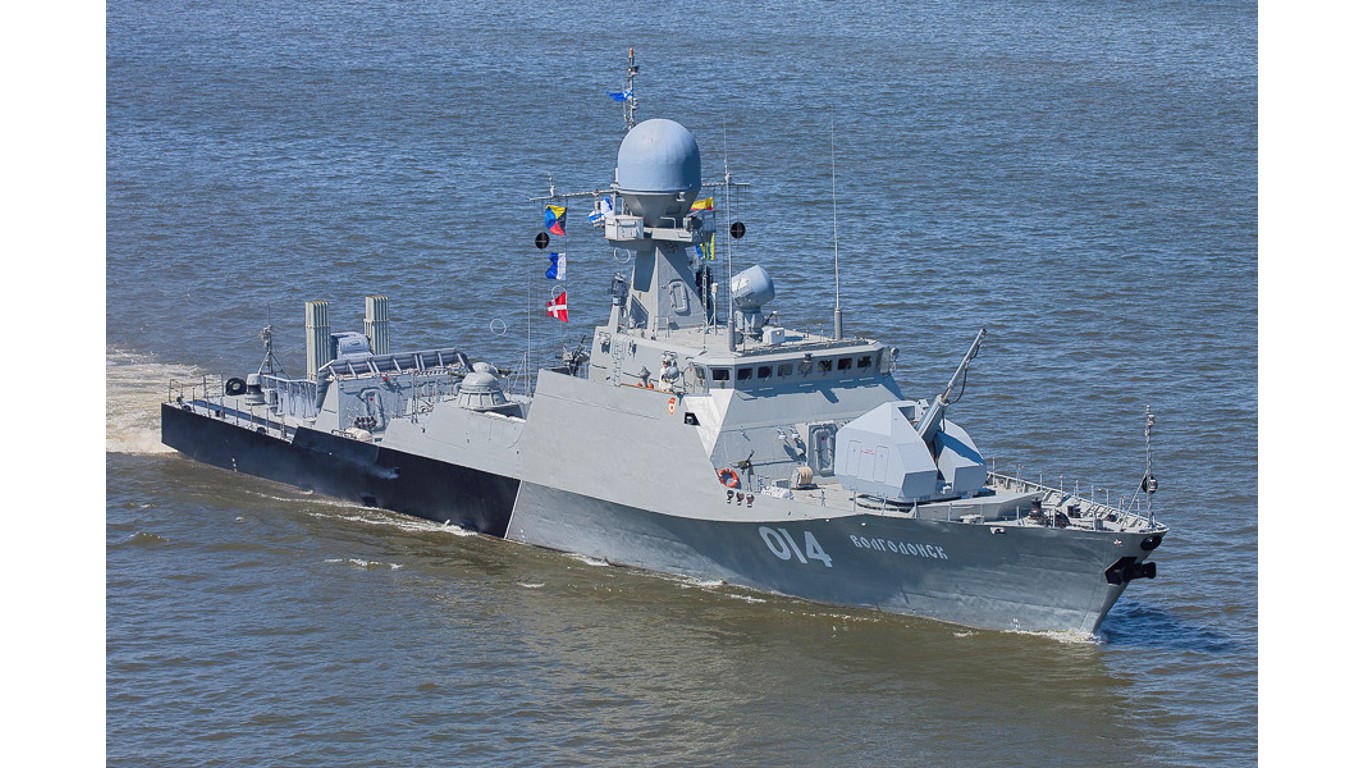

- Number in class: 9
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 2006
8. Kilo II
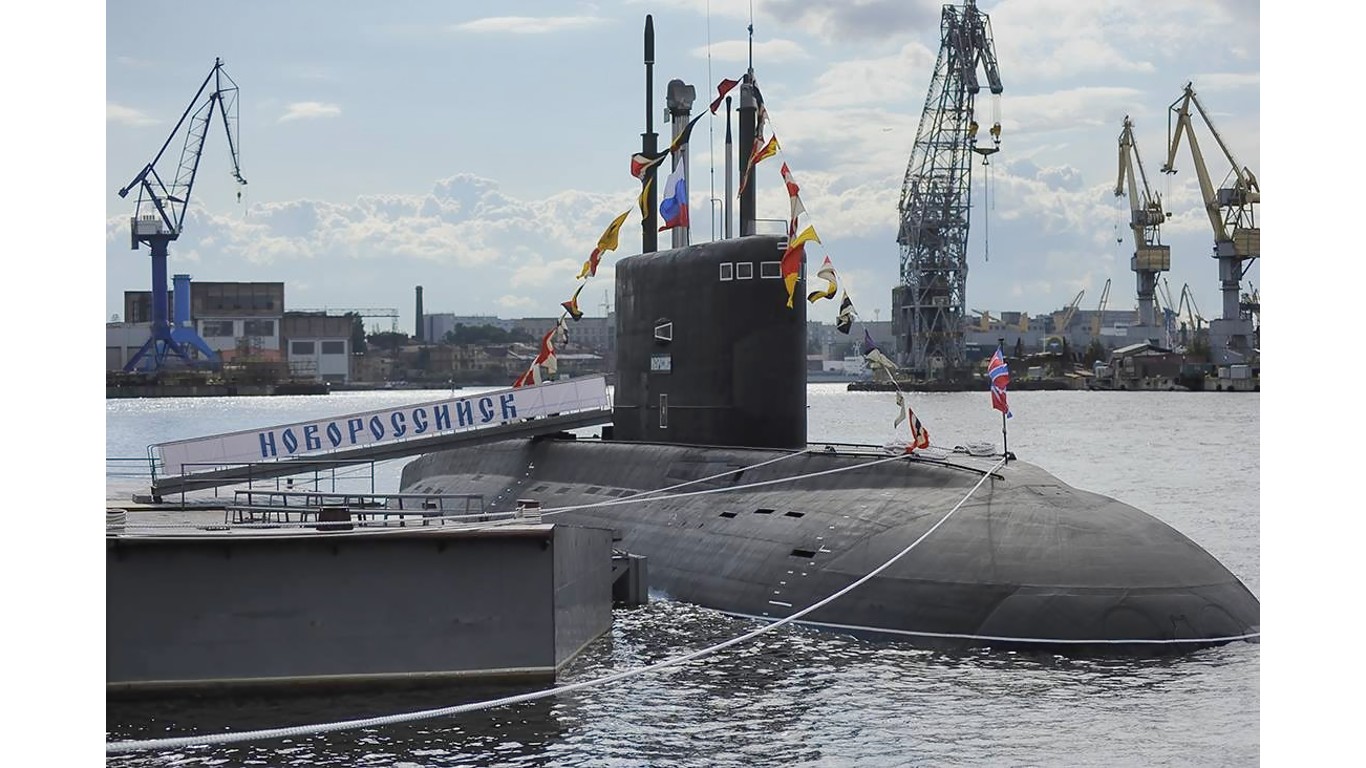

- Number in class: 9
- Type: Attack submarine
- Year introduced: 1980
7. Nanuchka
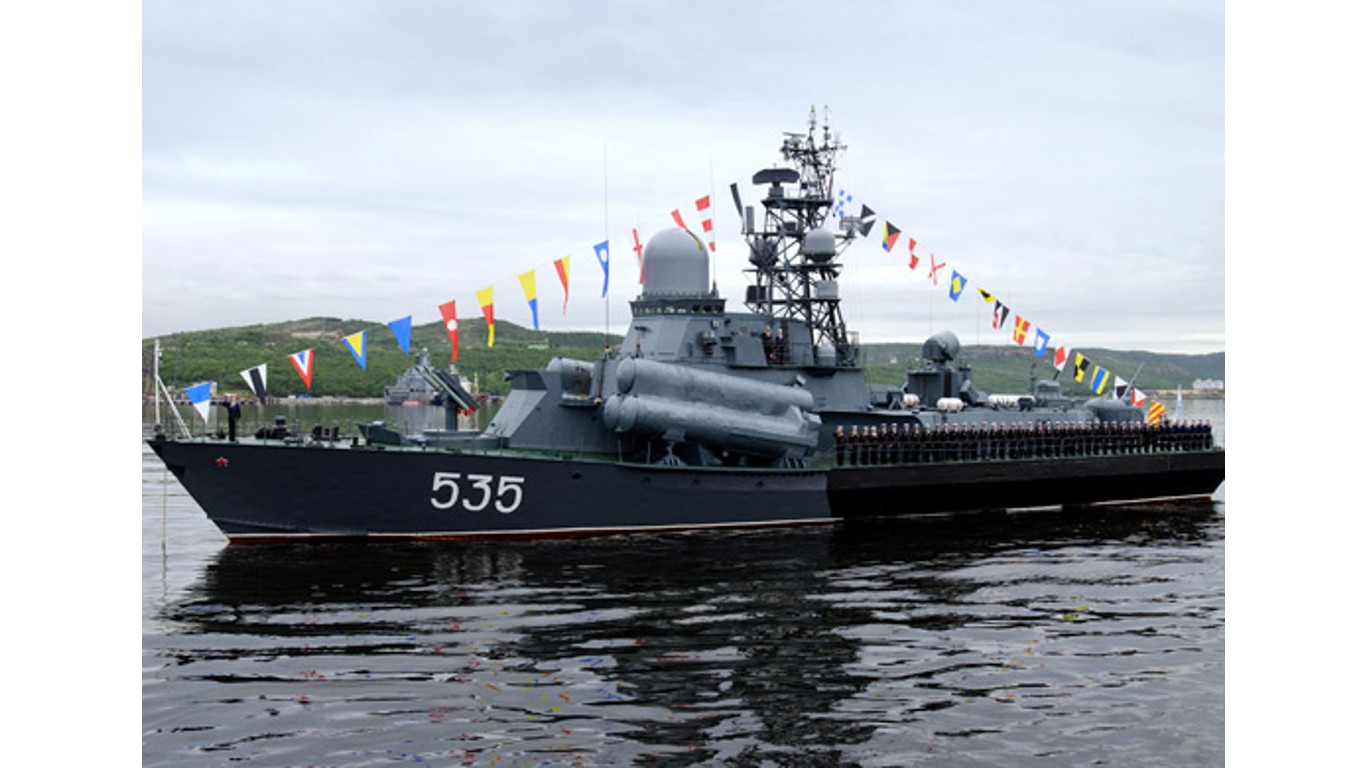

- Number in class: 10
- Type: Guided-missile corvette
- Year introduced: 1970
6. Kilo
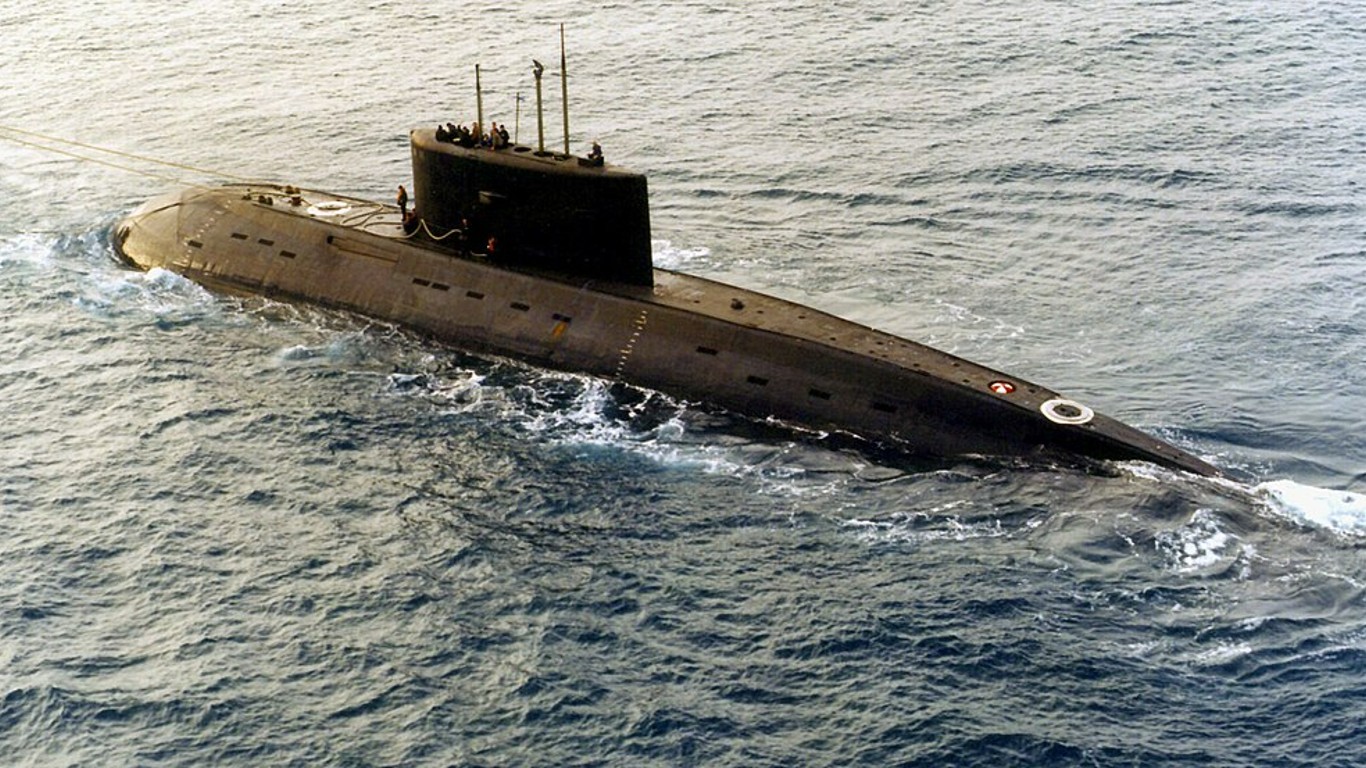

- Number in class: 12
- Type: Attack submarine
- Year introduced: 2014
5. Ropucha
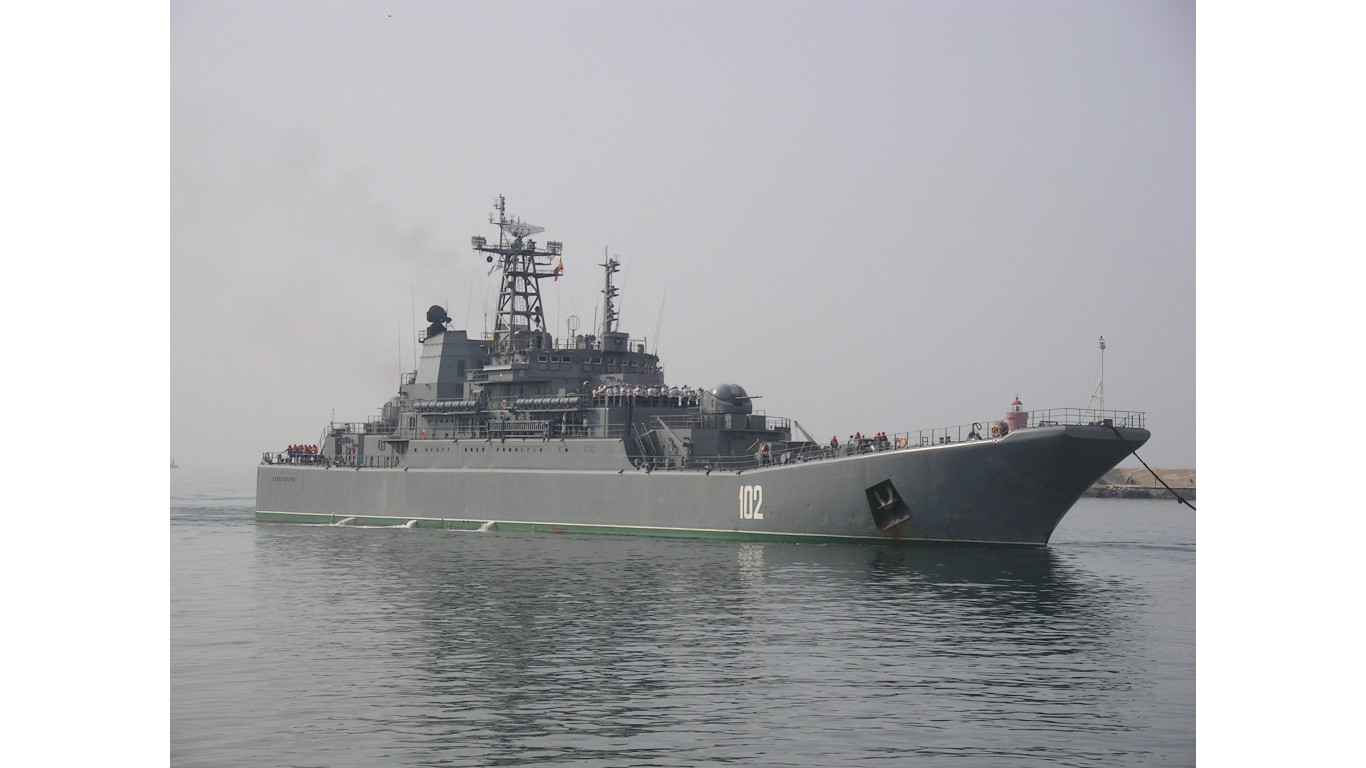

- Number in class: 15
- Type: Amphibious assault
- Year introduced: 1974
4. Grachonok

- Number in class: 20
- Type: Anti-saboteurship
- Year introduced: 2009
3. Grisha
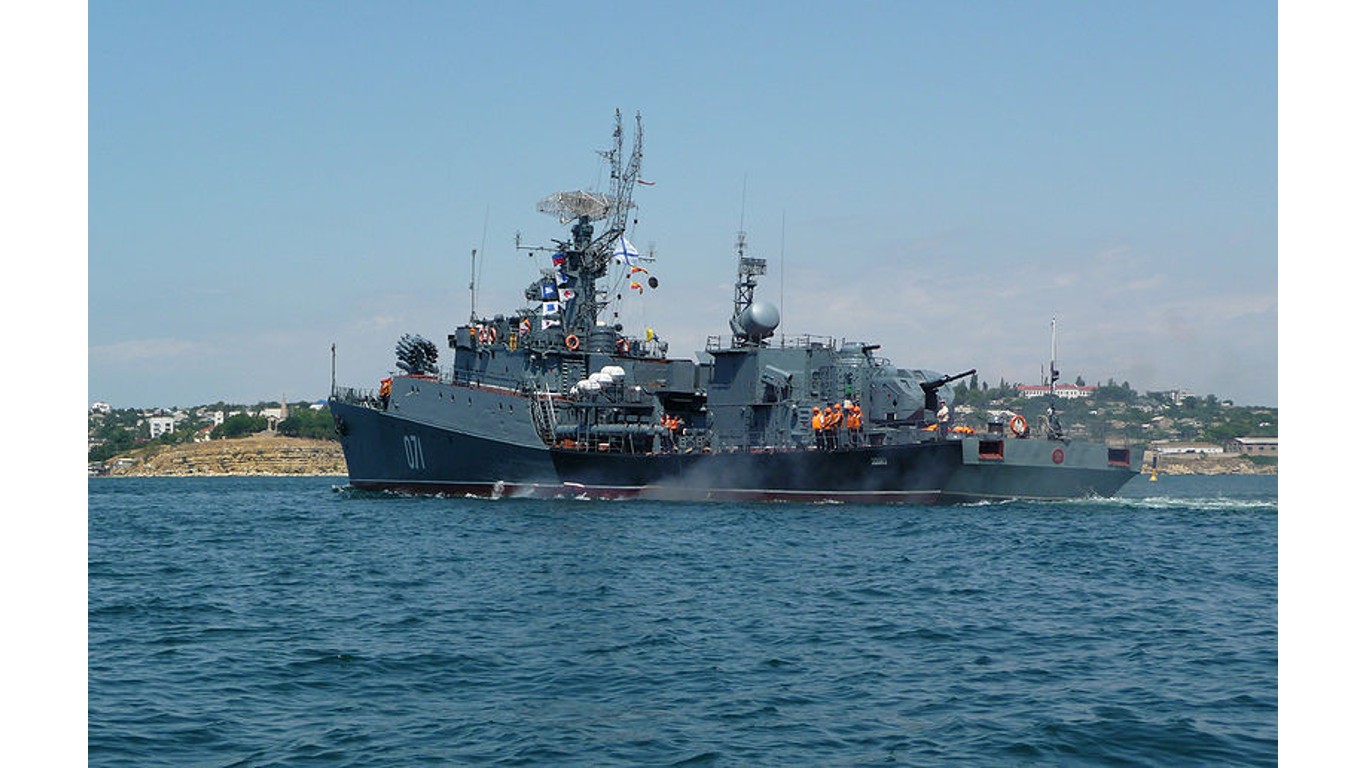

- Number in class: 20
- Type: Anti-submarine corvette
- Year introduced: 1970
2. Eridan
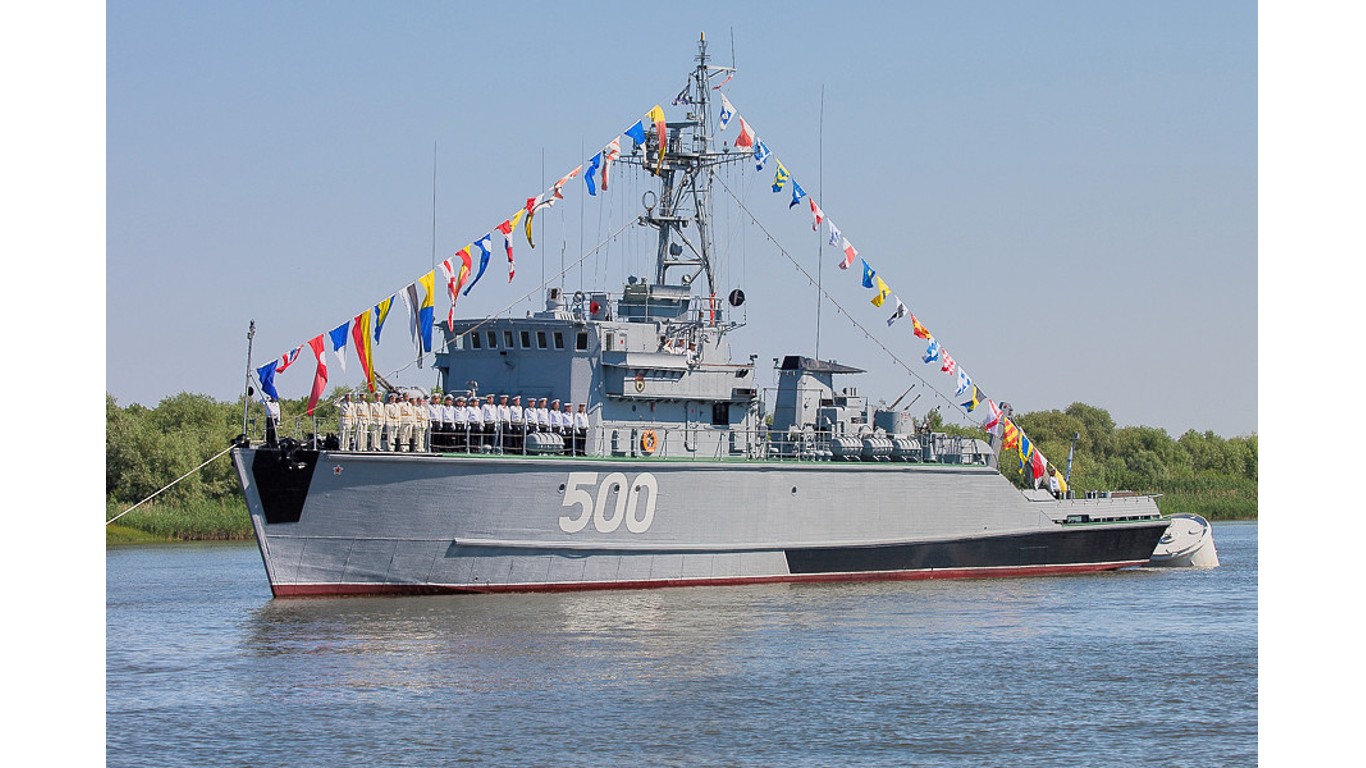

- Number in class: 22
- Type: Minesweeper
- Year introduced: 1983
1. Tarantul
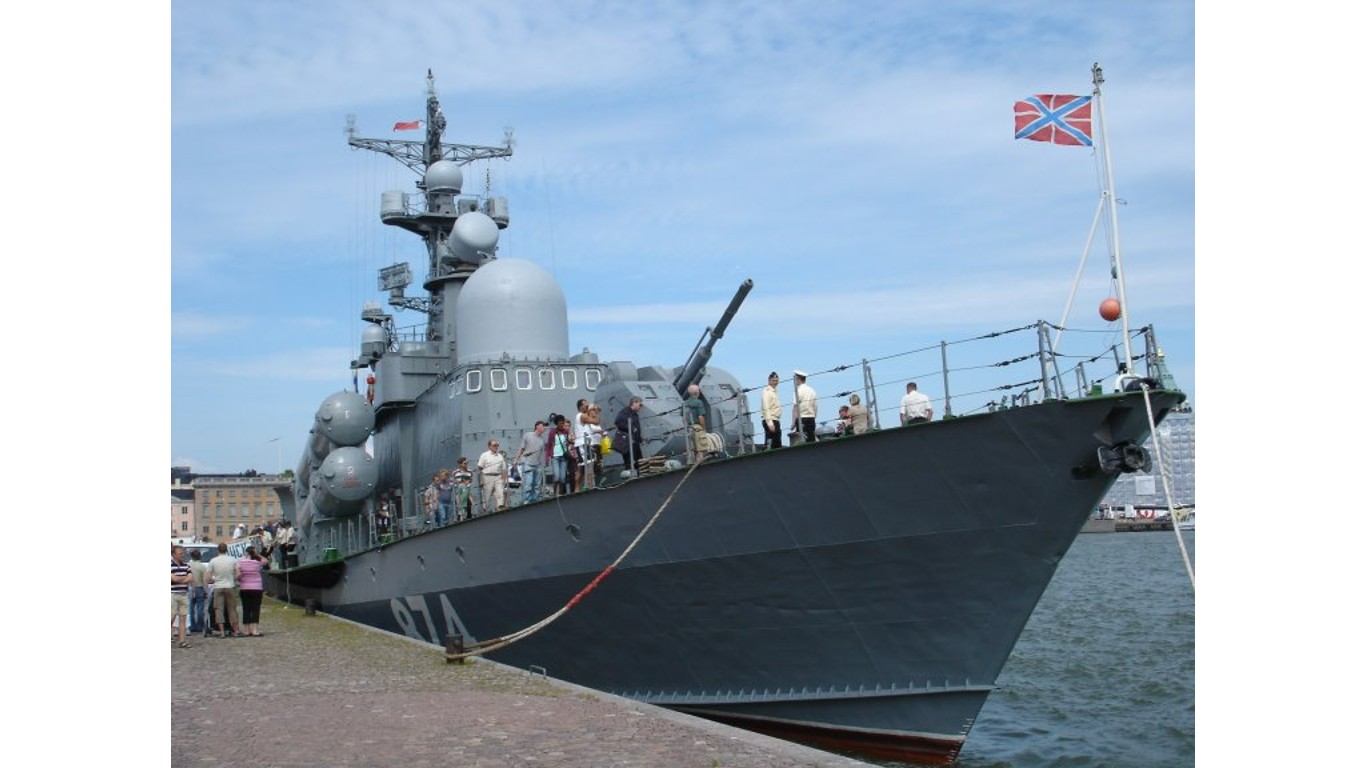

- Number in class: 22
- Type: Guided missile corvette
- Year introduced: 1977
Credit card companies are handing out rewards and benefits to win the best customers. A good cash back card can be worth thousands of dollars a year in free money, not to mention other perks like travel, insurance, and access to fancy lounges. See our top picks for the best credit cards today. You won’t want to miss some of these offers.
Flywheel Publishing has partnered with CardRatings for our coverage of credit card products. Flywheel Publishing and CardRatings may receive a commission from card issuers.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
