
Science and technology have advanced exponentially and show no signs of slowing down. But technological breakthroughs require decades of research and millions or billions of dollars of investment. With no guarantee these efforts will return a profit, private-sector businesses are not usually willing to take the risk. That’s where the organization with the deepest pockets—and the least concern about wasting money—steps in. This article is a compilation of some of the biggest scientific breakthroughs paid for by Uncle Sam.
24/7 Wall St. Insights
- The United States spends billions of dollars a year on research and development.
- This has produced breakthroughs in space science, military technology, medicine, and other areas.
- Check out: 2 Dividend Legends To Hold Forever and Discover “The Next NVIDIA
These are some of the most consequential breakthroughs the United States government has funded, sometimes in cooperation with the private sector and other countries. These are all multi-year or multi-decade projects, so the dates are given as a span of decades rather than a specific year.
1. Microwave Technology (1930s-1950s)

- Cost: hundreds of millions of dollars
- The government funded the development of radar systems using microwaves during World War II and later microwave relay towers for long-distance military and civilian communication.
- In the 1940s and 50s private companies commercialized the technology in microwave ovens, which have become ubiquitous in our fast-paced, eat-on-the-run lives.
2. Influenza Vaccine (1930s-present)
- Cost: $10 billion to date.
- This project created the first vaccine against influenza and continues to make updated flu vaccines for new variants every year.
- Hundreds of thousands of lives a year around the world are saved by controlling flu outbreaks.
3. Antibiotics Research (1940s)

- Cost: $14 million
- A cooperative U.S.-U.K. effort enabled the mass production of penicillin.
- Has saved millions of lives from life-threatening infections.
4. The First Computers (1940s)
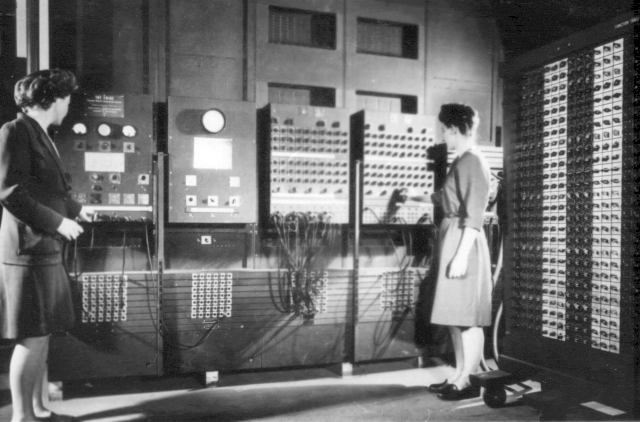
- Cost: $500,000
- ENIAC was the first programmable digital computer. It was developed f0r the military to perform rapid calculations of trajectories for artillery.
- It was a first step toward modern computers.
5. The Manhattan Project (194os)

- Cost: $2 billion
- Developed the world’s first atomic bomb.
- The technology was also used for nuclear power and advanced our understanding of physics.
6. Polio Vaccine (1950s)
- Cost: $7 million
- Discovered and began mass producing the Polio vaccine.
- Today the disease has almost been eradicated and millions of lives have been saved.
7. Satellite Technology (1950s)
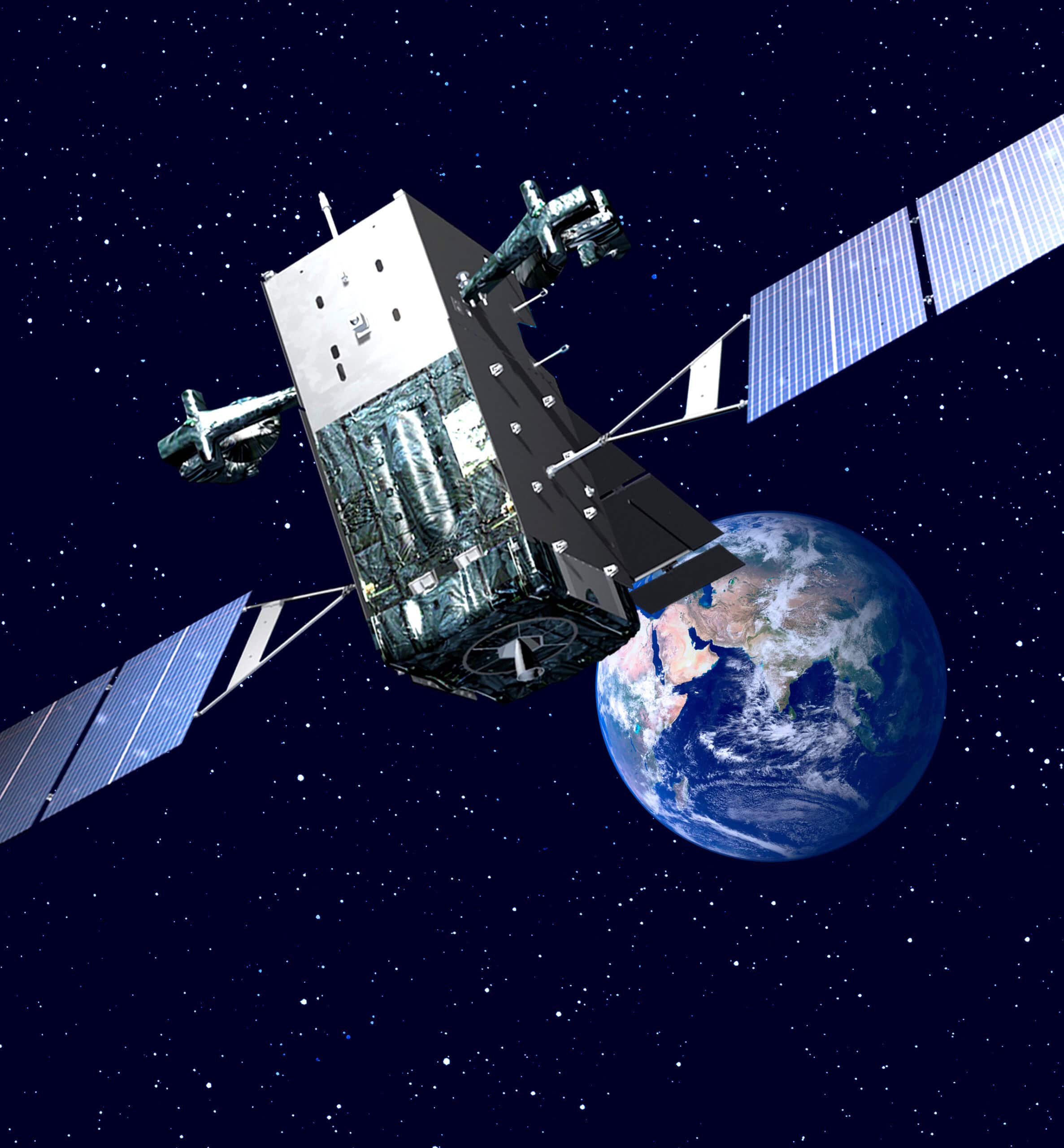

- Cost: $13 million.
- Explorer I ws the first U.S. satellite that sustained its orbit. It measured cosmic rays and discovered the Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts.
- Satellite technology is now integral to military and civilian communications, navigation, geolocation, research, intelligence-gathering, and weather-tracking.
8. Lasers (1950s-present)

- Cost: tens of billions
- Lasers have been under continuous research and development since the 1950s.
- They are now used in numerous military and civilian applications: targeting, communication, directed-energy weapons, mapping, surgery, manufacturing, telecommunications, barcode scanners, and scientific research.
9. Artificial Intelligence (1960s-present)

- Cost: $3 billion+ annually.
- Developed algorithms to produce natural-sounding human language and advanced data processing.
- The technology is revolutionizing all areas of life that use computer technology and advancing toward natural, conversational voice interfaces with technology and lifelike robots.
10. Apollo Program (1960s)
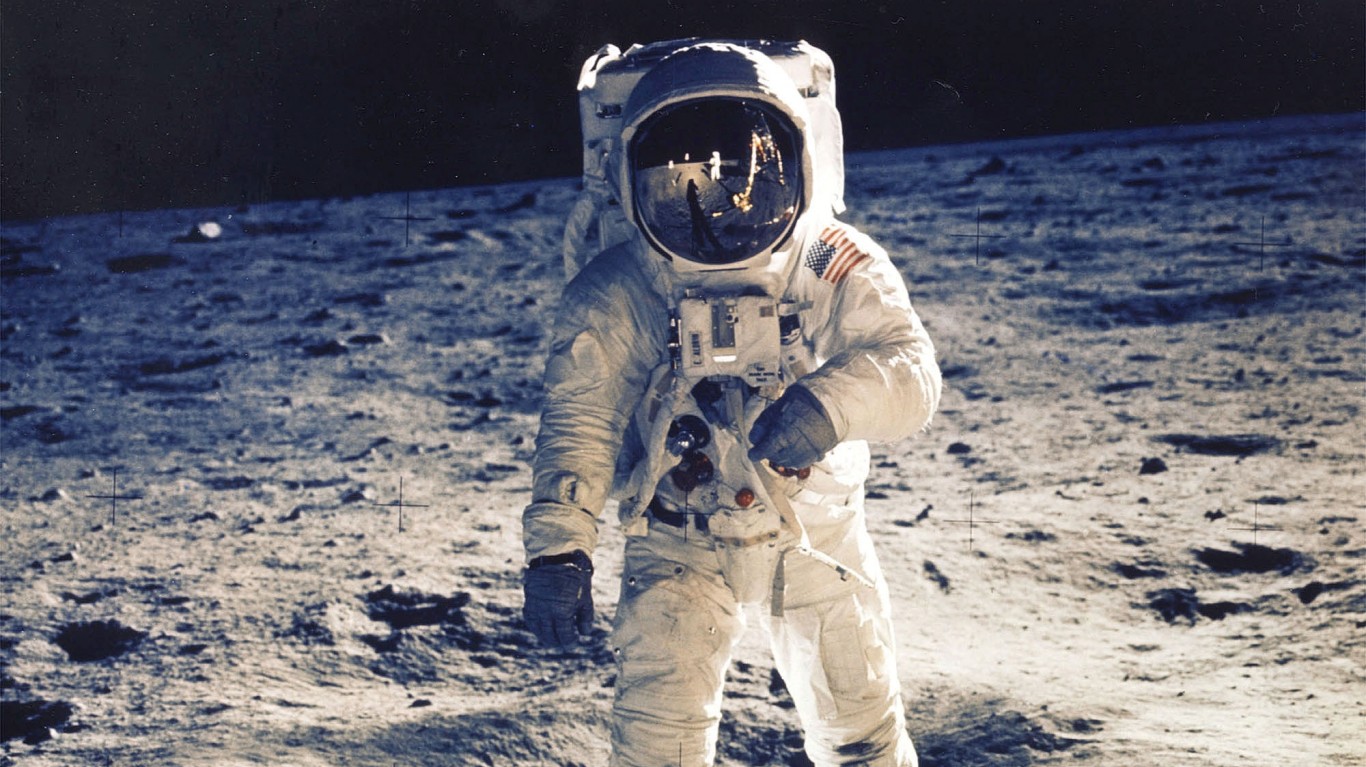

- Cost: $25 billion
- Put the first man on the moon, took high resolution photos of the near and dark sides.
- Developed technology for space exploration and improved computing.
11. The Internet (1960s)

- Cost: $20 million
- The government funded the development of ARPANET, the first internet.
- Led to the development of the World Wide Web and the explosion of knowledge and economic activity it brought.
12. Global Positioning Satellites (1970s-1990s)
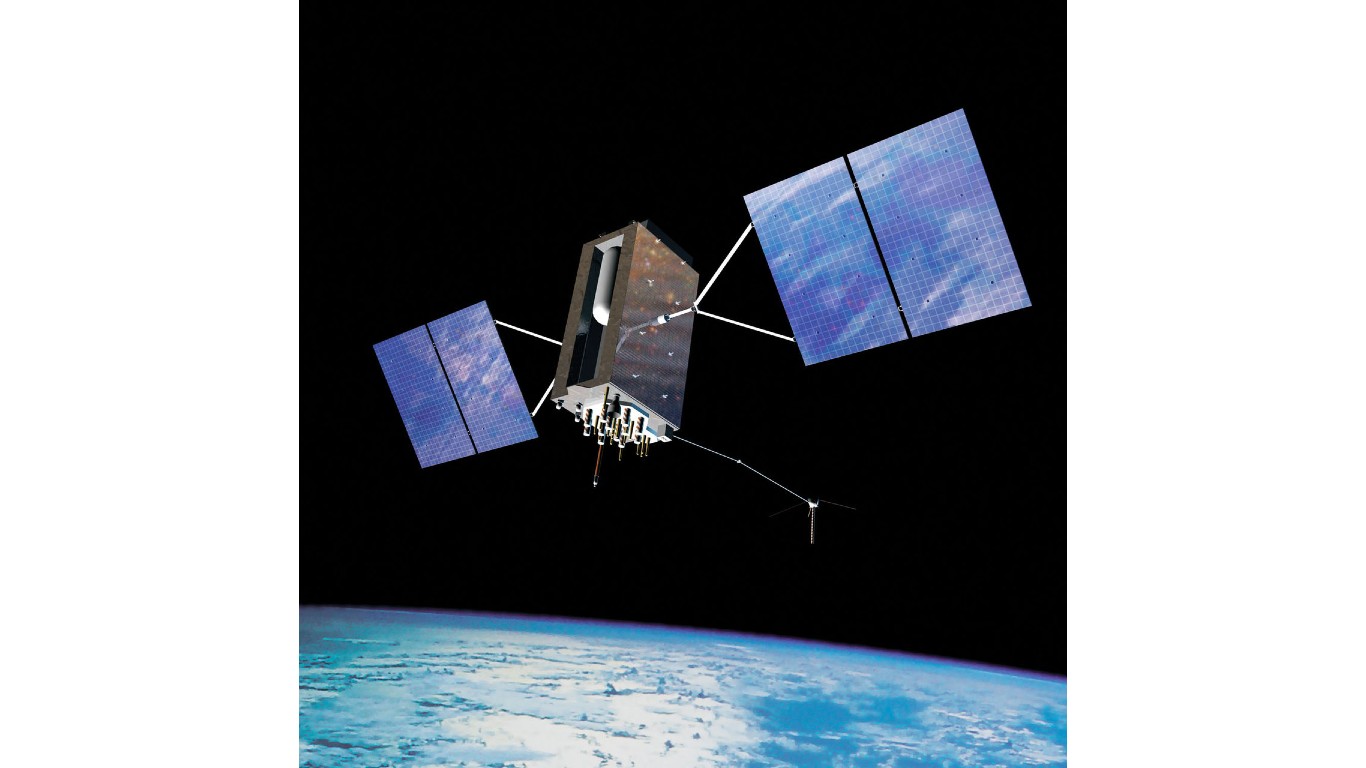

- Cost: $10-12 billion
- Developed the GPS system for military and civilian applications.
- Improved mapmaking, navigation, and allowed precise geolocation of people, animals, and objects.
13. HIV/AIDS Research (1980s-present)
- Cost: $60 billion to date.
- It developed antiretroviral therapy.
- HIV is no longer fatal but can be managed with medication. Tens of thousands of lives have been spared.
14. Hubble Space Telescope (1990s)
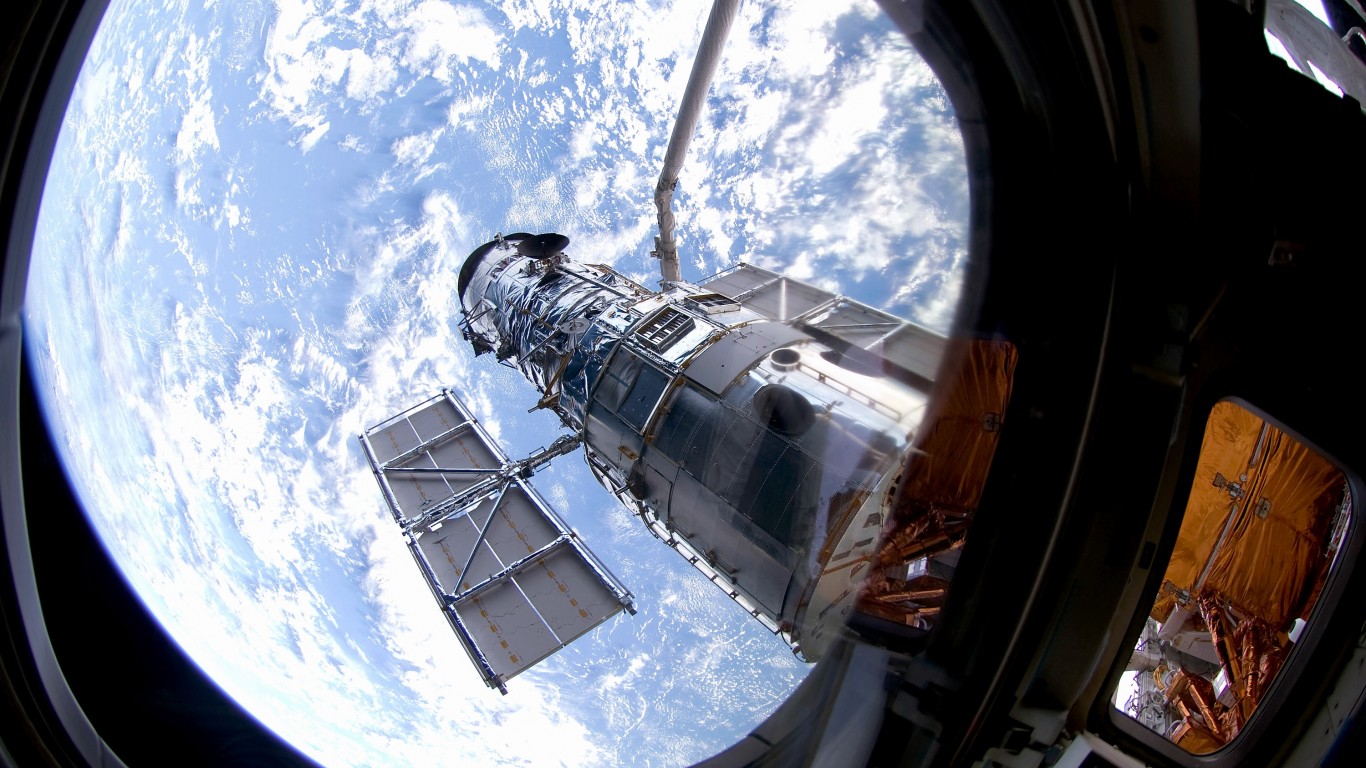

- Cost: $1.5 billion
- This space telescope greatly expanded how much of the universe we could study in detail with sharper-crisper images.
- It advanced our understanding of the universe, the search for exoplanets, and supported theoretical ideas like dark energy.
15. Advanced Batteries (199os-present)

- Cost: $1.3 billion
- The Department of Energy partnered with U.S. car companies to develop lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles.
- These advanced batteries extend the range of electric vehicles and bring down the price to make them more attractive to consumers.
16. Large Hadron Collider (1990s-present)
- Cost: $531 million contributed to an international effort.
- This facility in France and Switzerland has made numerous discoveries, the most significant of which was the Higgs boson particle.
- It has deepened understanding of sub-atomic particles and nuclear physics.
17. Human Genome Project (1990s-2000s)

- Cost: $3 billion
- This project mapped and sequenced human DNA
- It has advanced our understanding of genetics and created possibilities for advanced medicine and genetic engineering.
18. CRISPR Gene-Editing (2010s)

- Cost: $265 million
- This technology allows geneticists to edit DNA sequences for people, animals, and plants.
- It has resulted in disease-resistant, high-yield crops and new potential therapies for treating diseases.
19. Human Brain Mapping (2010s-present)

- Cost: $1 billion
- This government-funded project mapped brain activity in detail.
- It promises to help medical science understand and treat mental health issues.
20. Operation Warp Speed (2020)
- Cost: $18 billion
- Developed an effective COVID-19 vaccine in just 10 months and ended the pandemic.
- The new mRNA technology used to develop the vaccine will accelerate vaccine production for many other viral illnesses, potentially including influenza, HIV, Zika, and RSV.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.





