U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry waded cautiously into the debate surrounding the planned Keystone XL oil pipeline during last week’s meetings with his Canadian counterpart. Supporters describe the project as a panacea for a U.S. economy moving further away from overseas oil markets. Opponents, however, view the project as representative of the problems associated with a carbon-heavy economy. Kerry, seen as a supporter of pro-green regulations, said he was not getting into the merits of the project, but would make an announcement soon. Provincial leaders in Canada, however, may have already started preparing for a no vote.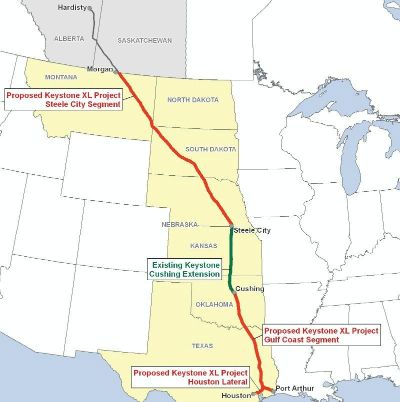
Kerry last week welcomed Canadian Foreign Minister John Baird to Washington as the first foreign leader to visit the State Department since Hillary Clinton stepped down early this year. Secretary Kerry lauded the importance of energy ties between the two North American energy leaders.
“Canada is the largest foreign energy supplier for the United States of America, and many people in America are not aware of that,” he said. “They always think of the Mideast or some other part of the world. But Canada is our largest energy supplier.”
That share could get even larger if the State Department approves the 1,700-mile Keystone XL pipeline. Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper has courted Asian leaders in an effort to diversify an economy that relies almost entirely on the United States for oil export revenue. Nevertheless, the Canadian foreign minister said Keystone XL is a “huge priority” for the Canadian economy.
TransCanada Corp. (NYSE: TRP) needs the U.S. government’s approval for the project because it would cross the U.S.-Canadian border. Kerry, as a Democratic senator from Massachusetts, touts a long record of environmental stewardship. In 1996, he backed efforts meant to ensure the quality of the nation’s water. Last year, TransCanada was forced to propose a revised route for the pipeline to allay state groundwater concerns in Nebraska. In 2009, meanwhile, Kerry backed efforts to encourage clean-energy growth in the United States. Despite his record as an “environmental champion,” however, he has had to sell off assets in BP PLC (NYSE: BP), ConocoPhillips (NYSE: COP), Exxon Mobil Corp. (NYSE: XOM) and Canadian oil company Cenovus Energy Inc. (NYSE: CVE), which could reap the benefits of Keystone XL construction, to avoid potential conflicts of interest.
Baird, meanwhile, noted that he and Kerry discussed what they could do together to address environmental concerns. Harper’s government, he said, was committed to a pledge to cut greenhouse gas emissions by as much as 17%. Opponents of Keystone XL told President Barack Obama that approving the pipeline would result in an increase in carbon emissions, a troubling scenario for some worried that last year’s climate disasters may become the new normal. Kerry, for his part, said a foundation for cooperation on energy issues was not Keystone XL, but “the needs of a secure clean energy future on this shared continent.”
In his weekly address, the president lashed out at Republican leaders for failing to heed a growing chorus of voices expressing concern about budgetary matters. In theory, Obama could act as the pro-green leader that oil hawks accuse him of being and reject Keystone XL if pushed over the fiscal cliff. While the decision would certainly anger groups like the American Petroleum Institute, Canadian leaders have already started looking at alternatives to the mega pipeline project. Last week, Alberta Premier Alison Redford met her New Brunswick counterpart, David Alward, to discuss ways to get oil sands to Canada’s largest refinery, the Irving Oil facility in St. John. Redford said what’s ultimately important for her province is “getting access to world markets,” regardless of the route.
By Daniel J. Graeber of Oilprice.com
Take Charge of Your Retirement: Find the Right Financial Advisor For You in Minutes (Sponsor)
Retirement planning doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. The key is finding professional guidance—and we’ve made it easier than ever for you to connect with the right financial advisor for your unique needs.
Here’s how it works:
1️ Answer a Few Simple Questions
Tell us a bit about your goals and preferences—it only takes a few minutes!
2️ Get Your Top Advisor Matches
This tool matches you with qualified advisors who specialize in helping people like you achieve financial success.
3️ Choose Your Best Fit
Review their profiles, schedule an introductory meeting, and select the advisor who feels right for you.
Why wait? Start building the retirement you’ve always dreamed of. Click here to get started today!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.




