Nuclear reactors are controversial with the public, but they generate enormous amounts of power compared to the alternatives. Surprisingly, although they generate radioactive waste, the United States and some other countries consider them a clean energy source because they do not pump greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere. In this article, we’ll run down the basics of nuclear power and tell you which states have opted to go nuclear, and which haven’t.
30 states have one or more nuclear reactors to help meet their energy needs. Nuclear power is considered by some states a viable, sustainable source of electricity that does not contribute to climate change. Check out these special reports: 2 Dividend Legends To Hold Forever and Discover “The Next NVIDIA
Key Points
How Do Nuclear Reactors Work?
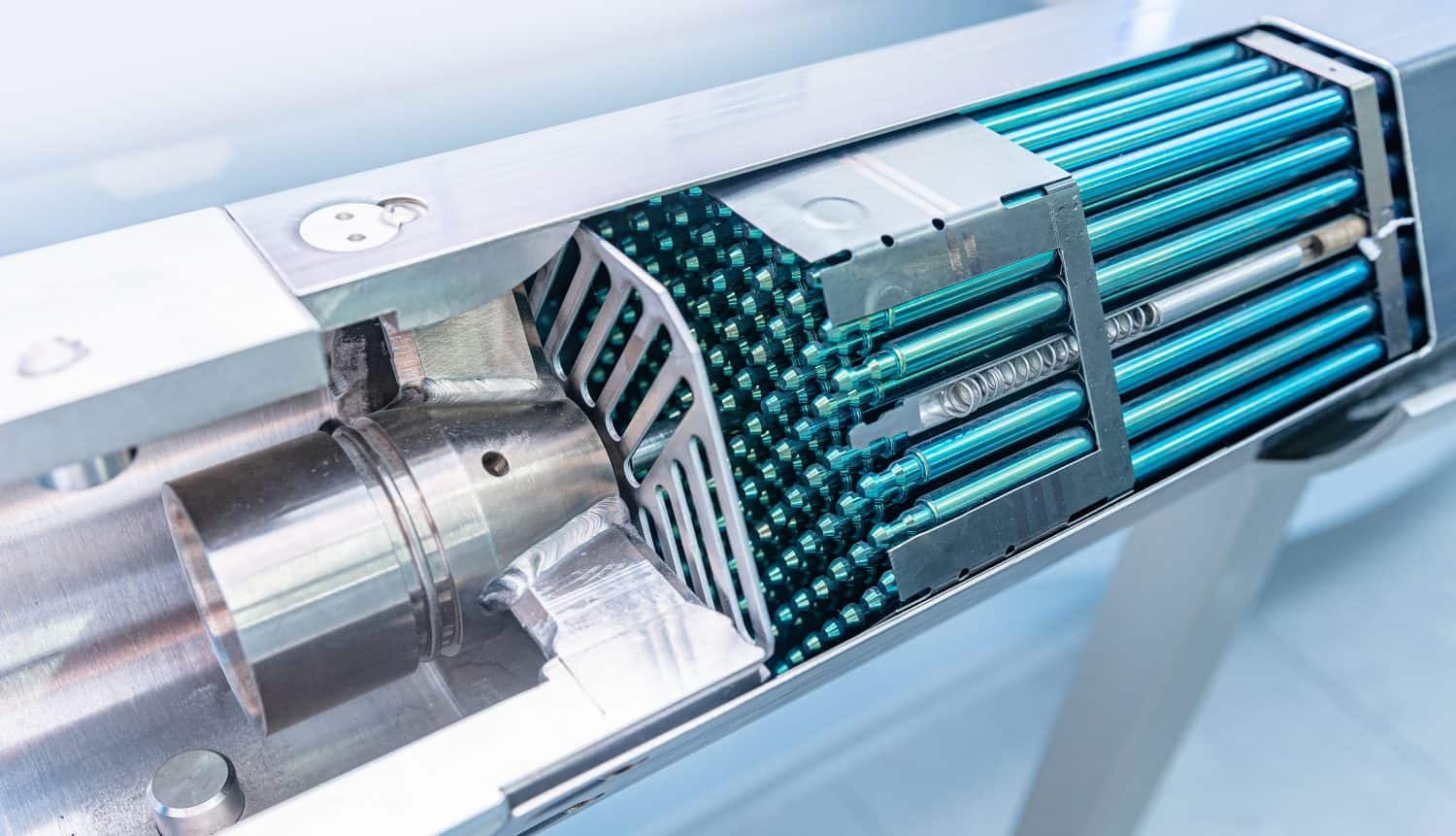

A typical nuclear reactor is powered by fuel rods filled with uranium. These use fission to split atoms and release energy. Control rods are inserted and retracted to absorb neutrons and regulate the rate of the reaction. The heat generated by the reactor boils water to turn a turbine and make electricity.
How Do We Decide Locations for Nuclear Reactors?

Nuclear power plants need to be located in places that are geologically stable, so that they won’t be disrupted by earthquakes, sinkholes, or other natural disasters. They need a large supply of water, so they are typically located near rivers. And because a lot of power is lost as it runs through transmission lines, reactors need to be located close to the place where the energy is needed, such as a large city or industrial zone.
How Do We Know They Are Safe?

Reactors are held to high standards by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. The whole process of construction and operation is reviewed by government inspectors. Employees go through regular training and safety drills. Reactors are built with failsafe measures to compensate for human error in their operation. The worst nuclear disaster in the United States was a partial meltdown of a reactor at the Three Mile Island reactor in Pennsylvania in 1979, which released radiation into the atmosphere. Although it created wide public concern, it did not release enough radiation to cause any adverse health effects for people living in the area.
Why Do Some States Avoid Nuclear Reactors?

Nuclear reactors suffer from the “not in my backyard” syndrome. We all want the affordable electricity they produce but we don’t want to live near them. The choice to build a nuclear reactor is often controversial and can elicit strong political opposition.
They’re expensive, with costs running into the billions, and building them can take years, or decades. They generate radioactive waste that has to be stored securely for thousands of years until it decays. And although in most cases they operate safely, a few nuclear disasters around the world have made the public fearful of them. And finally, some states just don’t need them because their energy needs are adequately met by other energy sources, or because they draw power from a reactor located in a neighboring state.
What Role Do Nuclear Reactors Play as a Clean Energy Source?

The environment is the biggest concern most people have about nuclear power. It is possible for a reactor to melt down, leading to a runaway fission reaction that can spread radiation widely. This is what happened to the reactor in Chernobyl, Ukraine. And the waste generated by normal reactor operations has to be stored safely.
On the flip side, though, nuclear power generates energy without releasing greenhouse gasses into the environment. They release only harmless steam and warm water. They don’t have to ship and store large quantities of fuel like coal- or gas-fired plants do. Because their carbon footprint is so much lower, nuclear power plants are considered by some countries to be a helpful contribution to the problem of climate change.
What About Fusion Power?
All of today’s reactors operate by fission, but research is going on to create fusion reactors, which would generate vastly more energy. The idea would be to compress and superheat a plasma to force the nuclei of light elements to fuse and release energy. It would generate much less radiation, and what it does create would decay more quickly than radioactive remnants from fission reactors. The fuel source for this type of reaction could be derived from common seawater, so this would create a boundless source of energy. So far, scientists have not been able to create fusion reactors that generate substantially more energy than they consume.
Next up: a survey of the states with and without nuclear reactors.
States Without Nuclear Reactors

20 states currently have no nuclear power plants. What do they have in common? Many of them are thinly populated, rural states with a widely disbursed population. Others are geographically small states in New England where power is distributed across the region and it is not necessary for each state to have its own power source. Some have a local natural resource that is cheaper to develop and use for energy, such as coal or hydroelectric power. Finally, in some western states, like Oregon, citizens are particularly committed to environmental preservation and do not want to support the nuclear power industry or the industrialization it might bring.
- Alaska
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Indiana
- Kentucky
- Maine
- Montana
- Nevada
- New Mexico
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- South Dakota
- Utah
- Vermont
- West Virginia
- Wyoming
States With 1 Nuclear Reactor

This list doesn’t look all that different from the previous one, but what we can say is that each of these has at least one major metropolis that can use the power generated by a nuclear reactor. Each also has ready access to abundant river water to cool reactors.
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- New Hampshire
- Washington
States With 2 Nuclear Reactors

Somewhat of a surprise on this list is California. It’s a state with immense power requirements, but it also has a large population of political progressives who are often ambivalent or hostile to nuclear energy. With this state’s propensity to earthquakes, foregoing nuclear power would seem like a good call. The state has been decommissioning its reactors, but still has 2 at Diablo Canyon, an ocean-side site surrounded by steep mountains and wilderness near San Luis Opisbo and far from the heavily populated Bay area or Southern California. Now that climate change has become a more urgent issue policymakers are considering keeping the current reactors as part of the state’s move to lower its carbon footprint.
- Arkansas
- California
- Connecticut
- Louisiana
- Maryland
- Ohio
- Wisconsin
States With 3 Nuclear Reactors

One of the states with three reactors is New Jersey, a small but densely populated state with major metropolises like New York City and Philadelphia on its borders. This region has an insatiable demand for electric power, so it is a profitable place to make a large investment in reactors.
- Arizona
- Minnesota
- New Jersey
States With 4 Nuclear Reactors

States operating four reactors are among the most densely populated in the country. Some of them are located in the Sun Belt and continue to grow in population, placing demands on energy infrastructure.
- Florida
- Michigan
- New York
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Virginia
States With 5 Nuclear Reactors

Alabama and North Carolina each have 5 reactors. Both states have large population concentrations around several large cities and extensive rural and forested land.
- Alabama
- North Carolina
States With 6 or More Nuclear Reactors

Although Illinois is a largely rural state, it also is home to Chicago and some other large metropolises, so it has large electric power needs. Georgia is the latest state to build new reactors, having opened two new units at an existing power plant in April 2024. It remains to be seen whether other states will join these heavy users as nuclear power goes through a renaissance as a climate-friendly energy source.
- Illinois: 11
- Pennsylvania: 8
- South Carolina: 7
- Georgia: 6
Get Ready To Retire (Sponsored)
Start by taking a quick retirement quiz from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes, or less.
Each advisor has been vetted by SmartAsset and is held to a fiduciary standard to act in your best interests.
Here’s how it works:
1. Answer SmartAsset advisor match quiz
2. Review your pre-screened matches at your leisure. Check out the advisors’ profiles.
3. Speak with advisors at no cost to you. Have an introductory call on the phone or introduction in person and choose whom to work with in the future
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.



