NASA has long been highly visible and is among the most celebrated programs in modern United States history. Some generations will undoubtedly remember that at the height of the space race in the 1960s, NASA was prominently battling against the Soviet Union to be the first to land a man on the moon.
NASA has played a prominent role in developing the technology we enjoy today, like GPS. The role of NASA early on was to beat the Soviet Union to the Moon. Today, NASA works with private companies to continue space exploration. Retiring early is possible, and may be easier than you think. Click here now to see if you’re ahead, or behind. (Sponsor)
Key Points
Fast-forward to today, the typical American is unclear about what NASA does and, better yet, how much NASA spends. This issue is not new, and one surprising statistic came in 2007 when Americans were surveyed, and they indicated they believed NASA accounted for one-fourth of the US budget.
For an agency responsible for quite a few technological achievements, NASA should receive far more credit. Better yet, it would help if the typical American could answer some questions about the agency.
1. Question

What does NASA stand for?
Answer: National Aeronautics and Space Administration

While the general understanding of NASA is that it stands for National Aeronautics and Space Administration, there’s more meaning here. “Aeronautics” was meant to refer to the science of flight. In contrast, “space administration” highlighted NASA’s role in space exploration and research.
2. Question

When was NASA founded, and why was it founded?
Answer: Response to Sputnik Launch

The federal government established NASA on July 29, 1958, when tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union were high. More directly, NASA was created as a direct response to the Soviet’s successful launch of Sputnik I in 1957, which saw the Americans intensely wanting to beat the Russians in space exploration and technology.
3. Question

What was NASA’s first mission, and when did it occur?
Answer: 1958

The first mission NASA underwent was the launch of Pioneer 1, a satellite that launched into space on October 11, 1958. While the launch failed because Pioneer 1 could not reach and orbit the Moon, it did help provide NASA with valuable data over its 43-hour flight that would be used for later missions that would reach and eventually land people on the Moon.
4. Question

What was the first satellite launched by the United States?
Answer: Explorer 1

The first American satellite, Explorer 1, was launched on January 31, 1958, in response to the launch of the Soviet Sputnik 1. Explorer 1 first discovered the Van Allen radiation belts and is widely regarded as the United States’ first true entry into the space race against the Soviet Union.
5. Question
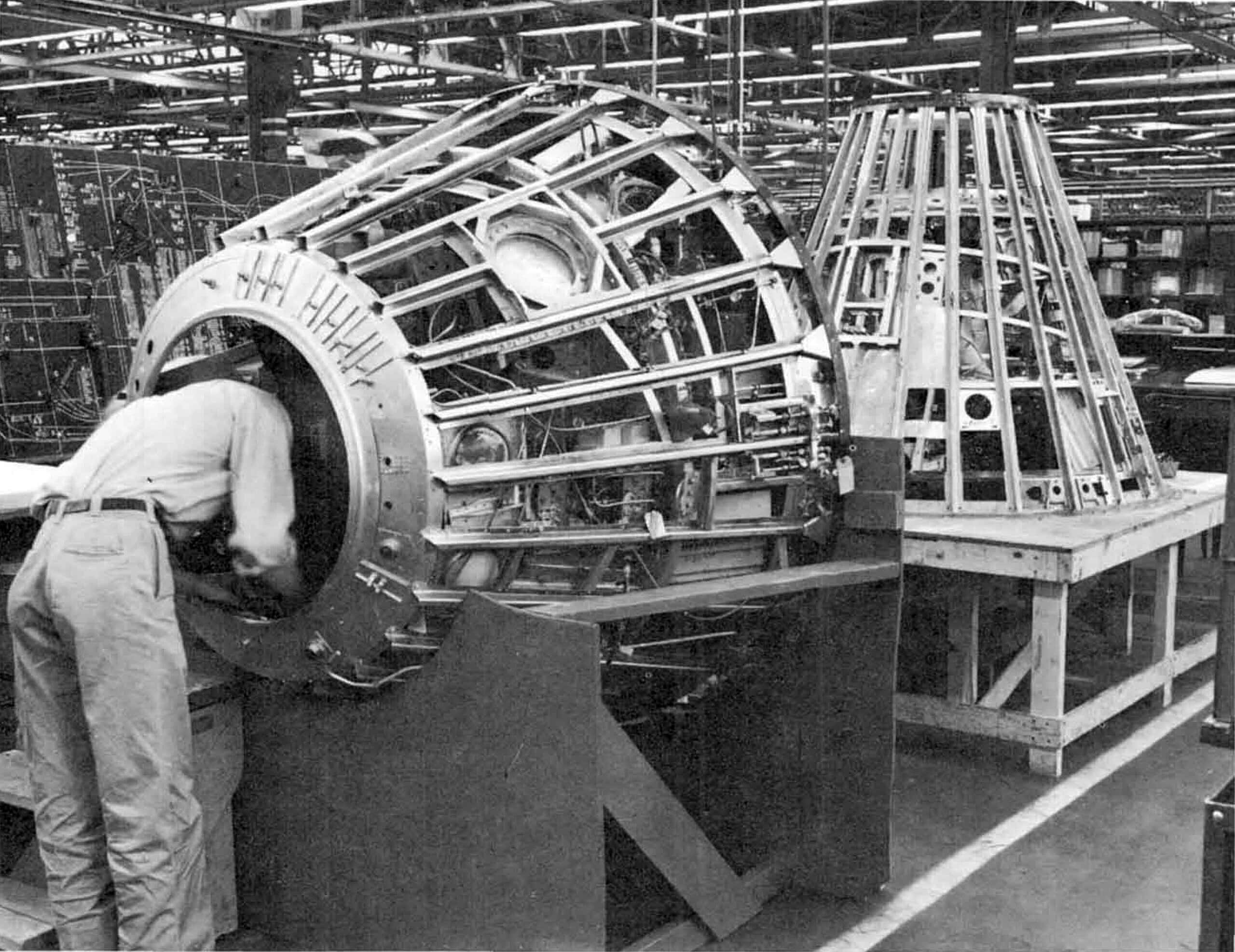
What was NASA’s first human spaceflight program known as?
Answer: Project Mercury

From 1958 to 1963, Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program in the United States. The program cost around $2.68 billion in 1960s dollars, and each spacecraft was given a name ending in “7” by its pilot.”
6. Question
Who was the first American to launch into space?
Answer: Alan Shepard
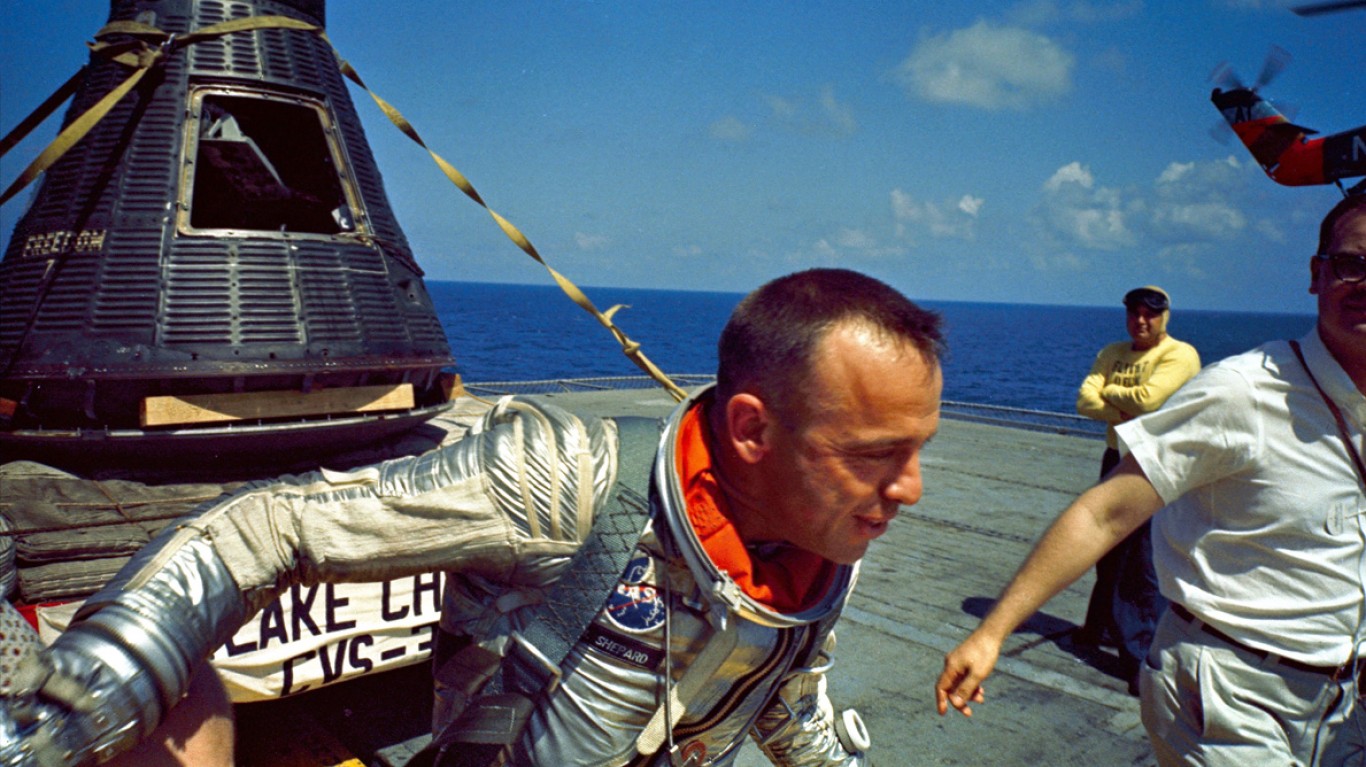

Alan Shepard famously became the first American to be launched into space on May 5, 1961, aboard the Freedom 7 spacecraft. While Shepard’s flight only lasted about 15 minutes, it was proof that all of NASA’s work up until this point was finally coming to fruition. The launch of Shepard boosted national pride and helped keep the public interested in the space race.
7. Question
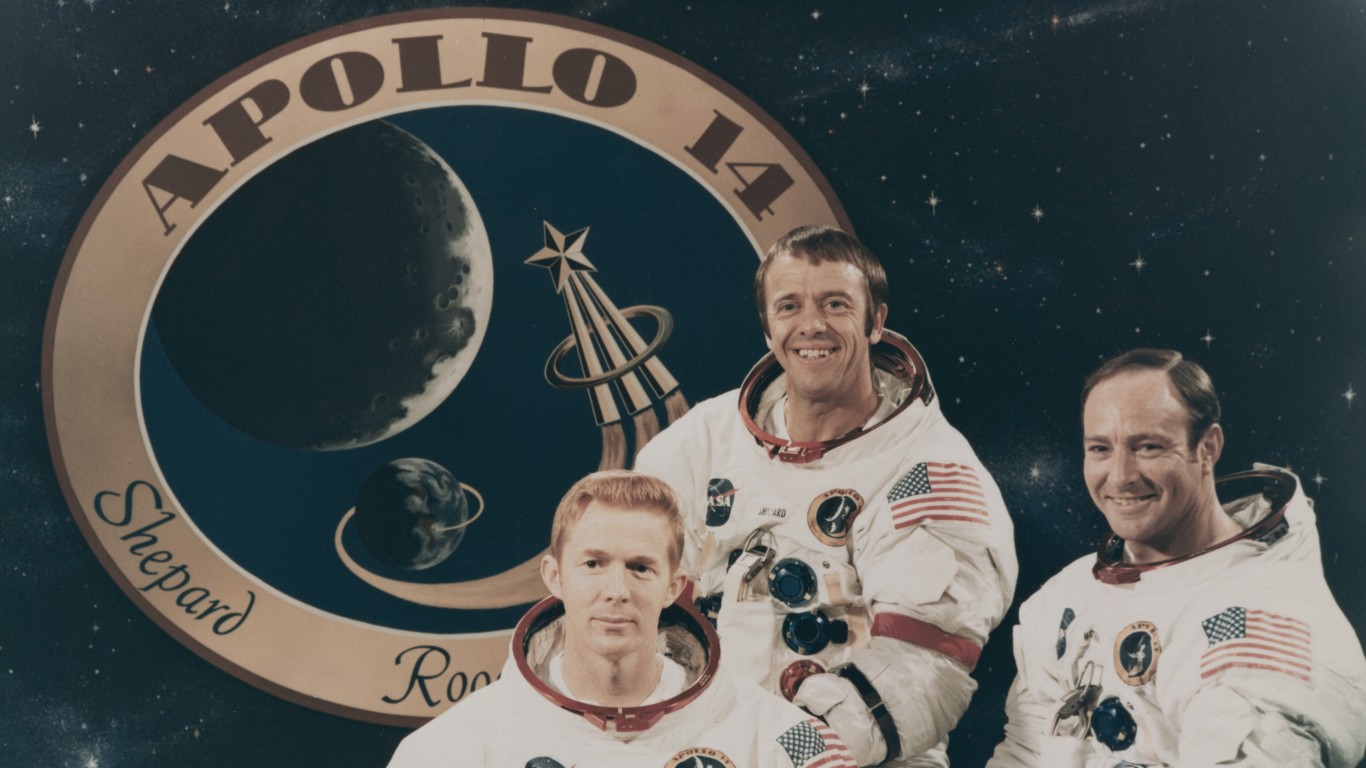

What was the goal of the Apollo program?
Answer: Land On the Moon
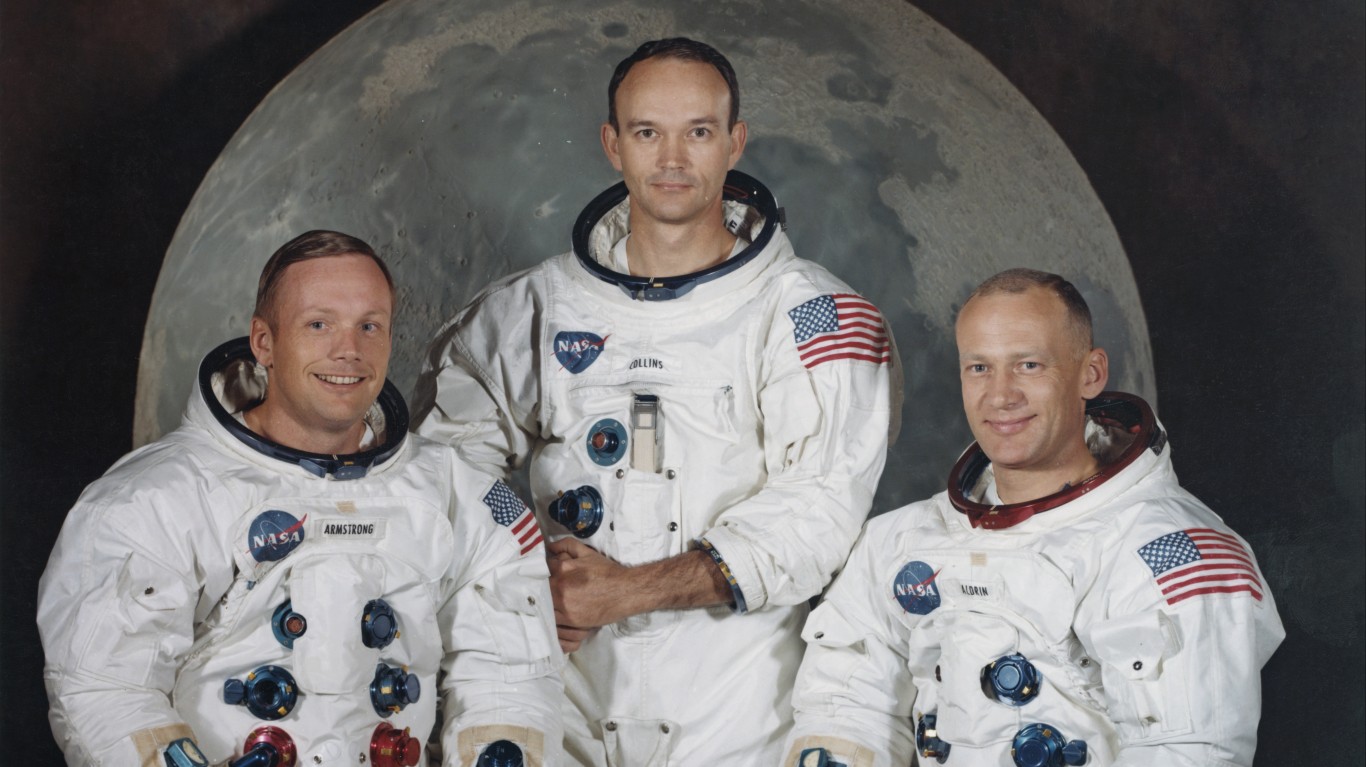

The wide fame of the Apollo program was likely taught to all Americans in school, focused specifically on landing humans on the Moon and returning them safely to Earth. President Kennedy wanted to see the US develop technology with the Apollo program that would further other US interests and make the country the leader in space exploration.
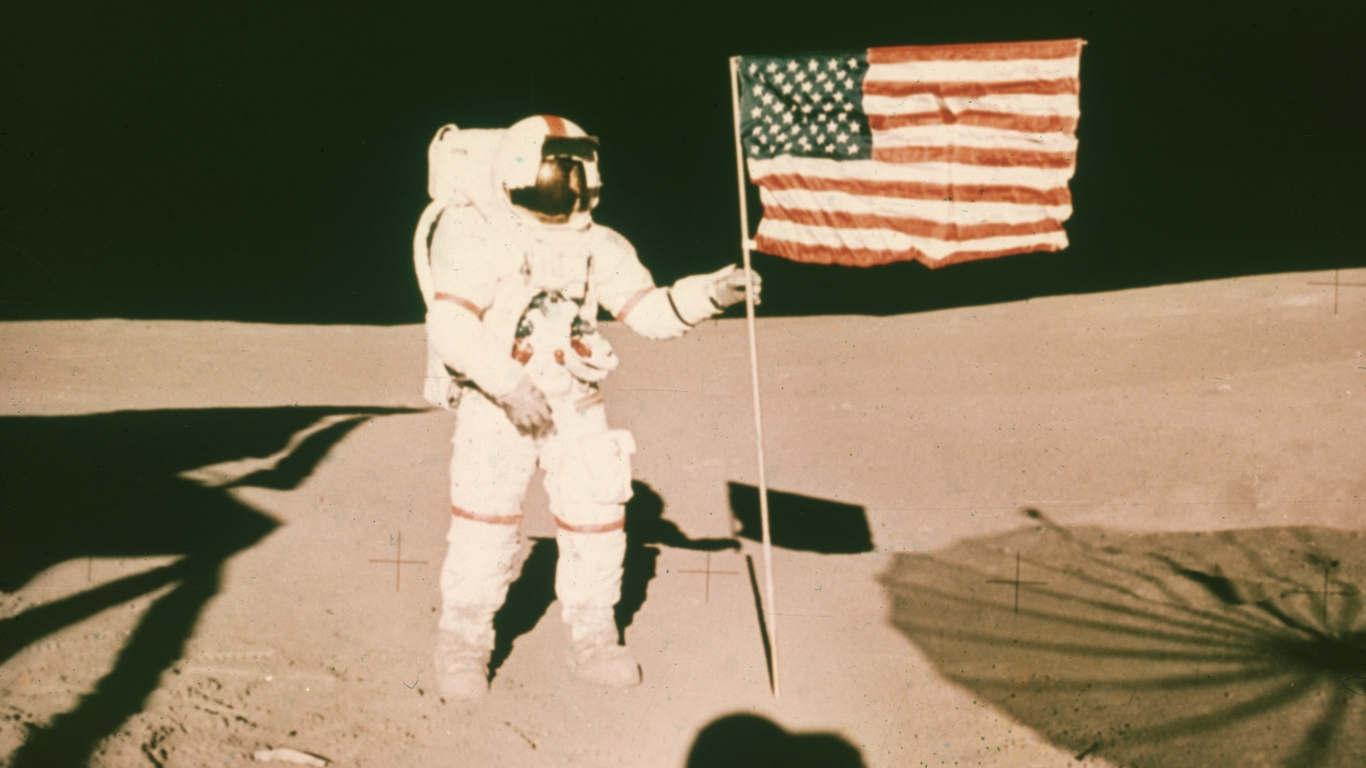
8. Question
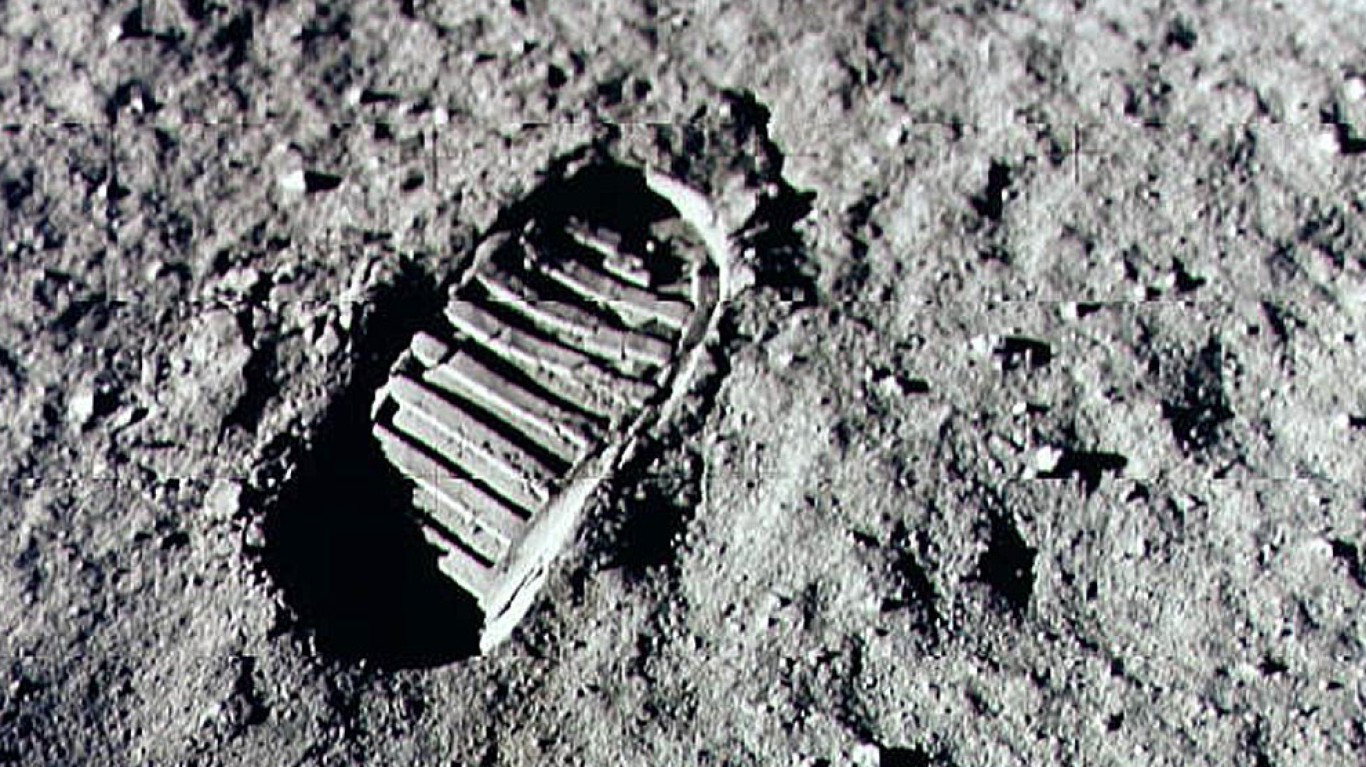

How many people have walked on the Moon?
Answer: 12
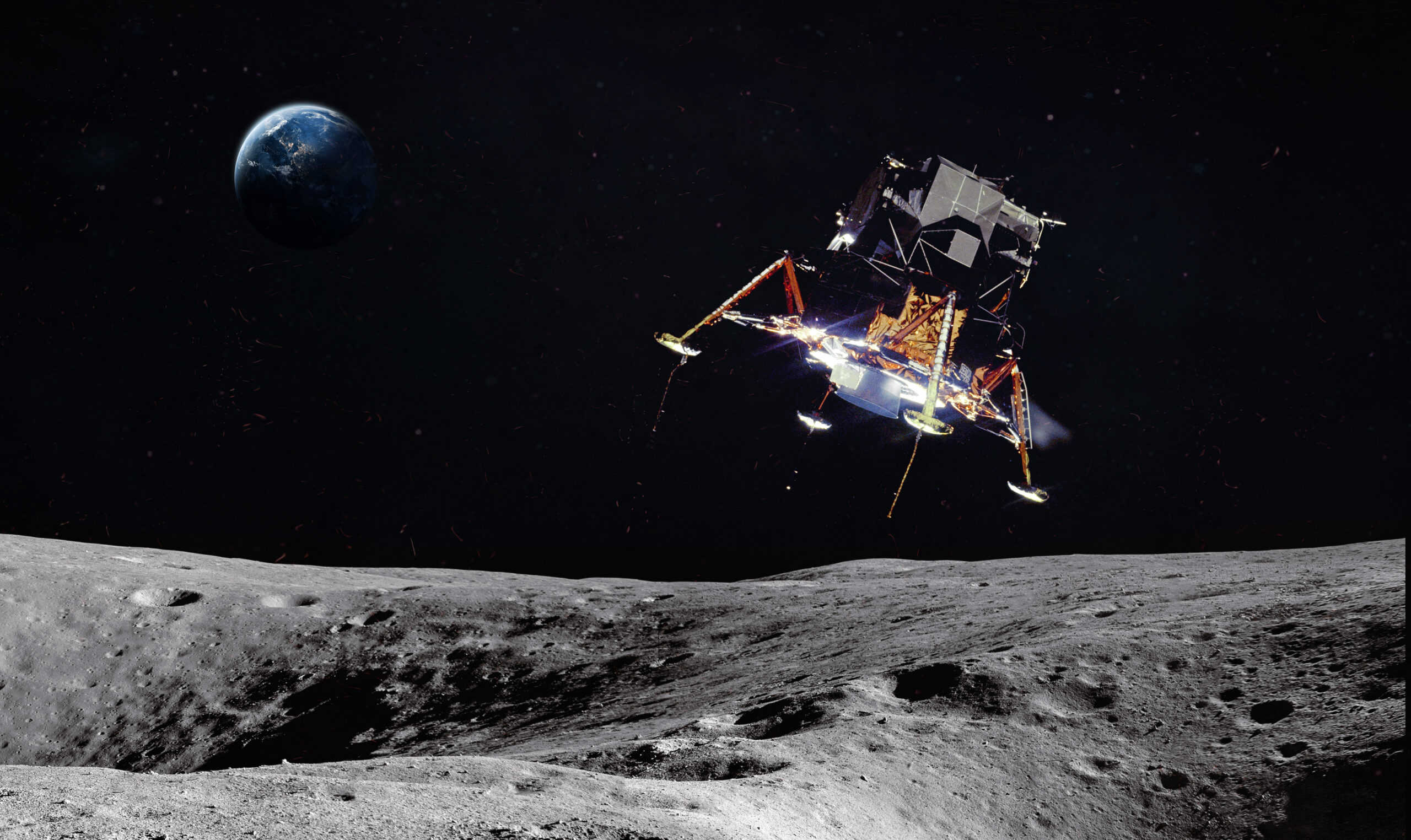

With Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin as the first Americans to ever walk on the Moon, 12 American astronauts in total have walked on the Moon. However, 24 American astronauts traveled to the Moon between 1968 and 1972, with three astronauts making the trip twice. Only four of the 12 Americans to walk on the Moon are still alive today.
9. Question

What was the goal of landing on the Moon?
Answer: Collect Lunar Samples

The original goal for all 12 American astronauts landing on the Moon during the six Apollo missions to successfully make it to the Moon and back was to collect valuable scientific data. This included lunar samples and geological studies of the Moon’s surface that would help scientists look at the formation and history of the Moon and its relationship to Earth.
10. Question
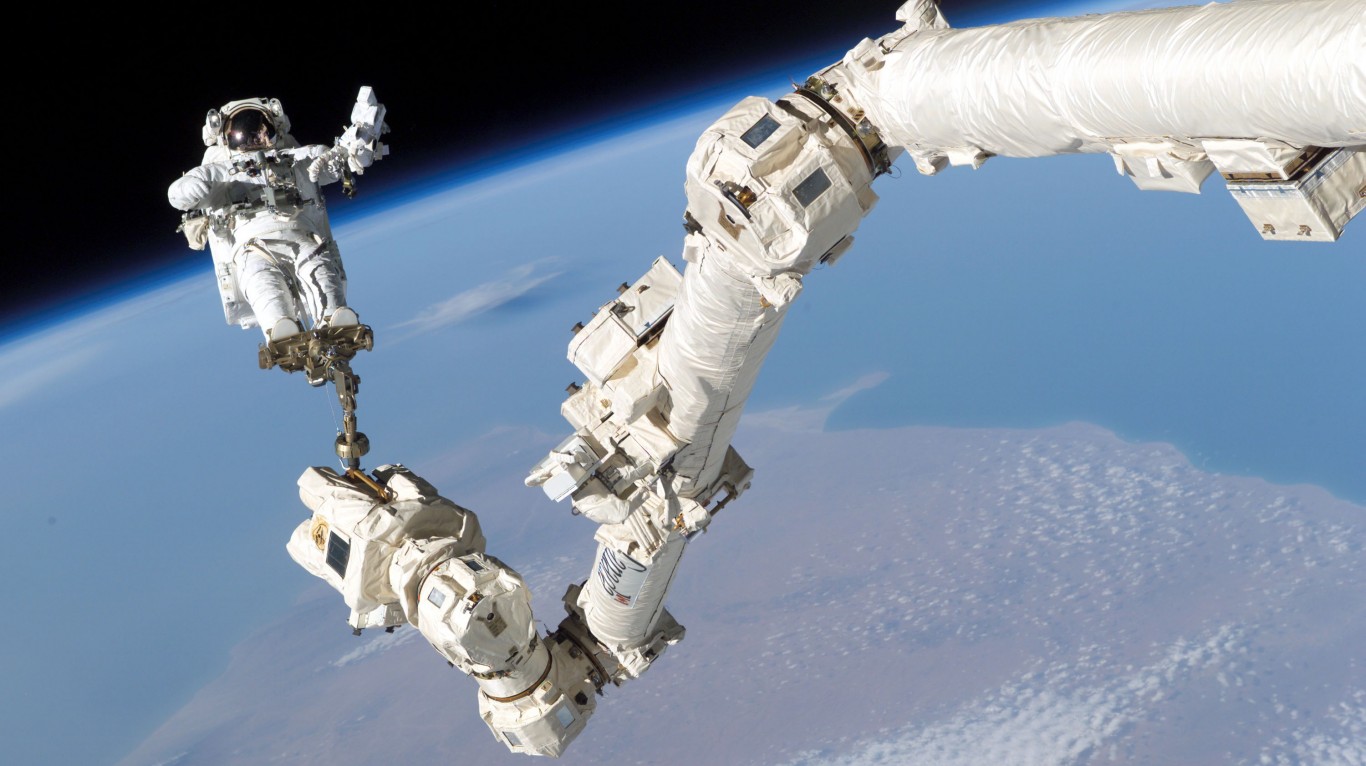

What is the International Space Station?
Answer: Multipurpose Goals
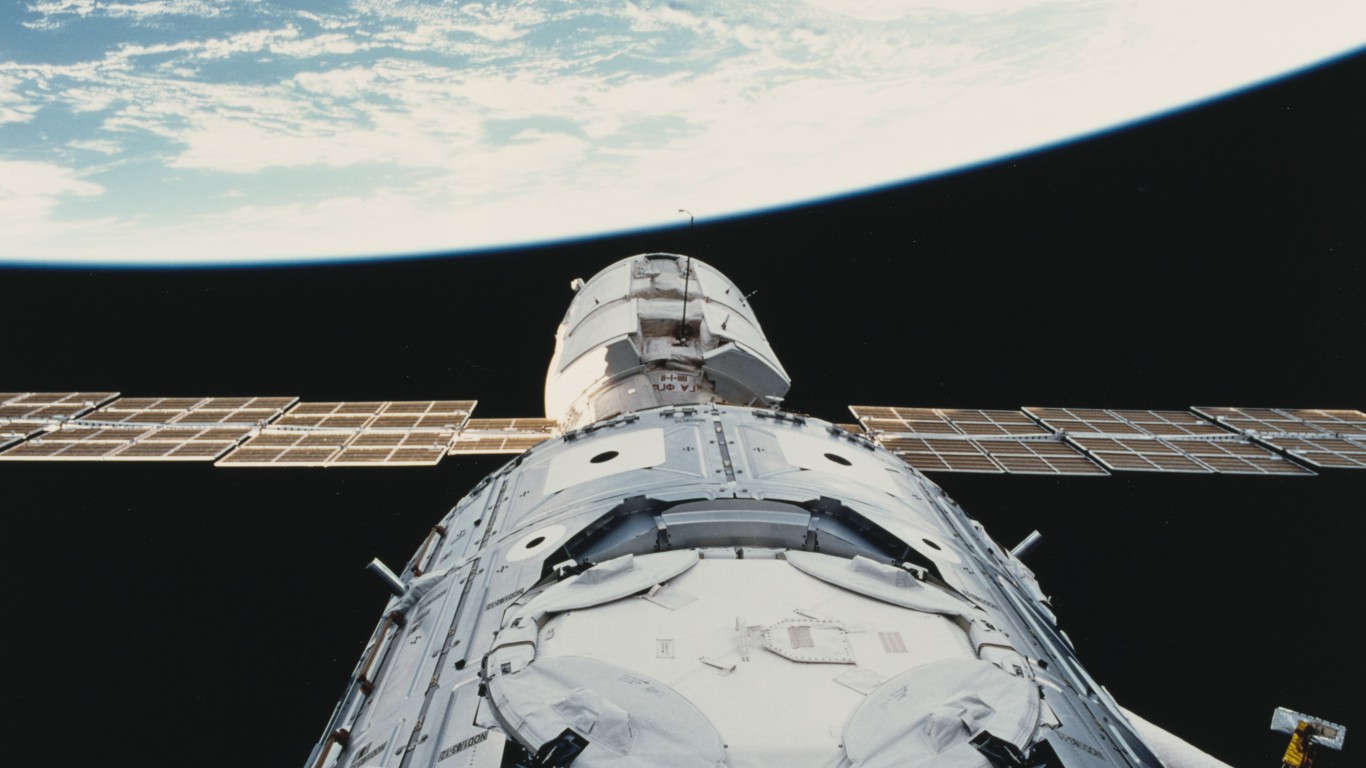

Launched in 1998 in coordination with NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA, the International Space Station continues to orbit Earth today and is a location for international science, biology, and technology research. Due to microgravity, experiments on the ISS are impossible on Earth, and the ISS serves as a beacon of international cooperation.
11. Question
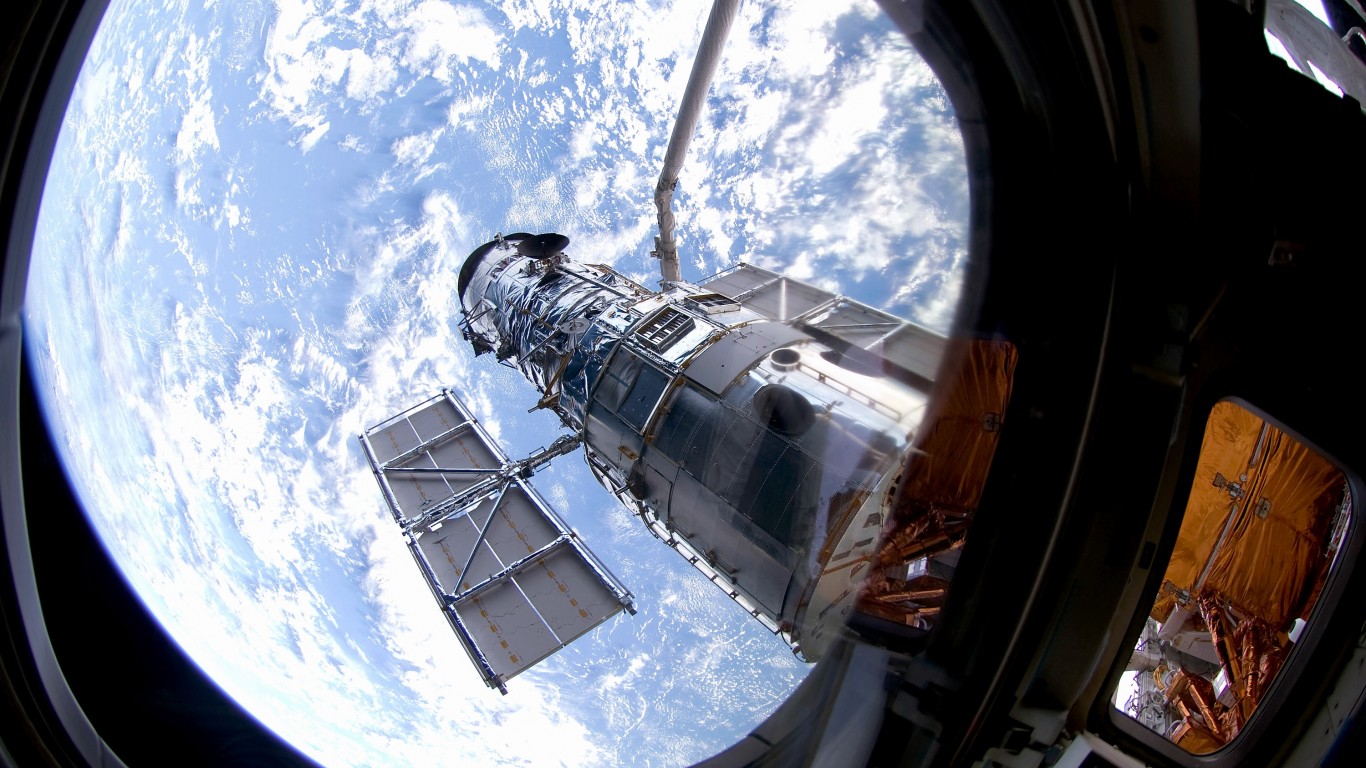

What is the Hubble Space Telescope?
Answer: Photographs Deep Into Space

One of the most significant launches in NASA history, the Hubble Space Telescope, which went into orbit in 1990, is an iconic part of space exploration. The Hubble, orbiting well above Earth, captures images of distant galaxies, planets, and stars. Hubble has made numerous contributions to scientific exploration and provided breathtaking images of space and the universe.
12. Question
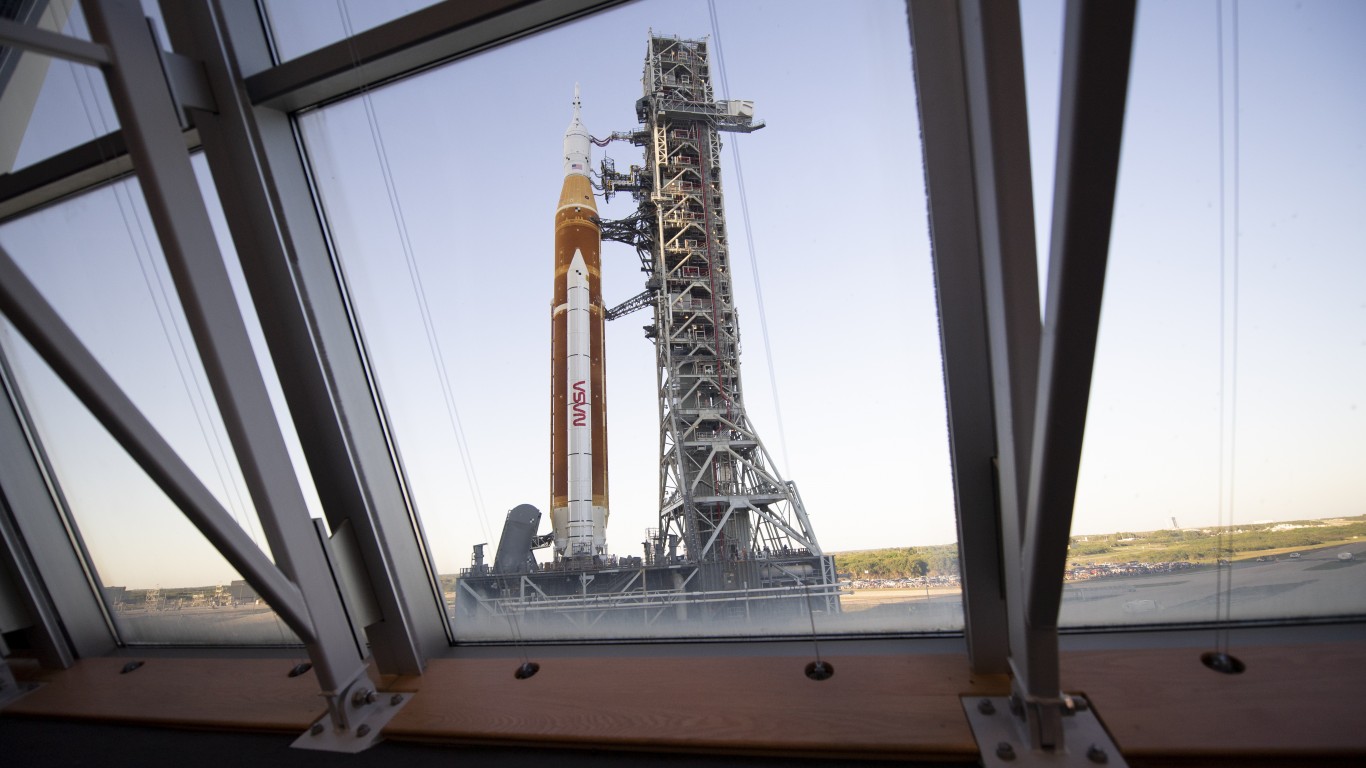

What is the Artemis Program?
Answer: Returning to the Moon
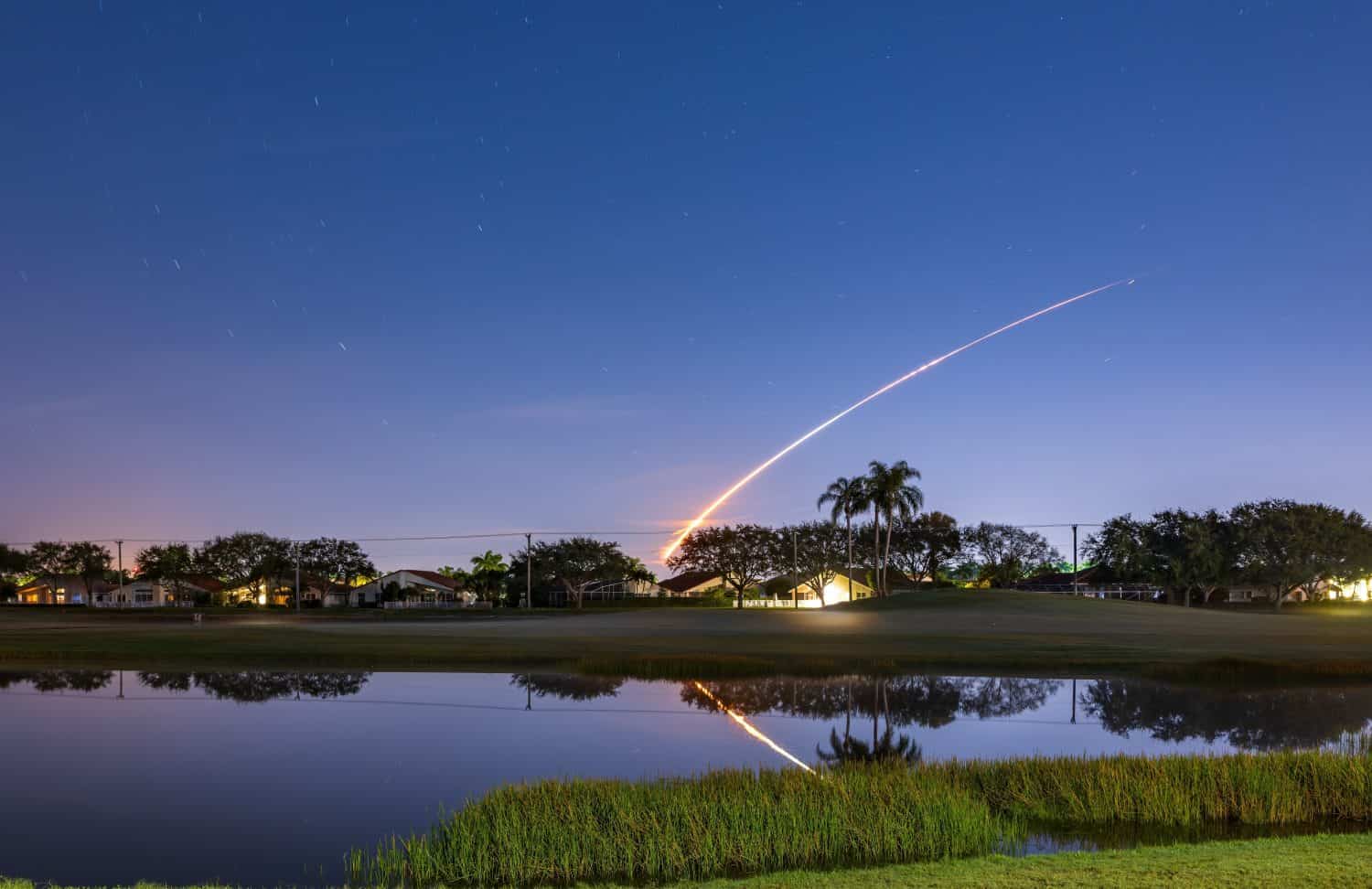

While the timeline has shifted slightly, the Artemis program was officially established in 2017 through Space Policy Directive 1. The program aims to establish a human presence on the Moon, which would be the first time Americans have been back to the Lunar surface since 1972. The program’s long-term goal is to create a permanent Moon base that would allow repetitive missions between Earth and the Moon.
13. Question
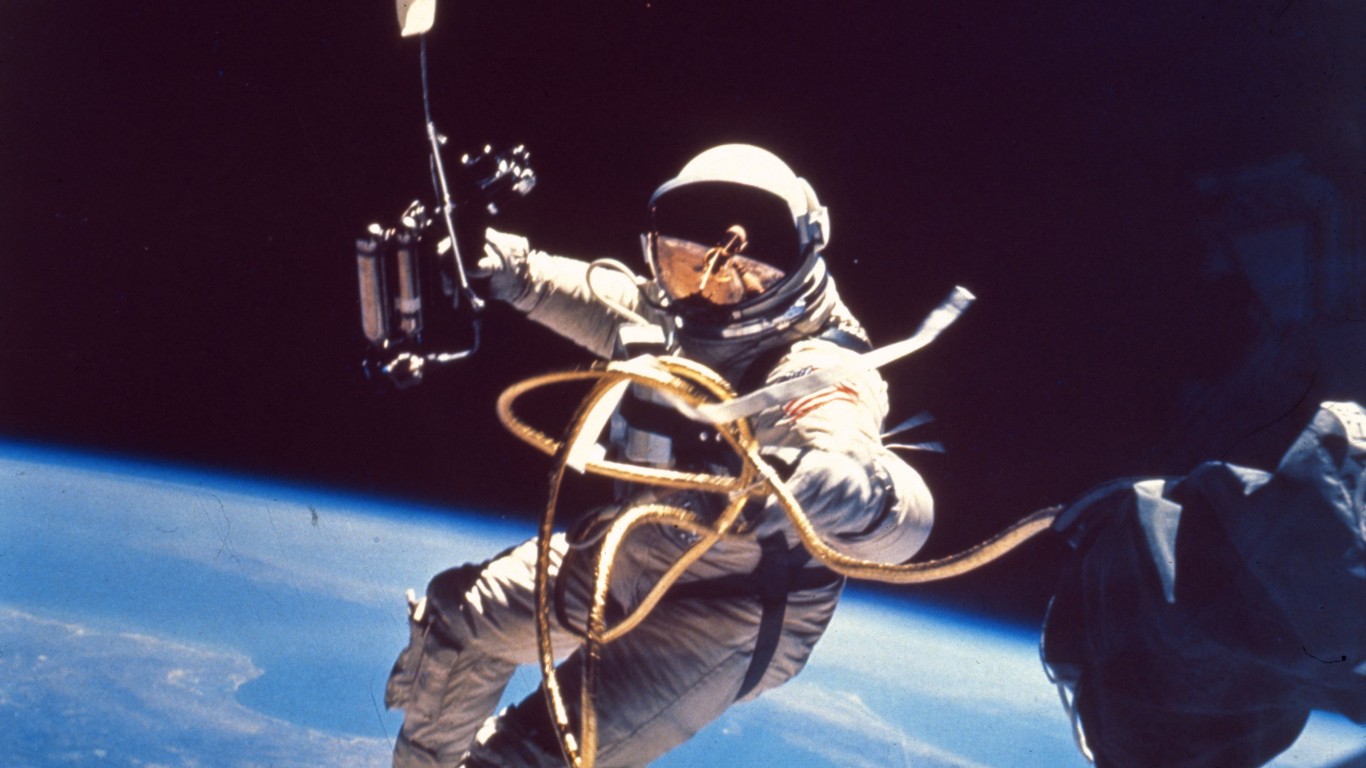

What is the record for the longest spaceflight by a NASA astronaut?
Answer: 355 Days

Mark Vande Hei holds the record for the longest single spaceflight by a NASA astronaut, at 355 days, which he completed in 2022. Mark orbited Earth approximately 5,680 times and traveled 150 million miles. This record stands longer than Scott Kelly’s, which is widely believed to be the longest, lasting only 340 days.
14. Question
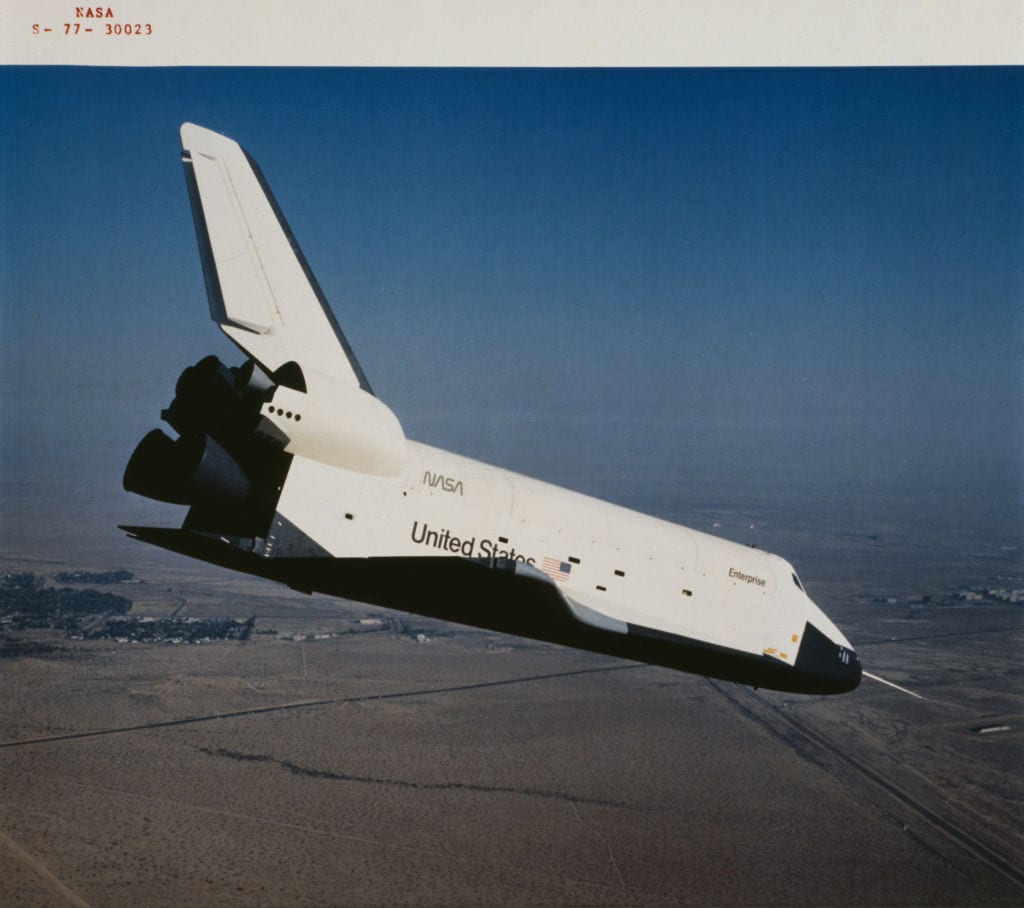

What was the Space Shuttle Program?
Answer: Reusable Spacecraft
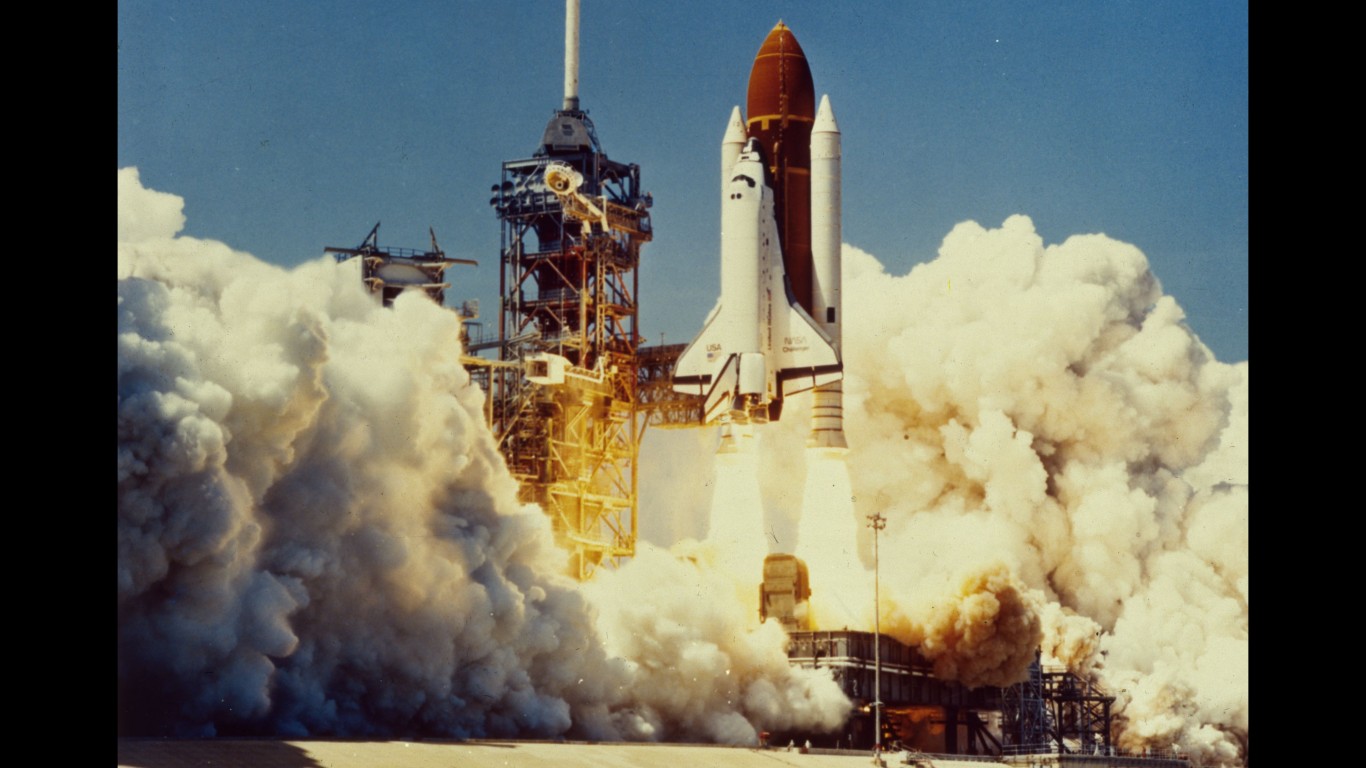

The NASA Space Shuttle program, utilized by NASA between 1981 and 2011, was a period during which the United States successfully launched reusable spacecraft to cut down on the cost of space travel. These shuttles, like Discovery and Challenger, were used to deploy new satellites, repair equipment like the Hubble Telescope, and bring and return astronauts to and from the International Space Station. NASA lost two shuttles during this period, including the Challenger in 1986 and Columbia in 2003, leading to the program’s retirement.
15. Question

Did NASA play a role in developing GPS technology?
Answer: Yes

NASA contributed to developing GPS or Global Positioning System technology. The Department of Defense manages the GPS program, but the technology stems from NASA’s research on satellite orbits and tracking. NASA continues to work on GPS technology for both scientific and commercial applications.
16. Question

How many planets has NASA explored with its space missions?
Answer: The Full Solar System

While manned missions have been limited, NASA has successfully sent probes and missions to every planet, including Mercury, Neptune, Jupiter, and even Pluto. These missions have provided valuable insight into the different atmospheres of each planet and the potential habitat of every planet’s surface compared to Earth.
17. Question

What is NASA’s budget?
Answer: $25 billion

At $25.4 billion for 2025, NASA’s budget is not even close to the one-fourth of all US spending that many Americans believe it is. Instead, it’s much closer to representing just 0.5% of the entire US federal budget. With this budget, NASA supports research, education, and technology development, which leads to advances on Earth around telecommunications and energy.
18. Question

Does NASA have a plan in place to colonize Mars?
Answer: Yes

The idea of colonizing Mars is more than just a movie these days; NASA’s Artemis program and Mars Sample Return mission are two key steps toward a future that includes human exploration of Mars. NASA is currently hard at work on its own. Together with third-party companies like SpaceX, it is developing the technology to support habitats and life on the Martian surface.
19. Question

Does NASA have strong relationships with private companies?
Answer: Yes

Yes, NASA’s ability to work with third-party companies like SpaceX, Boeing, and Blue Origin has successfully helped return NASA to the public eye positively. The combination of NASA and SpaceX has helped launch Crew Dragon, which has been on multiple missions to transport astronauts to the ISS. By moving into private sector partnerships, NASA is on its way to return to both the Moon and Mars.
20. Question
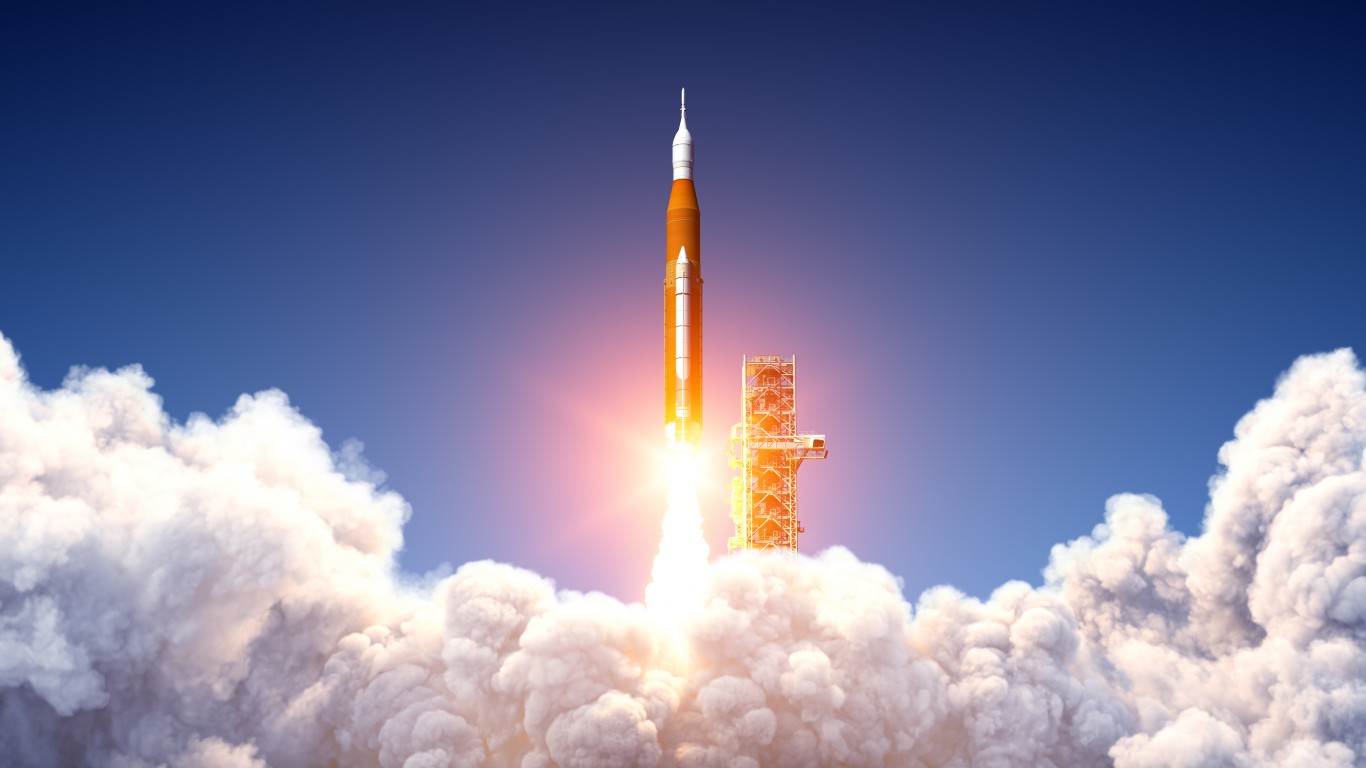

What is the largest rocket NASA has ever built?
Answer: 322 Feet Tall
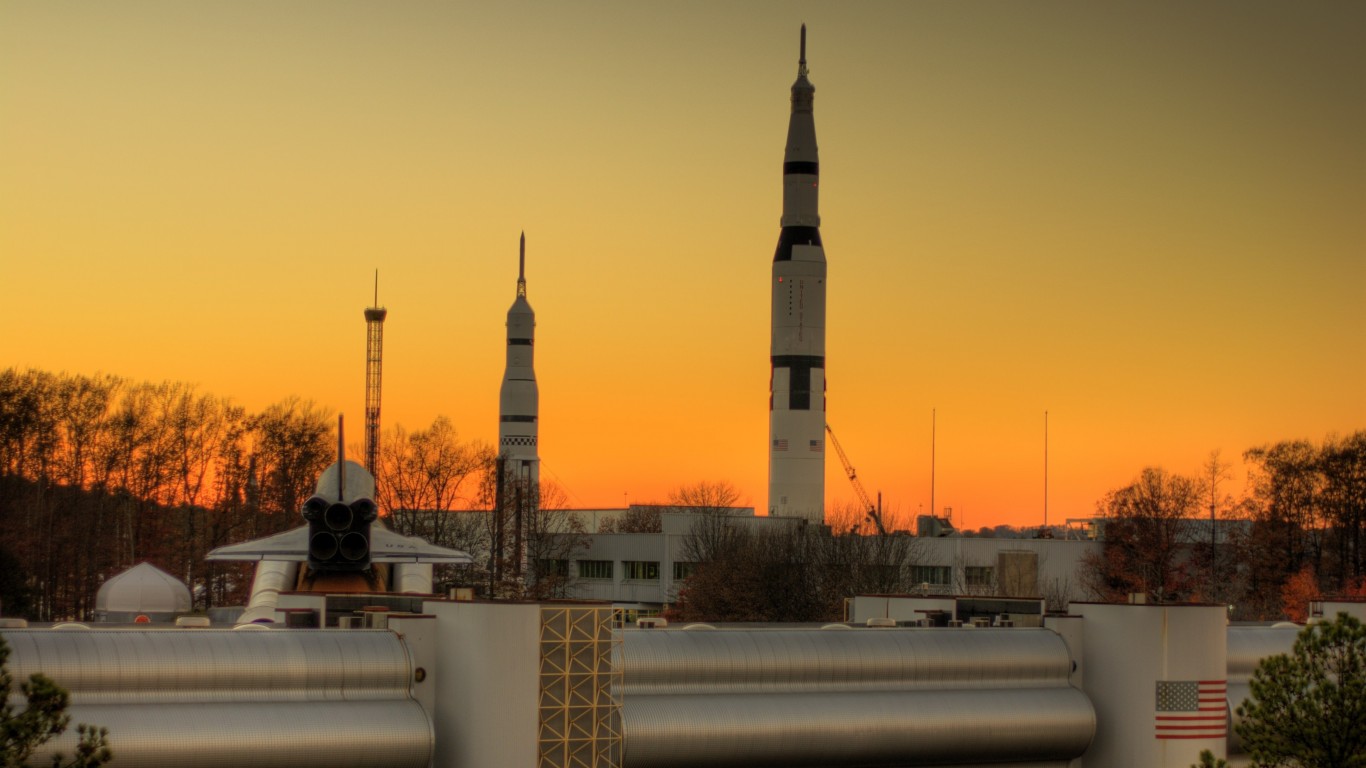

Standing more than 322 feet tall, the Space Launch System (SLS) is considered the largest and most powerful rocket NASA has ever built. Its size surpasses the Saturn V of the Apollo launch missions, which can be viewed at the John F. Kennedy Center at Cape Canaveral in Florida.
21. Question
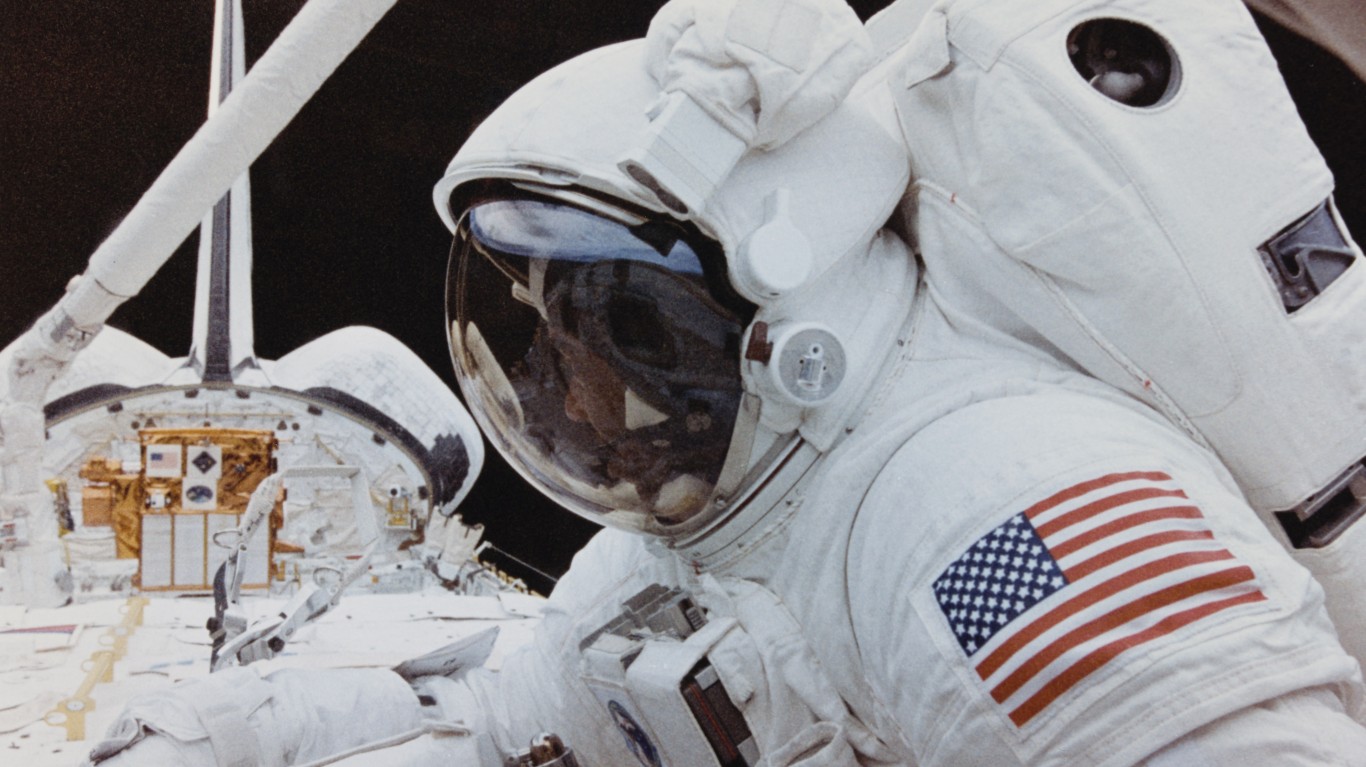

What percentage of astronaut applicants does NASA accept?
Answer: Very Small Percentage
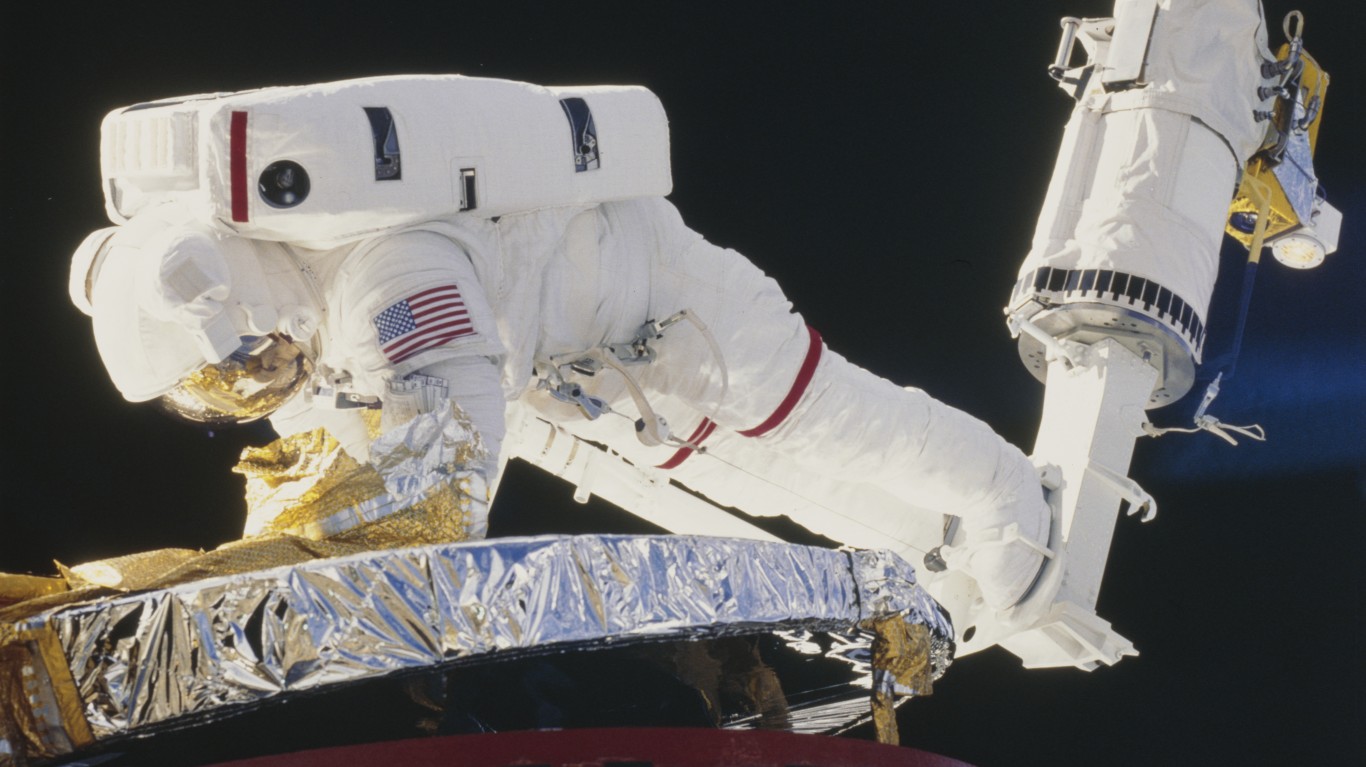

The process to become a NASA astronaut has long been competitive and continues to be so. The acceptance rate into the program is just 0.5% out of roughly 10,000 to 12,000 applications received annually. This means approximately 10 candidates are accepted annually for training, making the process more competitive than even the most elite college admissions worldwide.
It’s Your Money, Your Future—Own It (sponsor)
Retirement can be daunting, but it doesn’t need to be.
Imagine having an expert in your corner to help you with your financial goals. Someone to help you determine if you’re ahead, behind, or right on track. With SmartAsset, that’s not just a dream—it’s reality. This free tool connects you with pre-screened financial advisors who work in your best interests. It’s quick, it’s easy, so take the leap today and start planning smarter!
Don’t waste another minute; get started right here and help your retirement dreams become a retirement reality.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.




